Cystitis glandularis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Cystitis glandularis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
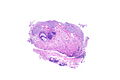
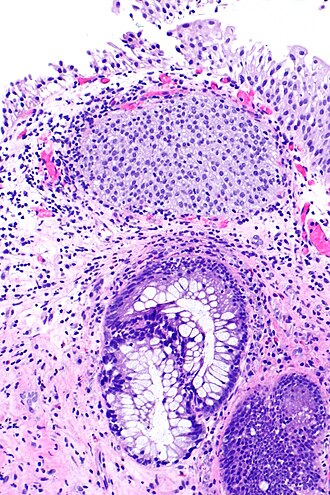 Cystitis glandularis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
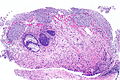
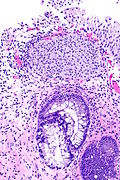
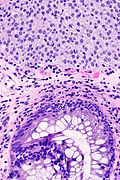
| LM | nests of urothelium within the lamina propria with cyst formation; lining cells are glandular (cuboidal and/or columnar epithelium); +/-goblet cells; nests should not extend into the muscularis propria |
| LM DDx | cystitis cystica, nested variant of urothelial carcinoma, tubular adenoma of the urinary bladder, adenocarcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder |
| Site | urinary bladder - see urothelium |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Cystitis glandularis | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10173 |
Cystitis glandularis is an uncommon type of inflammatory process that afflicts the urinary bladder (cystitis).
Cystitis cystica et glandularis and pyelitis cystica et glandularis redirect to here.
General
- Benign.[1]
- Can be thought of as cystitis cystica with mucin-secreting cells lining the cystic spaces.[4]
- When seen in conjunction with cystitis cystica it is called cystitis cystica et glandularis.
Note:
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Nests of urothelium within the lamina propria with cyst formation, i.e. lumens are present.
- Cyst lining cells are cuboidal and/or columnar epithelium.
- Produce mucin.
- +/-Goblet cells, i.e. intestinal metaplasia.[4]
Note:
- Nests should not extend into the muscularis propria.
DDx:
- Cystitis cystica.
- Nested variant of urothelial carcinoma.
- Tubular adenoma of the urinary bladder.
- Adenocarcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder.
Images
www:
Sign out
Extensive IM
Urinary Bladder Lesion, Transurethral Resection: - Cystitis cystica et cystica glandularis with extensive goblet cells. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Block letters
URINARY BLADDER NECK, BIOPSY: - CYSTITIS CYSTICA ET GLANDULARIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show urothelial mucosa with bland nests within the lamina propria with cyst formation. The stroma is edematous and has a mixed inflammatory infiltrate consisting of plasma cells, eosinophils, lymphocytes and neutrophils.
See also
References
- ↑ Yi, X.; Lu, H.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Cheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, F. et al. (Oct 2014). "Cystitis glandularis: A controversial premalignant lesion.". Oncol Lett 8 (4): 1662-1664. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2360. PMID 25202387.
- ↑ Smith AK, Hansel DE, Jones JS (May 2008). "Role of cystitis cystica et glandularis and intestinal metaplasia in development of bladder carcinoma". Urology 71 (5): 915–8. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2007.11.079. PMID 18455631.
- ↑ Corica FA, Husmann DA, Churchill BM, Young RH, Pacelli A, Lopez-Beltran A, Bostwick DG (September 1997). "Intestinal metaplasia is not a strong risk factor for bladder cancer: study of 53 cases with long-term follow-up". Urology 50 (3): 427–31. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00294-X. PMID 9301710.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 304. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Chan, YM.; Ka-Leung Cheng, D.; Nga-Yin Cheung, A.; Yuen-Sheung Ngan, H.; Wong, LC. (Dec 2000). "Female urethral adenocarcinoma arising from urethritis glandularis.". Gynecol Oncol 79 (3): 511-4. doi:10.1006/gyno.2000.5968. PMID 11104631.
- ↑ Yin, G.; Liu, YQ.; Gao, P.; Wang, XH. (Aug 2007). "Male urethritis glandularis: case report.". Chin Med J (Engl) 120 (16): 1460-1. PMID 17825180.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1028. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.