Difference between revisions of "Gangliocytic paraganglioma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
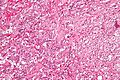
'''Gangliocytic paraganglioma''', abbreviated '''GP''', is an extremely rare tumour most often found in the [[duodenum]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Extremely rare.<ref name=pmid22340577>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wu | first1 = GC. | last2 = Wang | first2 = KL. | last3 = Zhang | first3 = ZT. | title = Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum: a case report. | journal = Chin Med J (Engl) | volume = 125 | issue = 2 | pages = 388-9 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22340577 }}</ref> | |||
*May be associated with [[neurofibromatosis type 1]].<ref name=pmid12754392>{{Cite journal | last1 = Castoldi | first1 = L. | last2 = De Rai | first2 = P. | last3 = Marini | first3 = A. | last4 = Ferrero | first4 = S. | last5 = De Luca | first5 = V. | last6 = Tiberio | first6 = G. | title = Neurofibromatosis-1 and Ampullary Gangliocytic Paraganglioma Causing Biliary and Pancreatic Obstruction. | journal = Int J Gastrointest Cancer | volume = 29 | issue = 2 | pages = 93-98 | month = | year = 2001 | doi = | PMID = 12754392 }}</ref> | |||
*Classified a [[neuroendocrine tumour]].<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.</ref> | |||
*Usually has a mix of the features seen in: [[neuroendocrine tumour]]s, [[paraganglioma]]s and [[ganglioneuroma]]s. | |||
Clinical - presentation:<ref name=pmid21599949/> | |||
*GI bleed ~ 45% of cases. | |||
*Abdominal pain ~ 43% of cases. | |||
*[[Anemia]] ~ 15% of cases. | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Classically in the duodenum ~90% of cases.<ref name=pmid21599949>{{Cite journal | last1 = Okubo | first1 = Y. | last2 = Wakayama | first2 = M. | last3 = Nemoto | first3 = T. | last4 = Kitahara | first4 = K. | last5 = Nakayama | first5 = H. | last6 = Shibuya | first6 = K. | last7 = Yokose | first7 = T. | last8 = Yamada | first8 = M. | last9 = Shimodaira | first9 = K. | title = Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma. | journal = BMC Cancer | volume = 11 | issue = | pages = 187 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2407-11-187 | PMID = 21599949 }}</ref> | |||
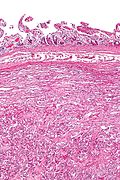
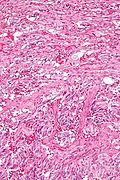
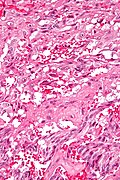
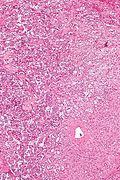
==Microscopic== | |||
Features - three components:<ref name=pmid15740625>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wong | first1 = A. | last2 = Miller | first2 = AR. | last3 = Metter | first3 = J. | last4 = Thomas | first4 = CR. | title = Locally advanced duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with adjuvant radiation therapy: case report and review of the literature. | journal = World J Surg Oncol | volume = 3 | issue = 1 | pages = 15 | month = Mar | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1186/1477-7819-3-15 | PMID = 15740625 }}</ref><ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gitumors/gangliocytic-paraganglioma/printable.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gitumors/gangliocytic-paraganglioma/printable.html]. Accessed on: 31 May 2012.</ref> | |||
#Ganglion cells = large cells with: | |||
#*Round large nucleus. | |||
#*Prominent [[nucleolus]]. | |||
#*Moderate or abundant cytoplasm. | |||
#Epithelioid cells (neuroendocrine component): | |||
#*Arranged in nests or cords. | |||
#*Stippled chromatin. | |||
#Spindle cells ([[Schwannoma|schwannian]] component): | |||
#*Moderate or abundant cytoplasm. | |||
#*Nucleus spindle-shaped or ellipsoid. | |||
DDx:<ref name=pmid15740625/> | |||
*Poorly differentiated carcinoma. | |||
*[[Neuroendocrine tumour]]. | |||
