Melanocytic lesions
Melanocytic lesions are commonly encountered in dermatopathology and an area which causes some difficulty, i.e. it is hard to decide in some cases whether a lesion is benign (e.g. Spitz nevus) or malignant (malignant melanoma).
Overview
Identifying melanocytes
- Clear or pigmented cytoplasm.
- +/-Nuclear pseudoinclusions.
- Epithelioid (superficial) or spindled (deep).
Benign lesions
| Name | Key feature | Microscopic | Clinical | Gross | Image | Ref. |
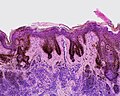
| Lentigo simplex | no nests, epidermis only | slender rete with melanocytes; no nests of melanocytes; no dermal melanocytes | < 40 years | small flat pigmented lesion | [1] | |
| Junctional melanocytic nevus | nests in epidermis | nests of melanocytes at tips of rete, no dermal melanocytes | usu. sun exposed skin, unusual in >50 years | small flat (uniformly) pigmented lesion | [1] | |
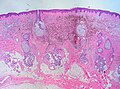
| Compound melanocytic nevus | benign nests in dermis & epidermis | nests of melanocytes at tips of rete and in dermis; dermal melanocytes lack nucleoli, lack mitoses and "mature with depth" -- see Note 1. | small slightly raised (uniformily) pigmented lesion | [2] | ||
| Intradermal melanocytic nevus | nested & individual melanocytes - only in dermis | nested & individual melanocytes - only in dermis, +/- multinucleation, +/-pseudovascular spaces | Clinical DDx: fibroepithelial polyp (skin tag), basal cell carcinoma | raised, non-pigmented lesion | [2] | |
| Spitz nevus (epithelioid and spindle-cell nevus) | long axis of nests perpendicular to surface, DE junction lesion | spindled, epithelioid or mixed melanocytes, long axis of nests perpendicular to surface, superficial mitoses common, +/-hyperkeratosis, +/-acanthosis, +/-hypergranulosis | Children & adolescents | usu. non-pigmented | Spitz nevus (drmihm.com), Spitz nevus - high mag. (WC), Spitz nevus - intermed. mag. (WC) | [2] |
| Pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed (AKA Pigmented spindle cell nevus) | nests of heavily pigmented spindle cells, DE junction lesion | heavily pigmented spindle cells in epidermis & dermis, form "basket weave" pattern, well-circumscribed | women in teens & 20s; location: shoulder, pelvic girdle region | Pigmented +++, small size | Reed nevus - low mag. (WC), Reed nevus - intermed. mag. (WC), Reed nevus - collection (histopathology-india.net) | [3] |
| Blue nevus | lentil-shaped (ovoid) nests btw collagen bundles, dermal lesion | lentil-shaped nests, mix of spindle or dendritic or epithelioid cell morphology, nests btw collagen | usu. head & neck or extremities; clinically confused with melanoma[4] | blue flat or slightly raised lesion | Blue nevus (WC), Blue nevus - very low mag. (WC), Blue nevus - intermed. mag. (WC) | [5] |
| Cellular blue nevus | dermal lesion with pigmented spindle cells & epithelioid cells | deep dermis +/-subcutis extension; cells lack nucleoli; biphasic: (1) epithelioid cells with pale cytoplasm, (2) pigmented spindle cells +/- melanophages | congenital or acquired; usu. scalp or butt | blue flat or raised lesion | [5] | |
| Congenital-pattern nevus | growth along dermal structures | extend along dermal structures (e.g. nerves, hair shafts, ducts); lacks atypia; +/-mitoses | congenital or acquired; large ones increased melanoma risk[6] | small, intermediate (2-20 cm) or large | [5] | |
| Dysplastic nevus (Clark's nevus) | melanocyte bridges, lamellar fibrosis | melanocytes "bridges" between sides of rete ridges, "lamellar fibrosis" (collagen deep to epidermis), mod. atypia | may be familial - precursor to melanoma | may have asymmetry in shape or pigmentation | Dysplastic nevus - low mag., Dysplastic nevus - high mag. | [7] |
| Halo nevus | lymphocytes +++ | lymphocytes at perimeter of melanocytic; epidermal melanocytes not nested; may be dermal, epidermal or both | central zone of pigment | [7] |
Note 1:
- "Maturation" in the context of melanocytic lesions means (1) the cells get smaller with depth, (2) cells are less mitotic with depth.
