Difference between revisions of "Yolk sac tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| IF = | | IF = | ||
| Gross = white/yellow mucinous infiltrative mass | | Gross = white/yellow mucinous infiltrative mass | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = [[orchiectomy grossing]] | ||
| Site = [[testis]], other | | Site = [[testis]], other | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 26 November 2014
| Yolk sac tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
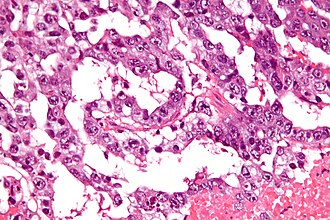 Yolk sac tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | Schiller-Duval bodies (glomerulerus-like structures), variable architecture - usually reticular or microcystic |
| LM DDx | embryonal carcinoma, mixed germ cell tumour |
| IHC | AFP +ve, glypican 3 +ve, OCT3 -ve |
| Gross | white/yellow mucinous infiltrative mass |
| Grossing notes | orchiectomy grossing |
| Site | testis, other |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Blood work | alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) elevated |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other germ cell tumours |
Yolk sac tumour is an uncommon germ cell tumour that primarily afflicts infants and young boys.
It may be seen as part of mixed germ cell tumour. It is abbreviated YST.
It may be referred to as endodermal sinus tumour.
General
- Rare in pure form.
- Aggressive - especially extragonadal tumours.[1]
Epidemiology:
- Most common GCT in infants and young boys.
- Bimodal age distribution:[1]
- <4 years.
- 10-30 years.
Clinical:
- Elevated AFP.
Gross
- White/yellow mucinous infiltrative mass.[2]
Microscopic
Classic feature:[2]
- Schiller-Duval bodies.
- Look like glomerulus - central blood vessel surrounded by epithelial-like cells a space and more epithelial-like cells
- Architecure - variable.
- +/-Eosinophilic hyaline globules (contain alpha-fetoprotein).
Notes:
- Has a loose stroma/vaguely discohesive -- unlike embryonal carcinoma.
- How to remember patterns REMember PlS GAP EH (or REM PS GAPEH) = reticular, endodermal sinus, microcystic, papillary, solid, glandular, alveolar, polyvesicular vitelline, enteric, hepatoid.
- Yolk sac tumours in adults are essentially always a component of a mixed germ cell tumour, i.e. if one sees a pure yolk sac tumour in an adult, it is probably under sampled.[5]
Variants:
- Hepatoid pattern.[6]
- Vaguely resembles liver.
- Hyaline globules (light red well-circumscribed globs).
- Bile canaculi.
- Vaguely resembles liver.
- Solid pattern.[7]
- Vaguely resembles seminoma.
DDx:
Images
www:
- Hepatoid Pattern (webpathology.com).
- Schiller-Duval body (webpathology.com).
- Hyaline globules (webpathology.com).
- Yolk sac tumour - case 1 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Yolk sac tumour - case 2 - several images (upmc.edu).
- Yolk sac tumour (moffitt.org).[8]
IHC
ISUP consensus paper by Ulbright et al.:[9]
- OCT3 -ve.
- Positive in seminoma and embryonal carcinoma.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (abbreviated AFP) +ve.
- Glypican 3 +ve.
- More sensitive than AFP.[10]
Others:
- Cytokeratin +ve.[citation needed]
- CD30 -ve.
- Positive in embryonal carcinoma.[11]
- OCT3/4 -ve.
- Alpha-1-antitrypsin +ve (abbreviated A1A).[12]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shah, JP.; Kumar, S.; Bryant, CS.; Ali-Fehmi, R.; Malone, JM.; Deppe, G.; Morris, RT. (Dec 2008). "A population-based analysis of 788 cases of yolk sac tumors: A comparison of males and females.". Int J Cancer 123 (11): 2671-5. doi:10.1002/ijc.23792. PMID 18767035.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 510. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 369. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=1. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ Talerman, A. (Jul 1975). "The incidence of yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor) elements in germ cell tumors of the testis in adults.". Cancer 36 (1): 211-5. PMID 1203848.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=6. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=8. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ Sesterhenn, IA.; Davis, CJ.. "Pathology of germ cell tumors of the testis.". Cancer Control 11 (6): 374-87. PMID 15625525.
- ↑ Ulbright TM, Tickoo SK, Berney DM, Srigley JR (August 2014). "Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in testicular tumors: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 38 (8): e50–9. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000233. PMID 24832161.
- ↑ Emerson, RE.; Ulbright, TM. (Jun 2010). "Intratubular germ cell neoplasia of the testis and its associated cancers: the use of novel biomarkers.". Pathology 42 (4): 344-55. doi:10.3109/00313021003767355. PMID 20438407.
- ↑ Gopalan, A.; Dhall, D.; Olgac, S.; Fine, SW.; Korkola, JE.; Houldsworth, J.; Chaganti, RS.; Bosl, GJ. et al. (Aug 2009). "Testicular mixed germ cell tumors: a morphological and immunohistochemical study using stem cell markers, OCT3/4, SOX2 and GDF3, with emphasis on morphologically difficult-to-classify areas.". Mod Pathol 22 (8): 1066-74. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.66. PMID 19396148.
- ↑ Beilby, JO.; Horne, CH.; Milne, GD.; Parkinson, C. (May 1979). "Alpha-fetoprotein, alpha-1-antitrypsin, and transferrin in gonadal yolk-sac tumours.". J Clin Pathol 32 (5): 455-61. PMID 89123.
