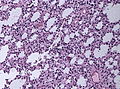
Diffuse astrocytoma
Diffuse astrocytoma (AKA: diffuse, low-grade astrocytoma) is a infiltrating astrocytoma occurring in the CNS white matter.
- Most common grade II WHO glioma in adults (peaks between 30-40 years).
- 10-15% of all astrocytomas.
- Usually shows progression to glioblastoma sooner or later.
Previously categorized as follows:The International Agency for Research on Cancer (Editors: Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.) (2007). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Tumors of the Central Nervous System (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours) (4th ed.). Lyon: World Health Organization. pp. 25. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4. ISBN 978-9283224303.
- Diffuse astrocytoma ICD-O: 9400/3
- Fibrillary astrocytoma ICD-O: 9420/3 - most frequent
- Gemistocytic astrocytoma ICD-O:9411/3
- Protoplasmatic astrocytoma ICD-O:9410/3 - rare
Note: This subtyping is no longer in use!
Histology
- Cell density higher than normal brain.
- Mild to moderate nuclear pleomorphism.
- Monotony of atypical nuclei hints at neoplasm.
- Cytoplasm highly variable (even within the same tumour).
- In normal CNS the cytoplasm blends within the neuropil.
- Mitoses absent or very rare.
- Microcystic changes of the background (none to extensive).
- No necrosis, no vascular proliferations.
IHC
- GFAP+ve.
- MAP2+ve (especially in cell processes).
- Vimentin+ve (often perinuclear).
- S-100+ve.
- MIB-1: 0-5% (mean: 2%).
- IDH-1 (R132H)+ve in 60-70%.
- ATRX loss in 70%.
Molecular
- Absence of LOH 1p/19q.
- Tp53 mutations in approx. 60% (80-90% in gemistocytic, 50% in fibrillary types).
- MGMT promotor methylated in approx. 50%.
DDx
- Reactive astrocytosis.
- Demyelinisation.