*[[Paraganglioma]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Gangliocytic_paraganglioma_-_intermed_mag.jpg | GP - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Gangliocytic_paraganglioma_-_high_mag.jpg | GP - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Gangliocytic_paraganglioma_-_very_high_mag.jpg | GP - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Gangliocytic_paraganglioma_-_2_-_intermed_mag.jpg | GP - 2 - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Gangliocytic_paraganglioma_-_2_-_high_mag.jpg | GP - 2 - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.wjso.com/content/3/1/15/figure/F2 Epithelioid cells of a GP (wjso.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.wjso.com/content/3/1/15/figure/F4 Ganglion cell in a GP (wjso.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.pubcan.org/images/large/Fig_5-17_A.jpg Ganglion cells in a GP (pubcan.org)].<ref>URL: [http://www.pubcan.org/printicdotopo.php?id=5028 http://www.pubcan.org/printicdotopo.php?id=5028]. Accessed on: 15 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*[http://www.surgicalpathologyatlas.com/glfusion/mediagallery/media.php?f=0&sort=0&s=20080802175012135 GP (surgicalpathologyatlas.com)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*Synaptophysin +ve. | |||
*CD56 +ve. | |||
*Chromogranin A +ve. | |||
*HU +ve in ganglion-like cells. | |||
*S100 +ve in spindle cells & sustentacular cells. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Duodenum]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Duodenum]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 19:12, 12 April 2014
Gangliocytic paraganglioma, abbreviated GP, is an extremely rare tumour most often found in the duodenum.
General
- Extremely rare.[1]
- May be associated with neurofibromatosis type 1.[2]
- Classified a neuroendocrine tumour.[3]
- Usually has a mix of the features seen in: neuroendocrine tumours, paragangliomas and ganglioneuromas.
Clinical - presentation:[4]
- GI bleed ~ 45% of cases.
- Abdominal pain ~ 43% of cases.
- Anemia ~ 15% of cases.
Gross
- Classically in the duodenum ~90% of cases.[4]
Microscopic
Features - three components:[5][6]
- Ganglion cells = large cells with:
- Round large nucleus.
- Prominent nucleolus.
- Moderate or abundant cytoplasm.
- Epithelioid cells (neuroendocrine component):
- Arranged in nests or cords.
- Stippled chromatin.
- Spindle cells (schwannian component):
- Moderate or abundant cytoplasm.
- Nucleus spindle-shaped or ellipsoid.
DDx:[5]
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma.
- Neuroendocrine tumour.
- Paraganglioma.
Images
www:
- Epithelioid cells of a GP (wjso.com).
- Ganglion cell in a GP (wjso.com).
- Ganglion cells in a GP (pubcan.org).[7]
- GP (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
IHC
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- CD56 +ve.
- Chromogranin A +ve.
- HU +ve in ganglion-like cells.
- S100 +ve in spindle cells & sustentacular cells.
See also
References
- ↑ Wu, GC.; Wang, KL.; Zhang, ZT. (Jan 2012). "Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum: a case report.". Chin Med J (Engl) 125 (2): 388-9. PMID 22340577.
- ↑ Castoldi, L.; De Rai, P.; Marini, A.; Ferrero, S.; De Luca, V.; Tiberio, G. (2001). "Neurofibromatosis-1 and Ampullary Gangliocytic Paraganglioma Causing Biliary and Pancreatic Obstruction.". Int J Gastrointest Cancer 29 (2): 93-98. PMID 12754392.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Okubo, Y.; Wakayama, M.; Nemoto, T.; Kitahara, K.; Nakayama, H.; Shibuya, K.; Yokose, T.; Yamada, M. et al. (2011). "Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma.". BMC Cancer 11: 187. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-187. PMID 21599949.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wong, A.; Miller, AR.; Metter, J.; Thomas, CR. (Mar 2005). "Locally advanced duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with adjuvant radiation therapy: case report and review of the literature.". World J Surg Oncol 3 (1): 15. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-3-15. PMID 15740625.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gitumors/gangliocytic-paraganglioma/printable.html. Accessed on: 31 May 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pubcan.org/printicdotopo.php?id=5028. Accessed on: 15 April 2012.