Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis is an uncommon intestinal pathology characterized by pseudocysts filled with air.
General
- Benign, generally asymptomatic subset of pneumatosis intestinalis.[1]
- Small or large bowel.[2]
Possible etiologies:[3]
- IBD.
- Infection.
- Bowel necrosis.
- Malignancy.
- Drugs, e.g. alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
- Idiopathic.
Others:
- Necrotizing enterocolitis. (???)
- Cystic fibrosis. (???)
Gross
- Polypoid lesions.
Images:
- www:
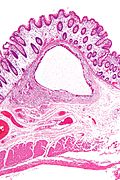
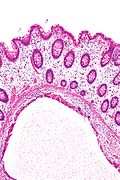
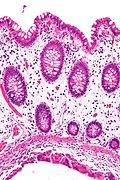
Microscopic
Features:
- Large submucosal pseudocysts lined by macrophages and multi-nucleated giant cells.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/371955-overview. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.
- ↑ Micklefield, GH.; Kuntz, HD.; May, B.. "Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: case reports and review of the literature.". Mater Med Pol 22 (2): 70-2. PMID 2102980.
- ↑ Wu, SS.; Yen, HH. (Aug 2011). "Images in clinical medicine. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.". N Engl J Med 365 (8): e16. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1013439. PMID 21864163.
- ↑ URL: http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/349/full.html. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ Takami, Y.; Koh, T.; Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, N. (2011). "Pneumatosis intestinalis leading to perioperative hypovolemic shock: Case report.". World J Emerg Surg 6: 15. doi:10.1186/1749-7922-6-15. PMC PMC3108289. PMID 21548980. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMCPMC3108289/.