Difference between revisions of "Herpes esophagitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+more) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Herpes_esophagitis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Herpes esophagitis | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = nuclear moulding, multinucleation, margination of chromatin | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = HSV-1 +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Staging = | |||
| Site = | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Herpes esophagitis''' is an inflammation of the [[esophagus]] due to [[herpes simplex virus]]. | '''Herpes esophagitis''' is an inflammation of the [[esophagus]] due to [[herpes simplex virus]]. | ||
Revision as of 20:58, 6 March 2025
| Herpes esophagitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Herpes esophagitis | |
|
| |
| LM | nuclear moulding, multinucleation, margination of chromatin |
| IHC | HSV-1 +ve |
Herpes esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus due to herpes simplex virus.
General
- Usually immunodeficient.[1]
Etiology:
Gross/endoscopic
Features:
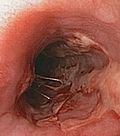
- Ulcers with a "punched-out" appearance with a brown/red edge.
Images
www:
Microscopic
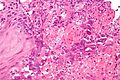
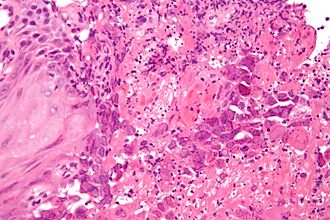
Features (3 Ms):
- Moulding.
- Multinucleation.
- Margination of chromatin.
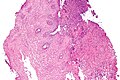
Images
IHC
- HSV-1 +ve.[2]
- Occasionally HSV-2 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Monsanto, P.; Almeida, N.; Cipriano, MA.; Gouveia, H.; Sofia, C. (Sep 2012). "Concomitant herpetic and eosinophilic esophagitis--a causality dilemma.". Acta Gastroenterol Belg 75 (3): 361-3. PMID 23082710.
- ↑ Canalejo Castrillero, E.; García Durán, F.; Cabello, N.; García Martínez, J. (Jul 2010). "Herpes esophagitis in healthy adults and adolescents: report of 3 cases and review of the literature.". Medicine (Baltimore) 89 (4): 204-10. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e3181e949ed. PMID 20616659.