Difference between revisions of "Ameloblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Ameloblastoma''' is an [[odontogenic cyst]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Osteous lesion. | |||
*Usually mandible.<ref>URL: [http://www.waent.org/archives/2010/Vol3-2/20100618-ameloblastoma/jaw-tumor.htm http://www.waent.org/archives/2010/Vol3-2/20100618-ameloblastoma/jaw-tumor.htm]. Accessed on: 30 November 2011.</ref> | |||
**In a review of 3677 cases, the mandible-to-maxilla ratio was 5 to 1.<ref name=pmid7633291>{{Cite journal | last1 = Reichart | first1 = PA. | last2 = Philipsen | first2 = HP. | last3 = Sonner | first3 = S. | title = Ameloblastoma: biological profile of 3677 cases. | journal = Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol | volume = 31B | issue = 2 | pages = 86-99 | month = Mar | year = 1995 | doi = | PMID = 7633291 }}</ref> | |||
*May arise from an odontogenic cyst,<ref name=pmid10587275>{{Cite journal | last1 = Eversole | first1 = LR. | title = Malignant epithelial odontogenic tumors. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 16 | issue = 4 | pages = 317-24 | month = Nov | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10587275 }}</ref> e.g. [[dentigerous cyst]].<ref name=pmid21957386>{{Cite journal | last1 = Moosvi | first1 = Z. | last2 = Tayaar | first2 = SA. | last3 = Kumar | first3 = GS. | title = Neoplastic potential of odontogenic cysts. | journal = Contemp Clin Dent | volume = 2 | issue = 2 | pages = 106-9 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.4103/0976-237X.83073 | PMID = 21957386 | PMC = 3180832 }}</ref> | |||
===Classification=== | |||
Location: | |||
#Intra-osseous. | |||
#*Locally aggressive. | |||
#Peripheral. | |||
#*Benign. | |||
====Subclassification of intra-osseous type==== | |||
Histology: | |||
#Solid/multicystic. | |||
#*More commonly reoccur. | |||
#Unicystic. | |||
#*Unlikely to reoccur. | |||
#*Classically found in younger individuals. | |||
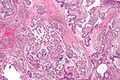
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970616-7 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970616-7]. Accessed on: March 9, 2010.</ref> | |||
*Stellate reticulum - star-shaped cells, found in a developing tooth. | |||
*Tall columnar cells. | |||
**Palisaded nuclei with reverse polarization. | |||
***Reverse polarization of nuclei = nuclei distant from the basement membrane/nuclei at pole opposite of basement membrane. | |||
***Palisaded nuclei = picket fence appearance; columnar-shaped nuclei with long axis perpendicular to the basement membrane -- '''key feature'''. | |||
**Subnuclear vacuolization. | |||
*+/-Giant cells. | |||
*+/-Subepithelial hyalinization (eosinophilic acellular amorphous material). | |||
**Seen deep to the basement membrane. | |||
*Variable morphology (see below - ''morphology''). | |||
DDx (nuclear palisading): | |||
*[[Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour]]. | |||
*[[Ameloblastic fibroma]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.estomatologia.com.br/diagnosticos_det2.asp?cod_diag=12 Ameloblastoma - several images (estomatologia.com.br)]. | |||
*[http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/digestive/devtooth9.jpg Stellate reticulum (cytochemistry.net)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Ameloblastoma - low mag.jpg | Ameloblastoma - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Ameloblastoma - intermed mag.jpg | Ameloblastoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Ameloblastoma - high mag.jpg | Ameloblastoma - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Ameloblastoma - very high mag.jpg | Ameloblastoma - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Morphology=== | |||
*Not prognostic. | |||
Morphologic variants: | |||
*Follicular ameloblastoma (classic appearance). | |||
*Plexiform ameloblastoma (does not have prominent palisading). | |||
*Acanthomatous ameloblastoma. | |||
*Desmoplastic ameloblastoma. | |||
*Basaloid ameloblastoma. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Odontogenic tumours and cysts]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Odontogenic tumours and cysts]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 15:08, 23 February 2014
Ameloblastoma is an odontogenic cyst.
General
- Osteous lesion.
- Usually mandible.[1]
- In a review of 3677 cases, the mandible-to-maxilla ratio was 5 to 1.[2]
- May arise from an odontogenic cyst,[3] e.g. dentigerous cyst.[4]
Classification
Location:
- Intra-osseous.
- Locally aggressive.
- Peripheral.
- Benign.
Subclassification of intra-osseous type
Histology:
- Solid/multicystic.
- More commonly reoccur.
- Unicystic.
- Unlikely to reoccur.
- Classically found in younger individuals.
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Stellate reticulum - star-shaped cells, found in a developing tooth.
- Tall columnar cells.
- Palisaded nuclei with reverse polarization.
- Reverse polarization of nuclei = nuclei distant from the basement membrane/nuclei at pole opposite of basement membrane.
- Palisaded nuclei = picket fence appearance; columnar-shaped nuclei with long axis perpendicular to the basement membrane -- key feature.
- Subnuclear vacuolization.
- Palisaded nuclei with reverse polarization.
- +/-Giant cells.
- +/-Subepithelial hyalinization (eosinophilic acellular amorphous material).
- Seen deep to the basement membrane.
- Variable morphology (see below - morphology).
DDx (nuclear palisading):
Images
www:
Morphology
- Not prognostic.
Morphologic variants:
- Follicular ameloblastoma (classic appearance).
- Plexiform ameloblastoma (does not have prominent palisading).
- Acanthomatous ameloblastoma.
- Desmoplastic ameloblastoma.
- Basaloid ameloblastoma.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.waent.org/archives/2010/Vol3-2/20100618-ameloblastoma/jaw-tumor.htm. Accessed on: 30 November 2011.
- ↑ Reichart, PA.; Philipsen, HP.; Sonner, S. (Mar 1995). "Ameloblastoma: biological profile of 3677 cases.". Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 31B (2): 86-99. PMID 7633291.
- ↑ Eversole, LR. (Nov 1999). "Malignant epithelial odontogenic tumors.". Semin Diagn Pathol 16 (4): 317-24. PMID 10587275.
- ↑ Moosvi, Z.; Tayaar, SA.; Kumar, GS. (Apr 2011). "Neoplastic potential of odontogenic cysts.". Contemp Clin Dent 2 (2): 106-9. doi:10.4103/0976-237X.83073. PMC 3180832. PMID 21957386. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3180832/.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970616-7. Accessed on: March 9, 2010.