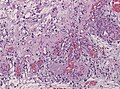
Pilocytic astrocytoma
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Pilocytic astrocytoma. Smear. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | piloid gliosis, oligodendroglioma, glioblastoma |
| Stains | PAS-D +ve (eosinophilic granular bodies) |
| IHC | GFAP +ve |
| Gross | usually cerebellar +/-cystic |
| Site | brain - usu. cerebellum |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common - esp. in children |
| Prognosis | good (WHO Grade I) |
Pilocytic astrocytoma is a low-grade astrocytoma. It the most common glioma in children.
General
- Low-grade astrocytoma - WHO Grade I by definition, but rare anaplastic forms have been described.
- Classically in the cerebellum in children; most common glioma in children.[1]
- The optic glioma is associated with neurofibromatosis 1.
- Usually enhances after CM application
Gross
Features:[1]
- Usually well-circumscribed.
- Often cystic with mural nodule.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Classically biphasic (though either may be absent):
- Fibrillar.
- Microcystic/loose.
- Hair-like fibres ~ 1 micrometer; pilo- = hair.[3]
- Best seen on smear or with GFAP IHC.
- Rosenthal fibres - key feature.
- May be rare. Not pathognomonic (see below).
- Eosinophilic granular bodies.
- Low cellularity - when compared to medulloblastoma and ependymoma.
Notes:
- +/-Microvascular proliferation.
- +/-Focal necrosis.
- Necrosis with pseudopalisading more likely glioblastoma.
- +/-Mitoses - not significant in the context of the Dx.
DDx (of Rosenthal fibers):[4]
- Chronic reactive gliosis.
- Subependymoma.
- Ganglioglioma.
- Alexander's disease (rare leukodystrophy).
DDx of pilocystic astrocytoma (brief):
- Piloid gliosis (esp. in sellar lesions).
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Glioblastoma (uncommon - but important).
- Tanycytic Ependymoma
- Pilocytic tumor components may be found in Ganglioglioma, DNET, RGNT
Images
Smears
Sections
www:
- Rosenthal fibre (ouhsc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (upmc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma - another case (upmc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma - pennies on a plate (upmc.edu).[5]
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (upmc.edu).
Stains
- PAS-D: eosinophilic granular bodies +ve.
IHC
Features:[6]
- GFAP +ve (fibres).
- CD68: may have a significant macrophage component.
- KI-67: may be "high" (~20% ???).
- Olig 2: Usually strongly present.[7]
Molecular
- Alteration usually associated with the MAPK pathway.
- KIAA1549-BRAF fusion transcripts most common in sporadic PA.
- Rarely BRAF mutations, SRGAP3-RAF1 or FAM131B-BRAF fusions.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 82. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 82-4. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pilo-. Accessed on: 24 November 2010.
- ↑ Munoz D. 9 Mar 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case195.html. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 84. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ Otero, JJ.; Rowitch, D.; Vandenberg, S. (Sep 2011). "OLIG2 is differentially expressed in pediatric astrocytic and in ependymal neoplasms.". J Neurooncol 104 (2): 423-38. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0509-x. PMID 21193945.