Lentiginous melanocytic lesions
Lentigo simplex
General
- Benign.
- Usually <40 years old.
Fits into the larger category of lentiginous melanocytic proliferations - these include:[9]
- Solar lentigo.
- Lentigo simplex.
- Lentiginous nevus.
- Lentiginous melanoma in situ.
Associated syndromes:[10]
Gross
- Small flat pigmented lesion.[1]
DDx - clinical:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Melanocytes in epidermis only.
- Melanocytes basally located (normal location) with hyperpigmentation.
- No melanocytic nests.
- +/-Mild/moderate elongation of the rete ridges.[11]
DDx:[12]
- Solar lentigo - solar elastosis, usu. in sun exposed areas.
- Ephelis (freckle) - change with UV light exposure.
- Melanotic macule.
- Lentiginous nevus - has melanocytic nests.
Images
Sign out
SKIN LESION, LEFT ABDOMEN, BIOPSY: - SIMPLE LENTIGO, COMPLETELY EXCISED IN THE PLANE OF SECTION.
SKIN LESION, LEFT ABDOMEN, BIOPSY: - BENIGN SIMPLE LENTIGO.
Micro
The sections show skin with increased numbers of small pigmented melanocytes at the dermal-epidermal junction. The rete ridges are mildly elongated. No solar damage is apparent. No dermal melanocytes are identified. No melanocytic nests are identified. No nuclear atypia is apparent.
Solar lentigo
- Plural solar lentigines.
General
- Benign.
Fits into the larger category of lentiginous melanocytic proliferations - these include:[9]
- Solar lentigo.
- Lentigo simplex.
- Lentiginous nevus.
- Lentiginous melanoma in situ.
Gross
Features:[9]
- Small (< 4 mm), irregular brown macule.
- Usu. sun-exposed area.
DDx (clinical):
- Lentigo maligna - melanoma in situ on sun damaged skin.
- Seborrheic keratosis, flat.[13]
Microscopic
Features:[14]
- Hyperpigmented melanocytes - may be present in increased quantities - key feature.
- Classically at the tips of the rete ridges.
- No (melanocyte) nuclear atypia.
- Solar damage (solar elastosis).[11]
Notes:
- Should not be present:[9]
- Nests of melanocytes.
- Pagetoid spread of melanocytes.
DDx:[14]
- Pigmented actinic keratosis.
- Lichen planus-like keratosis.
- Pigmented seborrheic keratosis.
- Ephelis (freckle).
Images
Sign out
FOREARM LESION, RIGHT, PUNCH BIOPSY: - SOLAR LENTIGO.
Micro
The sections show hair-bearing skin with basilar pigmentation at the tips of the rete ridges and solar elastosis. No melanocytic nests are identified. The epidermal cells mature to the surface. No significant inflammation is present.
Lentiginous melanocytic nevus
- AKA lentiginous nevus.
General
- Benign.
Fits into the larger category of lentiginous melanocytic proliferations - these include:[9]
- Solar lentigo.
- Lentigo simplex.
- Lentiginous nevus.
- Lentiginous melanoma in situ.
Gross
- Small flat pigmented lesion.
Microscopic
Features:[9]
- Melanocytes without atypia in the epidermis only - key feature.
- Melanocytic nests.
- +/-Rete ridge elongation.
DDx:
- Atypical lentiginous nevus.
- Dysplastic nevus.
- Melanoma in situ - especially if solar elastosis is present.
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, BACK, SHAVE EXCISION: - JUNCTIONAL LENTIGINOUS NEVUS. -- COMPLETELY EXCISED (LATERAL CLEARANCE 1 MM).
Micro
The sections show skin with non-nested melanocytes in the epidermis. The melanocytes have no significant cytologic atypia. There is no upward scatter of melanocytes. The lesion is completely excised the in plane of section.
