Difference between revisions of "Granuloma annulare"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Granuloma annulare''' is relatively uncommon problem in [[dermatopathology]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Benign and self-limited condition. | |||
*Etiology unknown - may be assoc. with trauma.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Typically extremities - usu. arms and hands.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> | |||
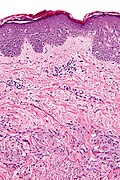
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP478>{{Ref WMSP|478}}</ref> | |||
*Dermal palisading [[granuloma]] - typically superficial-to-mid dermis - surrounds: | |||
**Necrotic collagen - '''key feature'''. | |||
***Nuclei "missing" - have undergone karyolysis. | |||
**Mucin - important. | |||
***Loose/pale, paucicellular, eosinophilic. | |||
*Chronic inflammatory cells. | |||
Notes: | |||
#There may be multiple small foci with intervening normal dermis.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> | |||
#Granuloma annulare can be subclassified into ''subcutaneous'' and ''interstitial''. | |||
#Histomorphologically similar to ''[[Rheumatoid nodule]]. | |||
#[[Neutrophil]]s may be seen.<ref name=pmid17544961>{{Cite journal | last1 = Requena | first1 = L. | last2 = Fernández-Figueras | first2 = MT. | title = Subcutaneous granuloma annulare. | journal = Semin Cutan Med Surg | volume = 26 | issue = 2 | pages = 96-9 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1016/j.sder.2007.02.006 | PMID = 17544961 }}</ref> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Necrobiosis lipoidica]] - little mucin, no normal dermis between foci,<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> plasma cells - common,<ref name=dermnetnz_nl>URL: [http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html]. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.</ref> may involve the fat - tend to be deeper. | |||
*[[Rheumatoid nodule]] - has fibrin in the core of the granuloma (instead of mucin), multinucleated macrophages more common.<ref name=Ref_Derm52-3>{{Ref Derm|52-3}}</ref> | |||
*[[Epithelioid sarcoma]] - esp. if the lesion appears to be mid-to-deep dermis. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Granuloma_annulare_-_add_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Granuloma annulare - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Granuloma_annulare_-_high_mag.jpg | Granuloma annulare - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Granuloma_annulare_-_add_-_high_mag.jpg | Granuloma annular - palisaded granuloma - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/61-i/1813-interstitial-granuloma-annulare-.html Granuloma annulare (dermaamin.com)]. | |||
==Stains== | |||
*[[Alcian blue stain|Alcian blue]] (pH 2.5) +ve (for mucin).<ref name=pmid20523767/><ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2861218/figure/F7/ Granuloma annulare (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid20523767>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yun | first1 = JH. | last2 = Lee | first2 = JY. | last3 = Kim | first3 = MK. | last4 = Seo | first4 = YJ. | last5 = Kim | first5 = MH. | last6 = Cho | first6 = KH. | last7 = Kim | first7 = MB. | last8 = Lee | first8 = WS. | last9 = Lee | first9 = KH. | title = Clinical and pathological features of generalized granuloma annulare with their correlation: a retrospective multicenter study in Korea. | journal = Ann Dermatol | volume = 21 | issue = 2 | pages = 113-9 | month = May | year = 2009 | doi = 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.113 | PMID = 20523767 | PMC = 2861218 }}</ref> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
Skin lesion, left elbow, excision: | |||
- Palisading granulomas with cores of necrobiotic collagen, and scant mucin | |||
consistent with granuloma annulare. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
An alcian-blue stain (pH 2.5) shows scant mucin. The granulomas are relatively deep; | |||
however, plasma cells are not apparent. The differential diagnosis is rheumatoid nodule. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Dermatopathology]]. | |||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 20:46, 25 June 2013
| Granuloma annulare | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short |
Granuloma annulare is relatively uncommon problem in dermatopathology.
General
- Benign and self-limited condition.
- Etiology unknown - may be assoc. with trauma.[1]
Gross
- Typically extremities - usu. arms and hands.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Dermal palisading granuloma - typically superficial-to-mid dermis - surrounds:
- Necrotic collagen - key feature.
- Nuclei "missing" - have undergone karyolysis.
- Mucin - important.
- Loose/pale, paucicellular, eosinophilic.
- Necrotic collagen - key feature.
- Chronic inflammatory cells.
Notes:
- There may be multiple small foci with intervening normal dermis.[1]
- Granuloma annulare can be subclassified into subcutaneous and interstitial.
- Histomorphologically similar to Rheumatoid nodule.
- Neutrophils may be seen.[3]
DDx:
- Necrobiosis lipoidica - little mucin, no normal dermis between foci,[1] plasma cells - common,[4] may involve the fat - tend to be deeper.
- Rheumatoid nodule - has fibrin in the core of the granuloma (instead of mucin), multinucleated macrophages more common.[5]
- Epithelioid sarcoma - esp. if the lesion appears to be mid-to-deep dermis.
Images
www:
Stains
- Alcian blue (pH 2.5) +ve (for mucin).[6][1]
Image:
Sign out
Skin lesion, left elbow, excision: - Palisading granulomas with cores of necrobiotic collagen, and scant mucin consistent with granuloma annulare. COMMENT: An alcian-blue stain (pH 2.5) shows scant mucin. The granulomas are relatively deep; however, plasma cells are not apparent. The differential diagnosis is rheumatoid nodule.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 51. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 478. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Requena, L.; Fernández-Figueras, MT. (Jun 2007). "Subcutaneous granuloma annulare.". Semin Cutan Med Surg 26 (2): 96-9. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2007.02.006. PMID 17544961.
- ↑ URL: http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 52-3. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yun, JH.; Lee, JY.; Kim, MK.; Seo, YJ.; Kim, MH.; Cho, KH.; Kim, MB.; Lee, WS. et al. (May 2009). "Clinical and pathological features of generalized granuloma annulare with their correlation: a retrospective multicenter study in Korea.". Ann Dermatol 21 (2): 113-9. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.113. PMC 2861218. PMID 20523767. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2861218/.