Difference between revisions of "Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the urinary bladder"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(fix) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| LMDDx = [[lymphoma]], [[urothelial carcinoma]] and inflammation, metastatic [[lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma]] | | LMDDx = [[lymphoma]], [[urothelial carcinoma]] and inflammation, metastatic [[lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = CK34betaE12 +ve, p63 +ve/-ve, CK7 +ve/-ve, CK20 -ve, CD30 -ve | | IHC = [[CK34betaE12]] +ve, p63 +ve/-ve, [[CK7]] +ve/-ve, [[CK20]] -ve, CD30 -ve | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
Latest revision as of 14:50, 4 August 2022
| Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the urinary bladder | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
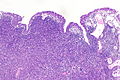
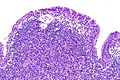
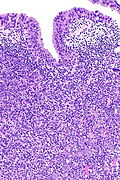
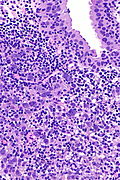
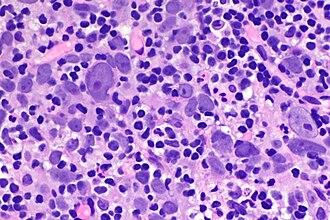 Urinary bladder lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | squamoid cells with abundant dense cytoplasm central nuclei +/- small/indistinct nucleoli, prominent lymphoid infiltrate |
| Subtypes | (subtype of urothelial carcinoma) |
| LM DDx | lymphoma, urothelial carcinoma and inflammation, metastatic lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma |
| IHC | CK34betaE12 +ve, p63 +ve/-ve, CK7 +ve/-ve, CK20 -ve, CD30 -ve |
| Site | urinary bladder - see urothelium |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | favourable on limited data |
| Other | not associated with EBV |
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the urinary bladder, also urinary bladder lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma (abbreviated UBLELC), is a rare variant of urothelial carcinoma.[1]
General
Microscopic
Features:
- Clusters of (cohesive) squamoid cells with:
- Abundant dense cytoplasm.
- Central nuclei +/- small/indistinct nucleoli.
- Prominent lymphoid infiltrate - key feature.
- +/-Urothelial carcinoma in situ.
Note:
- Peritumoural lymphoid aggregates are typical.[4]
DDx:
- Lymphoma.
- Urothelial carcinoma and inflammation.
- Metastatic lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma.
Images
www:
- LELC of the urinary bladder - low mag. (nih.gov).[4]
- LELC of the urinary bladder - high mag. (nih.gov).[4]
IHC
Features:[2]
- p53 +ve/-ve. (+ve in ~60% of cases).
- CK34betaE12 +ve (+ve in ~75% of cases).
- CK7 +ve/-ve (+ve in ~60% of cases).
- p63 +ve/-ve (+ve in ~50% of cases).
Others:[2]
- CK20 -ve.
- TTF-1 -ve.
- CD30 -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Amin, MB. (Jun 2009). "Histological variants of urothelial carcinoma: diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic implications.". Mod Pathol 22 Suppl 2: S96-S118. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.26. PMID 19494856.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Williamson, SR.; Zhang, S.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Shah, RB.; Montironi, R.; Tan, PH.; Wang, M.; Baldridge, LA. et al. (Apr 2011). "Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the urinary bladder: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (4): 474-83. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31820f709e. PMID 21383609.
- ↑ Fujino, T.; Kubota, M.; Nishiyama, R.; Kanno, T.; Okada, T.; Higashi, Y.; Yamada, H.; Okamoto, E. (Oct 2014). "[A case of lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the bladder].". Hinyokika Kiyo 60 (10): 507-11. PMID 25391783.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Singh, NG.; Mannan, AA.; Rifaat, AA.; Kahvic, M.. "Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the urinary bladder: report of a rare case.". Ann Saudi Med 29 (6): 478-81. doi:10.4103/0256-4947.57173. PMID 19847088.