Nested melanocytic lesions
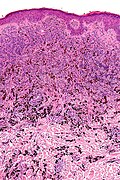
Common melanocytic nevus
- AKA common nevus.
- In common language: mole.
General
- Benign.
- Common.
- Think melanoma.
Clinical:
- ABCD = asymmetric, borders (irregular), colour (black), diameter (large).
Microscopic
Features:
- Symmetrical lesion.
- "Matures" with depth
- Less cellular with depth
- Less nuclear atypia with depth.
- Smaller cells with depth.
- Smaller nests with depth.
- Rare mitoses (superficial).
- No deep mitoses.
- No destruction of surrounding structures.
- No nucleoli.
Subtypes
Compound melanocytic nevus
- Abbreviated CMN and CN.
- In the dermis and epidermis - key feature.
Junctional melanocytic nevus
- Abbreviated JN.
- In the epidermis - key feature.
Intradermal melanocytic nevus
Sign out
Junctional melanocytic nevus
SKIN LESION, RIGHT LATERAL UPPER ARM, BIOPSY: - BENIGN JUNCTIONAL NEVUS.
Micro
The sections show melanocytes in nest confined to the epidermis. The lesion is symmetrical in its architecture and pigment distribution. There is no pagetoid spread of melanocytes in the epidermis. No significant nuclear atypia is identified. No mitotic activity is appreciated.
The lesion is completely excised in the plane of section.
Compound melanocytic nevus
Intradermal melanocytic nevus
Congenital-pattern nevus
- AKA congenital nevus.
General
- Congenital or acquired - thus "congenital-pattern".
- Large ones increase melanoma risk.[6]
- Small (<2 cm), intermediate (2-20 cm), large (>20 cm).
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Growth along dermal structures - key feature.
- Nerves, hair shafts, ducts.
- "Deep" melanocytes.
- Lacks nuclear atypia.
- +/-Mitoses.
- +/-Less nesting.[16]
DDx:
Images:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, LEFT UPPER BACK, BIOPSY: - COMPOUND MELANOCYTIC NEVUS WITH CONGENITAL FEATURES.
Recurrent melanocytic nevus
General
- Classically, arises at the site of a partially excised nevus.[17]
Microscopic
Features - three layers (often described as a "sandwich"):
- Features of a compound nevus or junctional nevus.
- Scar.
- Thick collagen bundles arranged parallel to the skin surface.
- Features of an intradermal nevus.
May have:[17]
- Pagetoid spread of melanocytes.
- Confluent nests at the DE junction.
- Nuclear atypia - uncommon.
DDx:[17]
- Melanoma in situ - classically spread beyond the scar, unlike pseudomelanoma - growth confined to epidermis.
- Sclerosing nevus.
IHC
- HMB-45 deep component -ve.
- Ki-67 - non-proliferative.
Sclerosing melanocytic nevus
- AKA sclerosing nevus.
General
- Similar to recurrent nevus.
- Clinically may be confused with melanoma.
- No history of trauma or prior excision.
Microscopic
Features:[18]
- Trizonal - may be described as a sandwich:
- Junctional or compound nevus.
- May have pagetoid spread of melanocytes, i.e. non-basal melanocytes in the epidermis.
- Cannot have cytologic atypia - presence of cytologic atypia in this layer makes it melanoma.
- Fibrotic tissue with irregular melanocytic nests.
- Nevus below scar - may be common, congenital-type, dysplastic, Spitz.
- Junctional or compound nevus.
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma.
- Recurrent melanocytic nevus - also trizonal; however, has a fibrotic layer that does not have melanocytes in it.[18]
Pigmented spindle cell nevus
- AKA pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed.
Spitz nevus
- AKA epithelioid and spindle cell nevus.
Acral nevus
General
- Palms or soles.
Note:
- Volar refers to the palmar aspect or plantar aspect.[19]
Gross
- Pigmented lesion.
Note:
- Should be bisected perpendicular to the dermatoglyphs (ridges).[20]
- Lesions sectioned parallel to the ridges (on microscopy) may appear to have confluent junctional nests (leading to the diagnosis of melanoma).
Microscopic
Features:
- Acral skin:
- Thick stratum corneum (hyperkeratotic).
