Difference between revisions of "Solitary fibrous tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Features - benign: | Features - benign: | ||
*Spindle cells in a patternless pattern. | *Spindle cells in a patternless pattern. | ||
**Occasionally epithelioid cells - rare.<ref name=pmid17577399>{{Cite journal | last1 = Martorell | first1 = M. | last2 = Pérez-Vallés | first2 = A. | last3 = Gozalbo | first3 = F. | last4 = Garcia-Garcia | first4 = JA. | last5 = Gutierrez | first5 = J. | last6 = Gaona | first6 = J. | title = Solitary fibrous tumor of the thigh with epithelioid features: a case report. | journal = Diagn Pathol | volume = 2 | issue = | pages = 19 | month = | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1186/1746-1596-2-19 | PMID = 17577399 }}</ref> | |||
*Hemangiopericytoma-like area ([[staghorn vessels]]). | *Hemangiopericytoma-like area ([[staghorn vessels]]). | ||
*Keloid-like collagen bundles - '''key feature'''. | *Keloid-like collagen bundles - '''key feature'''. | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 18 February 2014
| Solitary fibrous tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
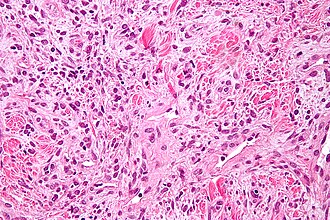 Solitary fibrous tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | spindle cells in a patternless pattern, hemangiopericytoma-like areas (staghorn vessels), keloid-like collagen bundles, +/-well-circumscribed (common) |
| Subtypes | benign (common), malignant (uncommon) |
| IHC | CD34 ~90% +ve, CD99 ~70% +ve, BCL2 ~50% +ve |
| Site | soft tissue - fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours, pleura |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Doege-Potter syndrome |
|
| |
| Prognosis | usu. good |
Solitary fibrous tumour, abbreviated SFT, is a type of soft tissue tumour that fits in the fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours. It is usually benign.
SFT of the pleura is dealt with in a separate article solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura.
General
- Grouped with hemangiopericytoma in the WHO classification - as it is thought to be the same tumour.[1]
- May be benign or malignant; more commonly benign.[2][3]
- May be associated with hypoglycemia.
- Known as Doege-Potter syndrome.[4]
Gross
- Soft tissue mass.
Microscopic
Features - benign:
- Spindle cells in a patternless pattern.
- Occasionally epithelioid cells - rare.[5]
- Hemangiopericytoma-like area (staghorn vessels).
- Keloid-like collagen bundles - key feature.
- +/-Well-circumscribed (common).
Criteria for malignancy:[1]
- Necrosis.
- Mitoses >4/10 HPF -- definition suffers from HPFitis.
- Increased cellularity.
- Marked nuclear atypia.
- Infiltrative margin.
Images
www:
IHC
- CD34 ~90% +ve.
- CD99 ~70% +ve.
- BCL2 ~50% +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 609. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970528-9. Accessed on: 25 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://wjso.com/content/6/1/86. Accessed on: 25 June 2010.
- ↑ Roy, TM.; Burns, MV.; Overly, DJ.; Curd, BT. (Nov 1992). "Solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura with hypoglycemia: the Doege-Potter syndrome.". J Ky Med Assoc 90 (11): 557-60. PMID 1474302.
- ↑ Martorell, M.; Pérez-Vallés, A.; Gozalbo, F.; Garcia-Garcia, JA.; Gutierrez, J.; Gaona, J. (2007). "Solitary fibrous tumor of the thigh with epithelioid features: a case report.". Diagn Pathol 2: 19. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-2-19. PMID 17577399.


