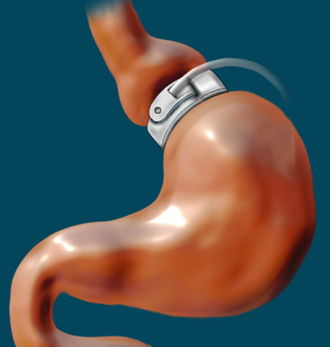
Gastric band
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Gastric band is an occasion pathology specimen and can be considered a ditzel.
Adjustable gastric band (abbreviated AGB[1]) redirects here.
General
- Gastric banding is done to treat obesity.
- An alternative to sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
- May be excised if the individual does not have a sufficient weight loss or weight gain.[2]
Microscopic
Features of laparoscopic gastric band capsule:[2]
- Foreign body reaction (giant cells).
- Inflammation (chronic).
- Fibrosis.
- Neovascularization.
Sign out
Gastric Band, Removal: - Gastric band (gross only). - Benign fibrous tissue with mild inflammation, consistent with capsule. - NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Alternate
Gastric Band, Removal:
- Foreign body, consistent with gastric band (gross only).
- Benign fibroadipose tissue, NEGATIVE for significant pathology.
Long version
Gastric Band, Removal: - Small fragments of gastric mucosa with moderate chronic inactive inflammation, and scant benign adipose tissue. - Mixed micro-organisms (rods, cocci, actinomycetes) compatible with oropharyngeal source; clinical correlation suggested. - Cellular debris (in keeping with erosion) and foreign material. - Foreign body compatible with gastric band (gross only). - NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
See also
References
- ↑ Albaugh, VL.; Abumrad, NN. (2018). "Surgical treatment of obesity.". F1000Res 7. doi:10.12688/f1000research.13515.1. PMID 29904577.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tan, MH.; Yee, GY.; Jorgensen, JO.; Kuzinkovas, V.; Talbot, ML.; Loi, KW.; Viswanathan, S.; Gill, AJ.. "A histologic evaluation of the laparoscopic adjustable gastric band capsule by tissue sampling during sleeve gastrectomy performed at different time points after band removal.". Surg Obes Relat Dis 10 (4): 620-5. doi:10.1016/j.soard.2014.02.037. PMID 24958647.