Difference between revisions of "Fibroadenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Fibroadenoma''' is a common benign tumour of the [[breast]]. | ||
==General== | |||
*Very common benign finding. | |||
*The pathology is in the stroma; so, the lesion is really a misnomer by the naming rules. | |||
**It ought to be called ''adenofibroma'' (as a few occasionally do<ref name=pmid15797289>{{Cite journal | last1 = Guinebretière | first1 = JM. | last2 = Menet | first2 = E. | last3 = Tardivon | first3 = A. | last4 = Cherel | first4 = P. | last5 = Vanel | first5 = D. | title = Normal and pathological breast, the histological basis. | journal = Eur J Radiol | volume = 54 | issue = 1 | pages = 6-14 | month = Apr | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.11.020 | PMID = 15797289 }}</ref>), as the glandular component is benign and the stromal component lesional; there is [[no truth in names]] in pathology. | |||
Management: | |||
*Local excision -- without a large margin. | |||
==Gross== | |||
Features:<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|550}}</ref> | |||
*Well-circumscribed. | |||
*Rubbery - '''classic descriptor'''. | |||
*Tan/white. | |||
*+/-Lobulated appearance. | |||
*+/-Slit-like spaces - short. | |||
*+/-Calcification. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://webpathology.com/image.asp?n=2&Case=276 Fibroadenoma - slit-like spaces (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=276&n=3 Fibroadenoma - lobulated appearance (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.surgical-tutor.org.uk/default-home.htm?tutorials/fibroadenoma.htm~right Fibroadenoma (surgical-tutor.org)]. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_BP110>{{Ref BP|110}}</ref> | |||
*Abundant (intralobular) stroma - most '''key feature'''. | |||
**Stroma is usually: | |||
***White/pale, i.e. [[myxoid stroma|myxoid]], on H&E (normal stroma is pink). | |||
****May be hyalinized (dark pink) if infarcted. | |||
***Paucicellular - typical. | |||
*Compression of glandular elements - very commonly seen. | |||
**Glandular elements have at least two cell layers - epithelial and myoepithelial. | |||
Notes: | |||
#There is stuff about ''intracanalicular'' vs. ''pericanalicular''.<ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970216-9 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970216-9]. Accessed on: 16 March 2011.</ref> It is irrelevant; there is no prognostic difference between the two. | |||
#Do '''not''' comment on the margin - it is irrelevant. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Phyllodes tumour]] - long slit-like spaces (seen grossly), stroma is more cellular. | |||
**+/-Mitoses, | |||
**+/-"Stromal overgrowth" = large area where there is a 'loss of glands'. | |||
*Sarcoma. | |||
*[[Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia]]. | |||
**Small capillary-like structures in the stroma. | |||
***Epithelial component often not compressed - as in fibroadenoma. | |||
*[[Adenomyoepithelioma]] - for [[tubular adenoma of the breast]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Breast fibradenoma (1).jpg | Fibroadenoma. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Breast_fibradenoma_(2).jpg | Fibroadenoma. (WC/KGH) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/27/suppl_1/S101/F40.expansion.html Infarcted fibroadenoma (rsna.org)].<ref name=pmid18180221>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sabate | first1 = JM. | last2 = Clotet | first2 = M. | last3 = Torrubia | first3 = S. | last4 = Gomez | first4 = A. | last5 = Guerrero | first5 = R. | last6 = de las Heras | first6 = P. | last7 = Lerma | first7 = E. | title = Radiologic evaluation of breast disorders related to pregnancy and lactation. | journal = Radiographics | volume = 27 Suppl 1 | issue = | pages = S101-24 | month = Oct | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1148/rg.27si075505 | PMID = 18180221 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.imagingpathways.health.wa.gov.au/includes/images/image/fibroadenoma_he.jpg Fibroadenoma (gov.au)].<ref>URL: [http://www.imagingpathways.health.wa.gov.au/includes/dipmenu/image/image.html http://www.imagingpathways.health.wa.gov.au/includes/dipmenu/image/image.html]. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.</ref> | |||
