Atypical lobular hyperplasia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Atypical lobular hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
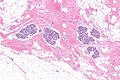
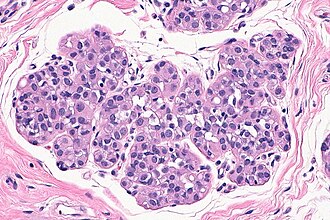 Atypical lobular hyperplasia. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron) | |
|
| |
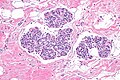
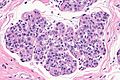
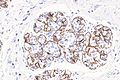
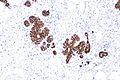
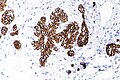
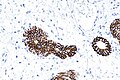
| LM | morphologic changes (atypia minimal - usually, borders of cells distinct/visible - dyscohesive, clear cytoplasm (focal), distend duct, eccentric nucleus, usu. round, filled ducts (no luminal spaces - key feature), limited extent (<50% of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) is involved) |
| LM DDx | lobular carcinoma in situ, lobular carcinoma |
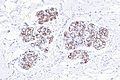
| IHC | E-cadherin -ve |
| Site | breast |
|
| |
| Prognosis | benign |
Atypical lobular hyperplasia, abbreviated ALH, a pre-malignant change in the breast characterized by cellular proliferation and cellular dyscohesion.
It can be seen as the precursor to lobular carcinoma in situ, the precursor of lobular carcinoma.
General
- May occur with ductal involvement by cells of atypical lobular hyperplasia (abbreviated DIALH).[1]
- ALH with DIALH has a risk of developing breast cancer that is similar to LCIS.
Microscopic
Features:
- Morphologic changes - memory device ABCDEF:
- Atypia minimal - usually.
- Relatively small ~1-2x size lymphocyte.
- Borders of cells distinct/visible - dyscohesive.
- Clear cytoplasm (focal).
- May have a signet ring cell-like appearance.
- Distend duct.
- Eccentric nucleus, usu. round.
- Filled ducts.
- No luminal spaces - key feature.
- Partially filled ducts are not LCIS.
- No luminal spaces - key feature.
- Atypia minimal - usually.
- Limited extent: <50% of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) is involved.
DDx:
Images
IHC
- E-cadherin -ve or incomplete membrane staining.