- Thick stratum spinosum (acanthotic).
- Nevus with intraepidermal ascent of cells.
- May be referred to as Pagetoid scatter.
- Should not be present at the edge of the lesion - key feature.[20]
Notes:
- Intraepidermal ascent of cells is usually suggestive of melanoma.
- In acral sites (esp. at the centre of a lesion) the criteria are relaxed, i.e. this is considered benign for this site.
- Nests in the ridges raise the suspicion of melanoma.
- Memory device "ridges are risky, furrows are fine".[20]
DDx:
- Acral lentiginous melanoma.
Dysplastic melanocytic nevus
- AKA dysplastic nevus.
- AKA Clark nevus.
- AKA nevus with architectural disorder.
- This term is recommended by the American NIH; however, it is not widely adopted.[20]
Desmoplastic melanocytic nevus
- AKA sclerosing melanocytic nevus.
General
- Benign.
Gross
- Usu. "small" and symmetric.
Clinical DDx:
Microscopic
Features:[21]
- Compound nevus or intradermal nevus with prominent dermal fibrosis.
- Fibrosis: extra pink - versus surrounding.
DDx:
- Desmoplastic neurotropic malignant melanoma - usually mitotic figures, nuclear atypia (enlarged, hyperchromatic).
- Dermatofibroma.
- Dermal scar - no adnexal structures.
IHC
Features:[21]
- Melan A (MART-1) +ve.
- Usually -ve in desmoplastic melanoma.[21]
- S-100 +ve.
- Should stain approximally the same number of cells as Melan A.
- Ki-67 -- only rare cells.
Miscellaneous
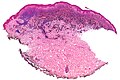
Blue nevus
- Common blue nevus redirects here.
- Abbreviated BN.
General
- Usually head & neck, extremities (e.g. dorsum of wrist or foot) or buttock.[22]
- Clinically confused with malignant melanoma.[4]
- Second most common melanocytic lesion of the oral cavity.[23]
- Most common melanocytic lesion intramucosal melanocytic nevus.
Gross
- Blue flat or slightly raised lesion.
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Lentil-shaped (ovoid) nests between collagen bundles.
- Mix of spindle or dendritic or epithelioid cell morphology.
Notes:[24]
- Classically no epidermal component.
- The entity compound blue nevus has been described; it is rare.[25]
- May be assoc. with a hair follicle.
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma - often lacks a Grenz zone (lesion in papillary dermis),[26] mitotic figures, necrosis, cytologic atypia, asymmetry (architecture, pigment).
- Atypical blue nevus - have some of the features of melanoma.
- Clear cell sarcoma.
- Dermatofibroma - esp. amelanotic BN.
- Combined melanocytic nevus - blue nevus found together with another nevus (classically common melanocytic nevus), superficial.
- Pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma - superificial dermis, has nuclear atypia.
- Vascular lesions (venous lake, hemangioma).
Images
www:
- Several types of blue nevi (dermatopathonline.com).
- Melanoma that looks a bit like a blue nevus (nature.com).[26]
Variants of blue nevus
Several histologic variants:[24]
- Common blue nevus - the blue nevus not otherwise specified.
- Cellular blue nevus.
- Amelanotic blue nevus - may be confused with a dermatofibroma.
- Sclerosing blue nevus - has stromal fibrosis.
- Epithelioid blue nevus.
Memory device:
- C CASE = Common, Cellular, Amelanotic, Sclerosing, Epithelioid.
IHC
- HMB-45 diffusely +ve.[citation needed]
- Melanoma patchy +ve.
- MART-1 diffusely +ve.
- Ki-67 low.
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT WRIST DORSUM, PUNCH BIOPSY: - COMMON BLUE NEVUS.
SKIN LESION, LEFT SHIN, PUNCH BIOPSY: - SCLEROSING BLUE NEVUS.
Micro
The sections show pigmented spindle cells in the dermis between collagen bundles. The spindle cells show no nuclear atypia and no mitotic activity is appreciated.
The lesion does not extend into the epidermis and is separated from it by a Grenz zone. There are no melanocyte nests. There is no significant inflammation. The lesion is completely excised.