===Variants=== | |||
Four variants are described by the ''Washington Manual'':<ref name=Ref_WMSP262>{{Ref WMSP|262}}</ref> | |||
#Juvenile. | |||
#Complex. | |||
#Myxoid. | |||
#Cellular. | |||
Considered a variant of fibroadenoma by many authorities:<ref name=Ref_BP116>{{Ref BP|116}}</ref> | |||
*''[[Tubular adenoma of the breast]]''. | |||
====Juvenile fibroadenoma==== | |||
*As the name suggests, is typically found in younger patients. | |||
*Classic history: rapid growth. | |||
Features (juvenile variant):<ref>URL: [http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#juvenile http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#juvenile]. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.</ref> | |||
*Stromal and epithelial hyperplasia - '''key feature'''. | |||
*+/-Tapering, thin micropapillae (''[[gynecomastoid hyperplasia]]'').<ref name=Ref_BP116>{{Ref BP|116}}</ref> | |||
*Mitoses uncommon. | |||
====Myxoid fibroadenoma==== | |||
*May be associated with ''[[Carney's complex]]''. | |||
Features: | |||
*[[Myxoid stroma]]. | |||
====Cellular fibroadenoma==== | |||
Features (cellular variant): | |||
*Cellular. | |||
*Mitoses. | |||
====Complex fibroadenoma==== | |||
*Contain proliferative epithelium which outside and inside a fibroadenoma is associated with an increased risk of malignancy. | |||
Features:<ref>URL: [http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#complex http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#complex]. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.</ref> | |||
# [[Apocrine metaplasia]]. | |||
# Cysts > 3 mm. | |||
# Calcification. | |||
# [[Sclerosing adenosis]]. | |||
Memory devices: | |||
*''FACS'': complex '''f'''ibroadenoma, '''a'''pocrine metaplasia, '''c'''alcs & '''c'''ysts, '''s'''clerosing adenosis. | |||
*''CAMS'': '''c'''alcs, '''a'''pocrine metaplasia, '''m'''icrocysts, '''s'''clerosing adenosis. | |||
====Tubular adenoma of the breast==== | |||
*Considered by many a variant of ''fibroadenoma''. | |||
**[[IHC]] features of ''tubular adenoma of the breast'' and ''fibroadenoma'' are similar.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Maiorano | first1 = E. | last2 = Albrizio | first2 = M. | title = Tubular adenoma of the breast: an immunohistochemical study of ten cases. | journal = Pathol Res Pract | volume = 191 | issue = 12 | pages = 1222-30 | month = Dec | year = 1995 | doi = | PMID = 8927570 }}</ref> | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_BP116>{{Ref BP|116}}</ref> | |||
*Fibromyxoid stroma (like in a fibroadenoma). | |||
*Small round glands. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=277&n=1 Tubular adenoma of the breast (webpathology.com)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Tubular_Adenoma_of_Breast_(myosin_immunostain)_(4351463966).jpg | TA of the breast - myosin IHC. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Breast pathology]]. | |||
*[[Phyllodes tumour]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Breast pathology]] | |||
Revision as of 04:17, 15 February 2014
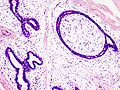
Fibroadenoma is a common benign tumour of the breast.
General
- Very common benign finding.
- The pathology is in the stroma; so, the lesion is really a misnomer by the naming rules.
- It ought to be called adenofibroma (as a few occasionally do[1]), as the glandular component is benign and the stromal component lesional; there is no truth in names in pathology.
Management:
- Local excision -- without a large margin.
Gross
Features:[2]
- Well-circumscribed.
- Rubbery - classic descriptor.
- Tan/white.
- +/-Lobulated appearance.
- +/-Slit-like spaces - short.
- +/-Calcification.
