Difference between revisions of "Sinus histiocytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
(+infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Sinus histiocytosis -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Sinus histiocytosis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[Rosai-Dorfman disease]], [[dermatopathic lymphadenopathy]], [[lymph node metastasis]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[lymph node]] - see ''[[lymph node pathology]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = varaible | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = common | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other causes of lymphadenopathy esp. [[lymphoma]], [[lymph node metastasis]] | |||
}} | |||
'''Sinus histiocytosis''', abbreviated '''SH''', is a common finding in [[lymph nodes]]. | '''Sinus histiocytosis''', abbreviated '''SH''', is a common finding in [[lymph nodes]]. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 63: | ||
*CD68 +ve. | *CD68 +ve. | ||
*S-100 -ve. | *S-100 -ve. | ||
*Pankeratin -ve. | |||
**Used to excluded metastatic carcinoma. | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 1 December 2013
| Sinus histiocytosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
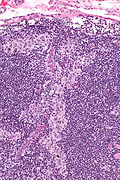
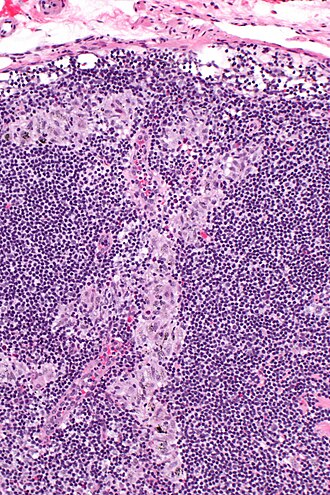 Sinus histiocytosis. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | Rosai-Dorfman disease, dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, lymph node metastasis |
| Site | lymph node - see lymph node pathology |
|
| |
| Clinical history | varaible |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other causes of lymphadenopathy esp. lymphoma, lymph node metastasis |
Sinus histiocytosis, abbreviated SH, is a common finding in lymph nodes.
It should not be confused with Rosai-Dorfman disease (also known as sinus histiocytosis and massive lymphadenopathy).
General
- Benign.
- Non-specific finding.
- Frequently associated with infections and neoplasia.[1]
- Reported in association with hip replacements.[2]
Gross
- +/-Enlargement of lymph node.[3]
Microscopic
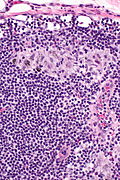
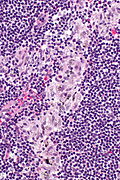
Features:[4]
- Sinuses distended with histiocytes - key feature.
- Histocytes: abundant foamy cytoplasm, +/-anthrocotic pigment.
- Plasma cells increased.
DDx:
- Rosai-Dorfman disease - histiocytes have a large round nucleus (~2-3x the size of a lymphocyte) with a prominent nucleolus.
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy - histiocytes have (melanin) pigment.
- Lymph node metastasis - usually not difficult if one compares with the germinal center macrophages and the primary tumour.
Images
IHC
- CD68 +ve.
- S-100 -ve.
- Pankeratin -ve.
- Used to excluded metastatic carcinoma.
Sign out
- The finding is often ignored; may be signed out as morphologically benign lymph nodes.
See also
References
- ↑ Hartmann, S.; Kriener, S.; Hansmann, ML. (Jul 2008). "[Diagnostic spectrum of reactive lymph node changes].". Pathologe 29 (4): 253-63. doi:10.1007/s00292-008-1003-5. PMID 18504582.
- ↑ Albores-Saavedra, J.; Vuitch, F.; Delgado, R.; Wiley, E.; Hagler, H. (Jan 1994). "Sinus histiocytosis of pelvic lymph nodes after hip replacement. A histiocytic proliferation induced by cobalt-chromium and titanium.". Am J Surg Pathol 18 (1): 83-90. PMID 8279630.
- ↑ Saito, T.; Kuwahara, A.; Kaketani, K.; Hirao, E.; Miyahara, M.; Shimoda, K.; Kobayashi, M. (Mar 1991). "Preoperative assessment of cervical lymph node involvement in esophageal cancer.". Jpn J Surg 21 (2): 145-53. PMID 2051659.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 179. ISBN 978-0781775960.