Vascular thrombus
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Vascular thrombus is an uncommon pathology specimen that may be from an artery or vein.
Venous thrombus and arterial thrombus redirect here.
General
- Uncommonly comes to pathology.
Risk factors - think Virchow's triad:
- Stasis, e.g. atrial fibrillation.
- Hypercoagulable states, e.g. cancer - see risks factors venous thromboembolism.
- Endothelial injury.
Gross
- See pulmonary embolism.
Features:
- Dull appearance.
- Laminations.
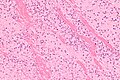
Microscopic
Features:
- Layers consisting of platelets and fibrin.
- Classically alternating with layers of RBCs - known as Lines of Zahn.[1]
Note:
- Multiple laminations (layers), in general, suggest that clot was formed in a dynamic environment, i.e. in the context of blood flow.
DDx:
- Tumour embolus - malignant cells.
- Thromboembolus - may require clinical history.
- Fat embolism.
- Amniotic fluid embolus - in the context of pregnancy/postpartum.
- Foreign body.
Images
www
Sign out
BLOOD CLOT, LEFT ILIAC ARTERY, THROMBECTOMY: - THROMBUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
BLOOD CLOT, LEFT ARM - BRACHIAL ARTERY, THROMBECTOMY/EMBOLECTOMY: - THROMBUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show layers of red blood cells alternating with fibrin and white blood cells (Lines of Zahn).
See also
References
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 124. ISBN 978-1416031215.