Images:
- Fibroadenoma - slit-like spaces (webpathology.com).
- Fibroadenoma - lobulated appearance (webpathology.com).
- Fibroadenoma (surgical-tutor.org).
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Abundant (intralobular) stroma - most key feature.
- Stroma is usually:
- White/pale, i.e. myxoid, on H&E (normal stroma is pink).
- May be hyalinized (dark pink) if infarcted.
- Paucicellular - typical.
- White/pale, i.e. myxoid, on H&E (normal stroma is pink).
- Stroma is usually:
- Compression of glandular elements - very commonly seen.
- Glandular elements have at least two cell layers - epithelial and myoepithelial.
Notes:
- There is stuff about intracanalicular vs. pericanalicular.[4] It is irrelevant; there is no prognostic difference between the two.
- Do not comment on the margin - it is irrelevant.
DDx:
- Phyllodes tumour - long slit-like spaces (seen grossly), stroma is more cellular.
- +/-Mitoses,
- +/-"Stromal overgrowth" = large area where there is a 'loss of glands'.
- Sarcoma.
- Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia.
- Small capillary-like structures in the stroma.
- Epithelial component often not compressed - as in fibroadenoma.
- Small capillary-like structures in the stroma.
- Adenomyoepithelioma - for tubular adenoma of the breast.
Images
www:
Variants
Four variants are described by the Washington Manual:[7]
- Juvenile.
- Complex.
- Myxoid.
- Cellular.
Considered a variant of fibroadenoma by many authorities:[8]
Juvenile fibroadenoma
- As the name suggests, is typically found in younger patients.
- Classic history: rapid growth.
Features (juvenile variant):[9]
- Stromal and epithelial hyperplasia - key feature.
- +/-Tapering, thin micropapillae (gynecomastoid hyperplasia).[8]
- Mitoses uncommon.
Myxoid fibroadenoma
- May be associated with Carney's complex.
Features:
Cellular fibroadenoma
Features (cellular variant):
- Cellular.
- Mitoses.
Complex fibroadenoma
- Contain proliferative epithelium which outside and inside a fibroadenoma is associated with an increased risk of malignancy.
Features:[10]
- Apocrine metaplasia.
- Cysts > 3 mm.
- Calcification.
- Sclerosing adenosis.
Memory devices:
- FACS: complex fibroadenoma, apocrine metaplasia, calcs & cysts, sclerosing adenosis.
- CAMS: calcs, apocrine metaplasia, microcysts, sclerosing adenosis.
Tubular adenoma of the breast
- Considered by many a variant of fibroadenoma.
Features:[8]
- Fibromyxoid stroma (like in a fibroadenoma).
- Small round glands.
Images:
See also
References
- ↑ Guinebretière, JM.; Menet, E.; Tardivon, A.; Cherel, P.; Vanel, D. (Apr 2005). "Normal and pathological breast, the histological basis.". Eur J Radiol 54 (1): 6-14. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.11.020. PMID 15797289.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 550. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 110. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970216-9. Accessed on: 16 March 2011.
- ↑ Sabate, JM.; Clotet, M.; Torrubia, S.; Gomez, A.; Guerrero, R.; de las Heras, P.; Lerma, E. (Oct 2007). "Radiologic evaluation of breast disorders related to pregnancy and lactation.". Radiographics 27 Suppl 1: S101-24. doi:10.1148/rg.27si075505. PMID 18180221.
- ↑ URL: http://www.imagingpathways.health.wa.gov.au/includes/dipmenu/image/image.html. Accessed on: 15 February 2012.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 262. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 116. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ URL: http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#juvenile. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.breastpathology.info/fibro_variants.html#complex. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.
- ↑ Maiorano, E.; Albrizio, M. (Dec 1995). "Tubular adenoma of the breast: an immunohistochemical study of ten cases.". Pathol Res Pract 191 (12): 1222-30. PMID 8927570.