The pigmented cells are negative on the Prussian blue stain.
Sclerosing blue nevus
The sections show pigmented spindle cells in the dermis between densely packed collagen fibres. The spindle cells show no significant nuclear atypia, and no mitotic activity is appreciated. The lesion extends up to the epidermis; however, it does not appear to involve the epidermis. The overlying epidermis has hyperkeratosis; otherwise, it is unremarkable. There are no nests of melanocytes. There is no significant inflammation. The lesion is completely excised in the plane of section.
Cellular blue nevus
General
- Congenital or acquired.
- Usually scalp or butt.
- Variant of the common blue nevus.
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Dermal lesion with pigmented spindle cells & epithelioid cells - key feature.
- Cells lack nucleoli.
- Biphasic:
- Epithelioid cells with pale cytoplasm.
- Pigmented spindle cells +/- melanophages.
Images:
Combined melanocytic nevus
- AKA combined nevus.
General
- Uncommon.
- Morphologic features of two types of melanocytic nevi.
- Most common: blue nevus and common nevus.[27]
Microscopic
Features:[27]
- Morphologic features of two types of melanocytic nevi.
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma.
- Pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma - superificial dermis, has nuclear atypia.
Sign out
A. SKIN LESION, LEFT UPPER ARM, PUNCH BIOPSY: - BENIGN COMBINED MELANOCYTIC NEVUS (INTRADERMAL MELANOCYTIC NEVUS AND BLUE NEVUS).
Neurocristic hamartoma
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 498. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 499. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 500. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 592. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 501. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1170. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 502. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermnetnz.org/lesions/lentigo-simplex.html. Accessed on: 27 March 2013.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 438. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 URL: http://dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/64-l/1852-lentigo-simplex-.html. Accessed on: 17 December 2012.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Hafner, C.; Stoehr, R.; van Oers, JM.; Zwarthoff, EC.; Hofstaedter, F.; Klein, C.; Landthaler, M.; Hartmann, A. et al. (Nov 2009). "The absence of BRAF, FGFR3, and PIK3CA mutations differentiates lentigo simplex from melanocytic nevus and solar lentigo.". J Invest Dermatol 129 (11): 2730-5. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.146. PMID 19536147.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 URL: http://www.humpath.com/?lentigo-simplex. Accessed on: 17 December 2012.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 URL: http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/53-a/1555-actinic-lentigo-.html. Accessed on: 6 May 2013.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 437. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Fullen, DR.; Reed, JA.; Finnerty, B.; McNutt, NS. (Sep 2001). "S100A6 preferentially labels type C nevus cells and nevic corpuscles: additional support for Schwannian differentiation of intradermal nevi.". J Cutan Pathol 28 (8): 393-9. PMID 11493376.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 URL: http://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/congenital-nevus. Accessed on: 27 December 2012.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 465. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Fabrizi, G.; Pennacchia, I.; Pagliarello, C.; Massi, G. (Nov 2008). "Sclerosing nevus with pseudomelanomatous features.". J Cutan Pathol 35 (11): 995-1002. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2007.00941.x. PMID 18537860.
- ↑ URL: http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=9907. Accessed on: 14 January 2013.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Elston, D. (Jul 2012). "Practical advice regarding problematic pigmented lesions.". J Am Acad Dermatol 67 (1): 148-55. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.04.006. PMID 22703907.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 464. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 456. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1079272-overview. Accessed on: 10 December 2012.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 457. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Kamino, H.; Tam, ST. (Oct 1990). "Compound blue nevus: a variant of blue nevus with an additional junctional dendritic component. A clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical study of six cases.". Arch Dermatol 126 (10): 1330-3. PMID 2221938.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Magro, CM.; Crowson, AN.; Mihm, MC. (Feb 2006). "Unusual variants of malignant melanoma.". Mod Pathol 19 Suppl 2: S41-70. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800516. PMID 16446716.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Baran, JL.; Duncan, LM. (Oct 2011). "Combined melanocytic nevi: histologic variants and melanoma mimics.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (10): 1540-8. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822e9f5e. PMID 21881487.
External links
- Dear 16 year-old me (youtube.com) - with Dr. G.