Difference between revisions of "Diverticular disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| IF = | | IF = | ||
| Gross = | | Gross = outpouching - best seen after sectioning | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Site = [[colon]] - classically sigmoid, other sites | | Site = [[colon]] - classically sigmoid, other sites | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
| Symptoms = usu. asymptomatic, diverticulitis presents with abdominal pain | | Symptoms = usu. asymptomatic, diverticulitis presents with abdominal pain | ||
| Prevalence = | | Prevalence = common - especially elderly | ||
| Bloodwork = | | Bloodwork = | ||
| Rads = | | Rads = | ||
Revision as of 20:02, 10 January 2014
| Diverticular disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
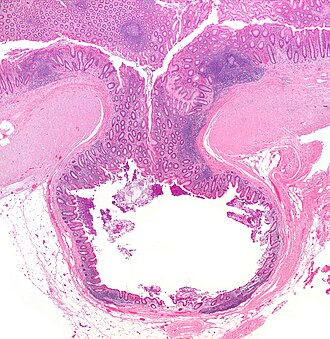 Diverticulum. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | mucosa/submucosa invaginate into the musuclaris propria |
| Gross | outpouching - best seen after sectioning |
| Site | colon - classically sigmoid, other sites |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | diverticulitis, peritonitis, diverticular disease-associated colitis |
| Symptoms | usu. asymptomatic, diverticulitis presents with abdominal pain |
| Prevalence | common - especially elderly |
| Clin. DDx | colorectal carcinoma |
Diverticular disease, also diverticulosis, is a common disease of the colon. Inflammation of diverticula is known as diverticulitis.
General
- Very common.
- Typically seen in elderly patients - 50s and 60s.
Complications:
- Diverticulitis.
- Peformation - peritonitis.
- Diverticular-associated colitis - see below.
Diverticular disease-associated colitis
Features:[1]
- Rare.
- Definitions vary somewhat - one is: IBD-like inflammation restricted to areas with diverticular disease.
- Considerable overlap with IBD histologically - no definite histologic findings.
- Rectal biopsy may be used to differentiate from ulcerative colitis.
Gross
- Corrugated - like cardboard.
- Wall thickening (reactive).[2]
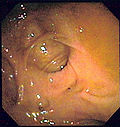
Endoscopic image
Grossing notes
Microscopic
Features:
- Mucosa/submucosa invagination into the musuclaris propria (MP).
- At the site the blood vessels supplying the mucosa and submucosa penetrate the MP.[3]
DDx:
- Colorectal carcinoma - may cause a stricture, usually obvious on microscopy.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
Images
www:
Sign out
SIGMOID COLON, SIGMOIDECTOMY: - DIVERTICULAR DISEASE WITHOUT DIVERTICULITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Perforated
RECTO-SIGMOID, LARGE BOWEL RESECTION: - PERFORATED DIVERTICULITIS WITH SEROSITIS AND ABSCESS FORMATION. - SUBMUCOSAL FIBROSIS. - ONE LYMPH NODE NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY ( 0 POSITIVE / 1 ). - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
SIGMOID COLON, RESECTION: - COLONIC PERFORATION ASSOCIATED WITH FAT NECROSIS, SEROSITIS AND MICROABSCESS FORMATION, IN THE SETTING OF DIVERTICULAR DISEASE. - ONE LYMPH NODE NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY ( 0 POSITIVE / 1 ). - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Mulhall, AM.; Mahid, SS.; Petras, RE.; Galandiuk, S. (Jun 2009). "Diverticular disease associated with inflammatory bowel disease-like colitis: a systematic review.". Dis Colon Rectum 52 (6): 1072-9. doi:10.1007/DCR.0b013e31819ef79a. PMID 19581849.
- ↑ Nicholson, BD.; Hyland, R.; Rembacken, BJ.; Denyer, M.; Hull, MA.; Tolan, DJ. (Aug 2011). "Colonoscopy for colonic wall thickening at computed tomography: a worthwhile pursuit?". Surg Endosc 25 (8): 2586-91. doi:10.1007/s00464-011-1591-7. PMID 21359889.
- ↑ West, AB.. "The pathology of diverticulitis.". J Clin Gastroenterol 42 (10): 1137-8. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181862a9f. PMID 18936652.
- ↑ URL: http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject. Accessed on: 23 August 2011.