Difference between revisions of "Paget's disease of the bone"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref name=emed_paget>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/311688-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/311688-overview]. Accessed on: 25 December 2010.</ref> | Features:<ref name=emed_paget>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/311688-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/311688-overview]. Accessed on: 25 December 2010.</ref> | ||
* | *Lytic and mixed Paget disease is a cellular, fibro-osseous (bone and fibrous components) | ||
*Mature Paget disease is sclerotic with thickened bone trabeculae. | *Mature Paget disease is sclerotic with thickened bone trabeculae. | ||
*Bone matrix has jigsaw-puzzle like pattern. | *Bone matrix has jigsaw-puzzle like pattern. | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 27 December 2014
| Paget's disease of the bone | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
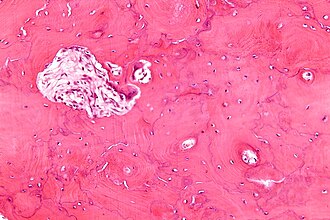 Paget's disease of the bone. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | bone matrix has jigsaw-puzzle like pattern (jigsaw-puzzle pieces each ~ 100-500 micrometres in size in largest dimension), increased osteoclast activity |
| Site | bone |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | fracture of bone, secondary osteosarcoma |
| Signs | +/-deafness |
| Symptoms | +/-bone pain |
| Blood work | elevated ALP |
| Radiology | bony deformity, "sunburst" skull |
| Prognosis | benign |
Paget's disease of the bone is an uncommon benign disorder of bone with distinctive radiographic findings.
It is unrelated to the Paget's disease of the breast and extramammary Paget's disease.
General
- Benign - unlike Paget disease of the breast.
- Afflicts ~ 3% of population > 55 years old.[1]
- Leading cause of secondary osteosarcoma.
- Uncommonly associated with giant cell tumour of bone.[2][3]
- Diagnosis based on radiology.[1]
- Genetic component - several genes implicated[4] including TNFRSF11A (AKA PDB2)[5] and PDB4.[6]
Clinical
Presentation:[1]
- Fracture.
- Bone pain.
- Bony deformity.
- Deafness.
- Incidental finding - radiologic or biochemical.
Serology:
- Elevated ALP.
Clinical features - mnemonic PANICS:[7]
- Pain (bone).
- Arthralgia and ALP elevated.
- Nerve compression - deafness.
- Increased bone density.
- Cardiac failure (high output) - due to AVM formation in bone.
- Sunburst skull on X-ray.
Stage
Classically divided into three phases:[8][9]
- Lytic (predominantly osteoclasts).
- Mixed lytic (osteoclastic) and blastic (osteoblastic).
- Sclerotic (burned-out).
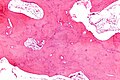
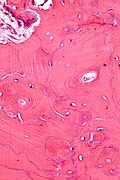
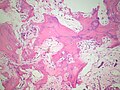
Microscopic
Features:[8]
- Lytic and mixed Paget disease is a cellular, fibro-osseous (bone and fibrous components)
- Mature Paget disease is sclerotic with thickened bone trabeculae.
- Bone matrix has jigsaw-puzzle like pattern.
- Jigsaw-puzzle pieces each ~ 100-500 micrometres in size (largest dimension).
- Increased osteoclast activity.
- Osteoclast = macrophage that reabsorbs bone matrix.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Britton, C.; Walsh, J. (Mar 2012). "Paget disease of bone - an update.". Aust Fam Physician 41 (3): 100-3. PMID 22396921.
- ↑ Hoch, B.; Hermann, G.; Klein, MJ.; Abdelwahab, IF.; Springfield, D. (Oct 2007). "Giant cell tumor complicating Paget disease of long bone.". Skeletal Radiol 36 (10): 973-8. doi:10.1007/s00256-007-0310-x. PMID 17437100.
- ↑ Karakida, K.; Ota, Y.; Aoki, T.; Akamatsu, T.; Kajiwara, H.; Hirabayashi, K. (Sep 2010). "Multiple giant cell tumors in maxilla and skull complicating Paget's disease of bone.". Tokai J Exp Clin Med 35 (3): 112-7. PMID 21319038.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 602080
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 603499
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 606263
- ↑ URL: http://www.medicalgeek.com/orthopedics/2743-orthopedics-mnemonics.html. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/311688-overview. Accessed on: 25 December 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/paget-disease-of-bone-1. Accessed on: 25 December 2010.