Difference between revisions of "Inflammatory fibroid polyp"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
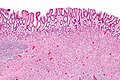
| Image = Inflammatory_fibroid_polyp_-_low_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Inflammatory fibroid polyp. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = proliferating spindle cells - loosely arranged round blood vessels with perivascular hypocellular zones, eosinophils (common), leiomyoma/schwannoma-like areas - with nuclear palisading | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour]], [[GIST]], [[schwannoma]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = CD34 +ve, vimentin +ve, CD117 -ve, S-100 -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[stomach]], other places in the GI tract | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good - benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Inflammatory fibroid polyp''' is an uncommon [[gastrointestinal polyp]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Benign. | |||
*Through-out GI tract. | |||
*Can be thought of as granulation tissue-like.<ref name=Ref_DCHH138/> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
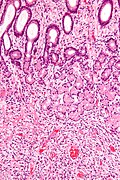
Features:<ref name=pmid20393746>{{Cite journal | last1 = Daum | first1 = O. | last2 = Hatlova | first2 = J. | last3 = Mandys | first3 = V. | last4 = Grossmann | first4 = P. | last5 = Mukensnabl | first5 = P. | last6 = Benes | first6 = Z. | last7 = Michal | first7 = M. | title = Comparison of morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features of inflammatory fibroid polyps (Vanek's tumors). | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 456 | issue = 5 | pages = 491-7 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-010-0914-8 | PMID = 20393746 }}</ref> | |||
*Proliferating spindle cells (fibroid) - '''key feature'''. | |||
**Loosely arranged, concentrically, around blood vessels.<ref name=Ref_GLP115>{{Ref GLP|115}}</ref> | |||
**Perivascular hypocellular zones.<ref name=Ref_DCHH138>{{Ref DCHH|138}}</ref> | |||
*Inflammation: | |||
**Eosinophils - often prominent. | |||
*+/-Leiomyoma/schwannoma-like areas - with nuclear palisading.<ref name=Ref_DCHH138>{{Ref DCHH|138}}</ref> | |||
*+/-Vascular for fibrous tissue. | |||
*Poorly circumscribed/infiltrates into the lamina propria. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour]]. | |||
*[[GIST]] - usually sharply demarcated border. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Concentric = share the same centre.<ref>URL: [http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/concentric http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/concentric]. Accessed on: 29 November 2011.</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Inflammatory_fibroid_polyp_-_low_mag.jpg | IFP - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Inflammatory_fibroid_polyp_-_high_mag.jpg | IFP - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid20393746/> | |||
*CD34 +ve. | |||
**There is a CD34 -ve variant. | |||
*Vimentin +ve -- diffuse.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kolodziejczyk | first1 = P. | last2 = Yao | first2 = T. | last3 = Tsuneyoshi | first3 = M. | title = Inflammatory fibroid polyp of the stomach. A special reference to an immunohistochemical profile of 42 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 17 | issue = 11 | pages = 1159-68 | month = Nov | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8214261 }}</ref> | |||
Others: | |||
*CD117 -ve.<ref name=pmid15163021>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ozolek | first1 = JA. | last2 = Sasatomi | first2 = E. | last3 = Swalsky | first3 = PA. | last4 = Rao | first4 = U. | last5 = Krasinskas | first5 = A. | last6 = Finkelstein | first6 = SD. | title = Inflammatory fibroid polyps of the gastrointestinal tract: clinical, pathologic, and molecular characteristics. | journal = Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol | volume = 12 | issue = 1 | pages = 59-66 | month = Mar | year = 2004 | doi = | PMID = 15163021 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
*S100 -ve. | |||
==Molecular== | |||
*A subset have mutations in PDGFRA.<ref name=pmid20393746>{{Cite journal | last1 = Daum | first1 = O. | last2 = Hatlova | first2 = J. | last3 = Mandys | first3 = V. | last4 = Grossmann | first4 = P. | last5 = Mukensnabl | first5 = P. | last6 = Benes | first6 = Z. | last7 = Michal | first7 = M. | title = Comparison of morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features of inflammatory fibroid polyps (Vanek's tumors). | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 456 | issue = 5 | pages = 491-7 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-010-0914-8 | PMID = 20393746 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Stomach]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | |||
Revision as of 12:34, 12 July 2013
| Inflammatory fibroid polyp | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
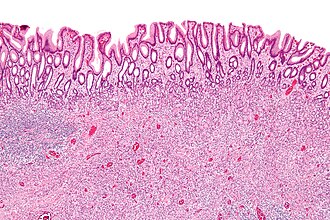 Inflammatory fibroid polyp. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | proliferating spindle cells - loosely arranged round blood vessels with perivascular hypocellular zones, eosinophils (common), leiomyoma/schwannoma-like areas - with nuclear palisading |
| LM DDx | inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour, GIST, schwannoma |
| IHC | CD34 +ve, vimentin +ve, CD117 -ve, S-100 -ve |
| Site | stomach, other places in the GI tract |
|
| |
| Prognosis | good - benign |
Inflammatory fibroid polyp is an uncommon gastrointestinal polyp.
General
- Benign.
- Through-out GI tract.
- Can be thought of as granulation tissue-like.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Proliferating spindle cells (fibroid) - key feature.
- Inflammation:
- Eosinophils - often prominent.
- +/-Leiomyoma/schwannoma-like areas - with nuclear palisading.[1]
- +/-Vascular for fibrous tissue.
- Poorly circumscribed/infiltrates into the lamina propria.
DDx:
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour.
- GIST - usually sharply demarcated border.
Notes:
- Concentric = share the same centre.[4]
Images
IHC
Features:[2]
- CD34 +ve.
- There is a CD34 -ve variant.
- Vimentin +ve -- diffuse.[5]
Others:
- CD117 -ve.[6]
- S100 -ve.
Molecular
- A subset have mutations in PDGFRA.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 138. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Daum, O.; Hatlova, J.; Mandys, V.; Grossmann, P.; Mukensnabl, P.; Benes, Z.; Michal, M. (May 2010). "Comparison of morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features of inflammatory fibroid polyps (Vanek's tumors).". Virchows Arch 456 (5): 491-7. doi:10.1007/s00428-010-0914-8. PMID 20393746.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 115. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/concentric. Accessed on: 29 November 2011.
- ↑ Kolodziejczyk, P.; Yao, T.; Tsuneyoshi, M. (Nov 1993). "Inflammatory fibroid polyp of the stomach. A special reference to an immunohistochemical profile of 42 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 17 (11): 1159-68. PMID 8214261.
- ↑ Ozolek, JA.; Sasatomi, E.; Swalsky, PA.; Rao, U.; Krasinskas, A.; Finkelstein, SD. (Mar 2004). "Inflammatory fibroid polyps of the gastrointestinal tract: clinical, pathologic, and molecular characteristics.". Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 12 (1): 59-66. PMID 15163021.