Difference between revisions of "Hibernoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Epidemiology: | Epidemiology: | ||
*Young adults. | *Young adults - disappears with age.<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Zoico E, Rubele S, De Caro A, Nori N, Mazzali G, Fantin F, Rossi A, Zamboni M |title=Brown and Beige Adipose Tissue and Aging |journal=Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) |volume=10 |issue= |pages=368 |date=2019 |pmid=31281288 |pmc=6595248 |doi=10.3389/fendo.2019.00368 |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
*Well-circumscribed. | *Well-circumscribed. | ||
*Lobulated and light-brown on sectioning. | *Lobulated and light-brown on sectioning. | ||
Locations: | |||
*cervical-supraclavicular region | |||
*periaortic - both thorax and the abdomen. | |||
*Perirenal fat | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 15:42, 22 April 2024
| Hibernoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
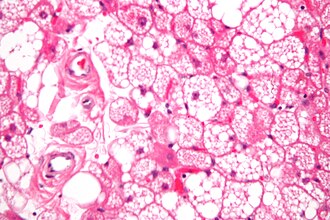 Hibernoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large polygonal/oval cells with central & small nucleus; nucleoli typically prominent; cytoplasm multivacuolated, oval, eosinophilic, granular |
| LM DDx | reaction to silicone implant |
| Gross | lobulated lesion, light-brown, usually extremities |
| Site | soft tissue - adipocytic lesions |
|
| |
| Clinical history | young adults |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | Lipoma |
Hibernoma, also tumour of brown fat,[1] is an uncommon adipocytic tumour.
General
- Consists of brown fat (present in the infants to generate heat).[2]
- Benign.
- Usually asymptomatic.[3]
Epidemiology:
- Young adults - disappears with age.[4]
Gross
- Well-circumscribed.
- Lobulated and light-brown on sectioning.
Locations:
- cervical-supraclavicular region
- periaortic - both thorax and the abdomen.
- Perirenal fat
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Large polygonal/oval cells:
- +/-Prominent blood vessels, central.[8]
DDx:
- Reaction to silicone implant.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ SHUTE, D. (Nov 1954). "Tumours of brown fat.". Can Med Assoc J 71 (5): 484-5. PMID 13209434.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 605. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Ahmed SA, Schuller I (December 2008). "Pediatric hibernoma: a case review". J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 30 (12): 900–1. doi:10.1097/MPH.0b013e318184e6dd. PMID 19131775.
- ↑ Zoico E, Rubele S, De Caro A, Nori N, Mazzali G, Fantin F, Rossi A, Zamboni M (2019). "Brown and Beige Adipose Tissue and Aging". Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10: 368. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00368. PMC 6595248. PMID 31281288. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6595248/.
- ↑ Chen DY, Wang CM, Chan HL (March 1998). "Hibernoma. Case report and literature review". Dermatol Surg 24 (3): 393–5. PMID 9537018.
- ↑ http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675(06)70271-6
- ↑ http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfat/hibernoma/
- ↑ URL: http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/24/5/1433.full. Accessed on: 11 February 2013.