Diffuse astrocytoma
Diffuse astrocytoma (AKA: diffuse, low-grade astrocytoma) is a infiltrating astrocytoma occurring in the CNS white matter.
- Most common grade II WHO glioma in adults (peaks between 30-40 years).
- 10-15% of all astrocytomas.
- Usually shows progression to glioblastoma sooner or later.
WHO 2016 categorization combines morphology and genetics into following groups:[1]
- Diffuse astrocytoma, IDH-mutant ICD-O: 9400/3 - most frequent.
- Gemistocytic astrocytoma, IDH-mutant ICD-O:9411/3
- Diffuse astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype ICD-O: 9400/3
- Diffuse astrocytoma,NOS ICD-O: 9400/3 - genetic data missing.
Note: Older terminologies included Fibrillary astrocytoma (ICD-O: 9420/3) and Protoplasmatic astrocytoma (ICD-O:9410/3)[2] This subtyping is no longer in use. These tumors are now classified according their IDH mutation status.
Radiology/Clinic
- Mass effect.
- Seizures.
- Neurologic decifit.
- Usually not contrast-enhanching, T2 bright.
Macroscopy
- No clear demarcation from white matter
- May contain larger cysts
- No necrosis
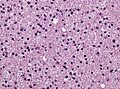
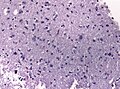
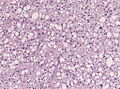
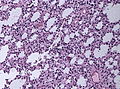
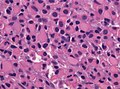
Histology
Features: [3]
- Cell density higher than normal brain.
- Mild to moderate nuclear pleomorphism.
- Monotony of atypical nuclei and irregular distribution indicates neoplasm.
- "naked nuclei" without recognizeable processes.
- No prominent nucleolus.
- Cytoplasm highly variable (even within the same tumour).
- In normal CNS the cytoplasm blends within the neuropil.
- Mitoses absent or very rare.
- Microcystic spaces of the background (none to extensive).
- No necrosis, no vascular proliferations.
- Except radiation necrosis.
- Lymphocytic cuffing (mostly in gemistocytic type)
- Abent to few rosenthal fibers.
IHC
- GFAP+ve.
- MAP2+ve (especially in cell processes).
- Vimentin+ve (often perinuclear).
- S-100+ve.
- p53: Nuclear staining in 30% of the tumours (usually few cells).
- MIB-1: 0-5% (mean: 2%).
- IDH-1 (R132H)+ve in 60-70%.
- 'Note: This antibody does not detect other rare IDH1/2 mutations.
- ATRX nuclear loss in 70%.
Molecular
- IDH1 R132- or IDH2 R172-point mutations classify the tumors as Diffuse astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Absence of LOH 1p/19q.
- Tp53 mutations in approx. 60% (80-90% in gemistocytic, 50% in fibrillary types).
- MGMT promotor methylated in approx. 50%.
DDx
- Reactive astrocytosis.
- Demyelinisation.
- Anaplastic astrocytoma - increased mitotic activity.
- Oligoastrocytoma, NOS - esp. when genetic data on IDH and LOH 1p/19q are lacking.
- Oligodendroglioma - esp. protoplasmatic forms. LOH 1p/19q testing required.
- SEGA - esp. gemistocytic forms.
See also
- ↑ Louis, DN.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, WK.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, OD. et al. (Jun 2016). "The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary.". Acta Neuropathol 131 (6): 803-20. doi:10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. PMID 27157931.
- ↑ The International Agency for Research on Cancer (Editors: Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.) (2007). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Tumors of the Central Nervous System (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours) (4th ed.). Lyon: World Health Organization. pp. 25. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4. ISBN 978-9283224303.
- ↑ Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W. (2007). Tumors of the Central Nervous System (Afip Atlas of Tumor Pathology) (4th ed.). Washington: American Registry of Pathology. pp. 34. ISBN 1933477016.