Difference between revisions of "Congestive heart failure"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Causes) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
*[[Atherosclerosis]] | *[[Atherosclerosis]] | ||
*[[Plume of froth]]. | *[[Plume of froth]]. | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Clinical]] | [[Category:Clinical]] | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 15 November 2015
Congestive heart failure, abbreviated CHF, is a clinical diagnosis that is often due to coronary atherosclerosis; however, there are a large number of potential causes.
General
Clinical:
- Dyspnea.
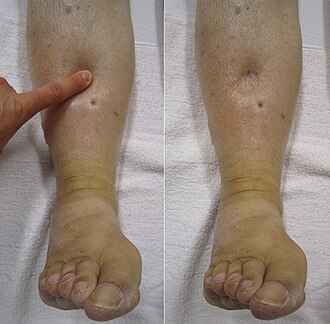
- Pitting edema.
- Pleural effusion.
- Elevated JVP.
Treatment - LMNOP:
- Lasix (furosemide).
- Morphine.
- Nitrates.
- Oxygen.
- Position (elevate head).
Causes
- Coronary atherosclerosis.
- Interstitial lung disease.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.[1]
- Others.
See also
References
- ↑ Lang, I. (Jun 2015). "Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a distinct disease entity.". Eur Respir Rev 24 (136): 246-52. doi:10.1183/16000617.00001115. PMID 26028636.