Difference between revisions of "Vascular thrombus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*Endothelial injury. | *Endothelial injury. | ||
==Gross== | |||
: See ''[[pulmonary embolism]]''. | : See ''[[pulmonary embolism]]''. | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Laminations. | *Laminations. | ||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Layers consisting of platelets and fibrin. | *Layers consisting of platelets and fibrin. | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 5 April 2016
Vascular thrombus is an uncommon pathology specimen that may be from an artery or vein.
Venous thrombus and arterial thrombus redirect here.
General
- Uncommonly comes to pathology.
Risk factors - think Virchow's triad:
- Stasis, e.g. atrial fibrillation.
- Hypercoagulable states, e.g. cancer - see risks factors venous thromboembolism.
- Endothelial injury.
Gross
- See pulmonary embolism.
Features:
- Dull appearance.
- Laminations.
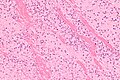
Microscopic
Features:
- Layers consisting of platelets and fibrin.
- Classically alternating with layers of RBCs - known as Lines of Zahn.[1]
Note:
- Multiple laminations (layers), in general, suggest that clot was formed in a dynamic environment, i.e. in the context of blood flow.
DDx:
- Tumour embolus - malignant cells.
- Thromboembolus - may require clinical history.
- Fat embolism.
- Amniotic fluid embolus - in the context of pregnancy/postpartum.
- Foreign body.
Images
www
Sign out
BLOOD CLOT, LEFT ILIAC ARTERY, THROMBECTOMY: - THROMBUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
BLOOD CLOT, LEFT ARM - BRACHIAL ARTERY, THROMBECTOMY/EMBOLECTOMY: - THROMBUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show layers of red blood cells alternating with fibrin and white blood cells (Lines of Zahn).
See also
References
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 124. ISBN 978-1416031215.