Verruca vulgaris
| Verruca vulgaris | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
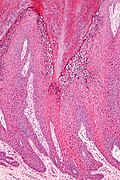
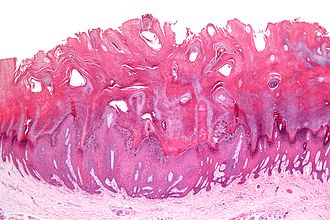 Verruca vulgaris. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | papillomatous hyperplasia (rete ridges long & curve inward), hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, large blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction, +/-viral changes - perinuclear halo, nucleus small and hyperchromatic (virtually diagnostic when present), +/-binucleation |
| LM DDx | Squamous cell carcinoma, hypertrophic actinic keratosis, actinic keratosis with superimposed lichen simplex chronicus, seborrheic keratosis, condyloma acuminatum |
| Site | skin - classically hands |
|
| |
| Prevalence | very common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Verruca vulgaris, also known as common wart, is a common non-malignant skin disease caused by human papilloma virus.
General
- Etiology - HPV.
- Very common.
Notes:
- Related to condyloma acuminatum.
Gross
Features:
Images:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Hyperkeratosis (more keratin - thick stratum corneum) - in "columns"; keratin in separate towers - not a flat thick sheet.
- Hypergranulosis (thicker stratum granulosum).
- Papillomatous hyperplasia:
- Rete ridge lengthening (~7-10x normal) and thickening.
- Rete ridge curvature toward the centre of the lesion (like the roads to the Palace of Versailles) - important.
- Large blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction - between the rete ridges.
- +/-Viral changes - perinuclear halo, nucleus small and hyperchromatic[2] - virtually diagnostic when present.
- +/-Binucleation.
Memory device: there is more of everything - more s. corneum, s. granulosum, s. spinosum, longer rete ridges, more (larger) blood vessels.
DDx:
- Squamous cell carcinoma - nuclear atypia full thickness and often more pronounced.
- Hypertrophic actinic keratosis - often accompanied by solar elastosis.
- Actinic keratosis with superimposed lichen simplex chronicus.[3]
- Seborrheic keratosis - may have focal clear cell changes.
- Condyloma acuminatum - genital region.
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT LOWER LEG, SHAVE BIOPSY: - VERRUCA VULGARIS.
Micro
The sections show skin with elongated rete ridges, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis in vertical columns, focal parakeratosis, dilated blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction and koilocytic change. Mild basilar nuclear atypia is present.
Without koilocytes
The sections show skin with elongated rete ridges that curve toward the centre of the lesion, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis in vertical columns, and dilated blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction. Minimal basilar nuclear enlargement is present. No definite koilocytic change is apparent.
No parakeratosis is identified. Mild solar elastosis is identified. No melanocytic nests are apparent. Mitotic activity is not apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/verruca_vulgaris.html. Accessed on: 14 July 2010.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 106-7. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 353. ISBN 978-0443066542.