Difference between revisions of "Wilms tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Wilms tumour''', also '''nephroblastoma''' and '''Wilms' tumour''', is the most common [[Pediatric_kidney_tumours|pediatric kidney tumour]]. | ||
==General== | |||
*Common abdominal [[pediatric pathology|pediatric]] tumour. | |||
*May be associated with a syndrome:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/989398-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/989398-overview]. Accessed on: 9 March 2011.</ref> | |||
**WAGR syndrome (Wilms tumour, Aniridia (absence of iris), GU abnormalities, Retardation).<ref>{{OMIM|194072}}</ref> | |||
**[[Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome]].<ref>{{OMIM|130650}}</ref> | |||
**[[Denys-Drash syndrome]].<ref>{{OMIM|194080}}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Lobulated tan mass. | |||
Image: [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/EXAM/IMGQUIZ/rnfrm.html Wilms tumour (med.utah.edu)]. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
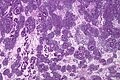
Features - classically three components (blastema, immature stroma, tubules):<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_254-5>{{Ref PCPBoD8|254-5}}</ref> | |||
#Malignant [[Small round blue cell tumours|small round blue cells]] ("blastema"): | |||
#*Size = ~ 2x RBC diameter. | |||
#*Nuclear pleomorphism (variation of size, shape and staining). | |||
#**Irregular nuclear membrane - '''important'''. | |||
#*Scant/difficult to discern cytoplasm - basophilic (light blue). | |||
#*Mitoses - common. | |||
#Stroma ("immature stroma"): | |||
#*Spindle cells: | |||
#**Elliptical nuclear membrane. | |||
#**Abundant loose cytoplasm. | |||
#Tubular structures ("tubules"): | |||
#*Usually clustered. | |||
#*Vaguely resemble a glomerulus. | |||
#*Usu. have a central (clear/white) space surrounded by a rim of intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
#*Nuclei of tubular structures often elongated and palisaded. | |||
Other findings: | |||
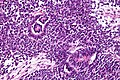
*Commonly seen in association with ''nephrogenic rests''. | |||
**Cluster of cells small (blue) cells; lack nuclear atypia seen in Wilms tumour.<ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970416-8 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970416-8]. Accessed on: 28 March 2011.</ref> | |||
*+/-Heterologous elements (skeletal muscle, smooth muscle adipose tissue, cartilage).<ref name=Ref_WMSP282>{{Ref WMSP|282}}</ref> | |||
**Heterologous = doesn't normally belong there.<ref>URL: [http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Heterologous http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Heterologous]. Accessed on: 1 October 2011.</ref> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Metanephric adenoma]]. | |||
*Nephrogenic nests. | |||
*Other [[small round cell tumours]]. | |||
*[[Synovial sarcoma]], biphasic - especially in adults. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Palisade = fence made of stakes driven into the ground.<ref>URL: [http://www.thefreedictionary.com/palisaded http://www.thefreedictionary.com/palisaded]. Accessed on: 2 February 2011.</ref> | |||
*Approximately 30-40% Wilms tumour cases have nephrogenic rests.<ref name=pmid8047084>{{cite journal |author=Coppes MJ, Haber DA, Grundy PE |title=Genetic events in the development of Wilms' tumor |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=331 |issue=9 |pages=586–90 |year=1994 |month=September |pmid=8047084 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199409013310906 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*The three phases are also called ''blastemal, epithelial and stromal''.<ref name=Ref_WMSP282>{{Ref WMSP|282}}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Wilms_tumour_-_low_mag.jpg | Wilms tumour - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Wilms tumour - intermed mag.jpg | Wilms tumour - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Wilms tumour - high mag.jpg | Wilms tumour - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Wilms_tumour_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Wilms tumour - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.biologydisease.com/images/kidney/nephrogenic-rests/nephrogenic-rest.jpg.php Nephrogenic rests (biologydisease.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=1&Case=73 Wilms tumour (webpathology.com)]. | |||
===Anaplasia=== | |||
Subclassified as:<ref name=Ref_WMSP282>{{Ref WMSP|282}}</ref> | |||
#Focal anaplasia. | |||
#Diffuse anaplasia. | |||
Criteria (all of the following):<ref name=Ref_WMSP282>{{Ref WMSP|282}}</ref> | |||
#Atypical mitoses. | |||
#Nuclear hyperchromasia. | |||
#Nuclear size variation (of the tumour cells) > 3x. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*WT-1 +ve. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pediatric kidney tumours]]. | |||
*[[Kidney tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatric kidney tumours]] | |||
Revision as of 03:19, 3 May 2014
Wilms tumour, also nephroblastoma and Wilms' tumour, is the most common pediatric kidney tumour.
General
- Common abdominal pediatric tumour.
- May be associated with a syndrome:[1]
- WAGR syndrome (Wilms tumour, Aniridia (absence of iris), GU abnormalities, Retardation).[2]
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.[3]
- Denys-Drash syndrome.[4]
Gross
- Lobulated tan mass.
Image: Wilms tumour (med.utah.edu).
Microscopic
Features - classically three components (blastema, immature stroma, tubules):[5]
- Malignant small round blue cells ("blastema"):
- Size = ~ 2x RBC diameter.
- Nuclear pleomorphism (variation of size, shape and staining).
- Irregular nuclear membrane - important.
- Scant/difficult to discern cytoplasm - basophilic (light blue).
- Mitoses - common.
- Stroma ("immature stroma"):
- Spindle cells:
- Elliptical nuclear membrane.
- Abundant loose cytoplasm.
- Spindle cells:
- Tubular structures ("tubules"):
- Usually clustered.
- Vaguely resemble a glomerulus.
- Usu. have a central (clear/white) space surrounded by a rim of intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Nuclei of tubular structures often elongated and palisaded.
Other findings:
- Commonly seen in association with nephrogenic rests.
- Cluster of cells small (blue) cells; lack nuclear atypia seen in Wilms tumour.[6]
- +/-Heterologous elements (skeletal muscle, smooth muscle adipose tissue, cartilage).[7]
- Heterologous = doesn't normally belong there.[8]
DDx:
- Metanephric adenoma.
- Nephrogenic nests.
- Other small round cell tumours.
- Synovial sarcoma, biphasic - especially in adults.
Notes:
- Palisade = fence made of stakes driven into the ground.[9]
- Approximately 30-40% Wilms tumour cases have nephrogenic rests.[10]
- The three phases are also called blastemal, epithelial and stromal.[7]
Images
www:
Anaplasia
Subclassified as:[7]
- Focal anaplasia.
- Diffuse anaplasia.
Criteria (all of the following):[7]
- Atypical mitoses.
- Nuclear hyperchromasia.
- Nuclear size variation (of the tumour cells) > 3x.
IHC
- WT-1 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/989398-overview. Accessed on: 9 March 2011.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 194072
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 130650
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 194080
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 254-5. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970416-8. Accessed on: 28 March 2011.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 282. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Heterologous. Accessed on: 1 October 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.thefreedictionary.com/palisaded. Accessed on: 2 February 2011.
- ↑ Coppes MJ, Haber DA, Grundy PE (September 1994). "Genetic events in the development of Wilms' tumor". N. Engl. J. Med. 331 (9): 586–90. doi:10.1056/NEJM199409013310906. PMID 8047084.