Difference between revisions of "Medical liver disease"
m (touch) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
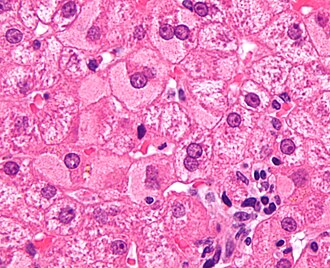
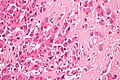
[[Image:Ground glass hepatocytes high mag cropped 2.jpg|thumb|right|[[Micrograph]] showing ground glass hepatocytes, as seen in chronic [[hepatitis B]]. [[H&E stain]].]] | [[Image:Ground glass hepatocytes high mag cropped 2.jpg|thumb|right|[[Micrograph]] showing ground glass hepatocytes, as seen in chronic [[hepatitis B]]. [[H&E stain]].]] | ||
This article deals with '''medical [[liver]] disease'''. An introduction to the liver and approach is found in the ''[[liver]]'' article. | This article deals with '''medical [[liver]] disease'''. An introduction to the liver and approach is found in the ''[[liver]]'' article. | ||
Revision as of 12:59, 10 June 2016
This article deals with medical liver disease. An introduction to the liver and approach is found in the liver article.
Every differential in liver pathology has "drugs"[1] -- if it isn't clearly malignancy.
Liver neoplasms are dealt with in the liver neoplasms article.
Medical liver biopsies are often non-specific, as the liver has the same appearance for many mechanisms of injury, especially when the injury is marked. The clinical history, serology and imaging are essential for proper interpretations in this domain of pathology.
Review of liver blood work
Inflammation activity
- ALT.
- AST.
Cholestatic markers
- ALP.
- GGT - used to assess whether the ALP is an "honest" value, elevated in cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis/decompensation
- PLT - low is suggestive of dysfunction.
- INR - high is bad, unless anticoagulated.
Other
- Bilirubin.
- Direct (AKA conjugated).
- Indirect (AKA unconjugated).
A short DDx of elevated:[2]
- Indirect:
- Gilbert syndrome.
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1.
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2.
- Direct:
- Rotor syndrome.
- Dubin-Johnson syndomre.
Viral hepatitis
- HBV DNA.
- HCV RNA.
- HBs Ag, HBs Ab, HBe Ag, HBe Ab.
- HCV Ab.
Others:
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) - especially in the immune incompetent.
Hepatitis B
Meaning & utility of the various Hepatitis B tests:[3][4]
| Test name | Location | Positive test | Negative test | Usual question |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBs Ag | Surface | Virus active | No active infection | Active infection? |
| HBs Ab | Surface | Exposed OR vaccinated | No exposure OR no vaccine OR loss of Ab | Immunization status? |
| HBe Ag | Virus core | Infect. w/ viral replication | No active infection | Active infect. w/ viral replication? |
| HBe Ab | Virus core | Exposed to virus | Infect. w/o antibody response OR not exposed | Immune response to infection? |
| HBV DNA | - | Active | Not active/no exposure | Viral load/how active? |
| HBc Ab | Virus core | Virus active/previous exposure | No exposure | Early active infection? |
Notes:
- HBc Ab may test for acute (IgM) or chronic infection - dependent on specific antibody test; it is often used to look for early infection.[4]
- Carriers of hepatitis B: HBs Ag +ve, HBs Ab -ve, HBc Ag -ve, HBc Ab +ve, HBe Ag -ve, HBe Ab +ve.[5]
Markers for rare liver diseases
- Ceruloplasm - low think Wilson's disease; typical value for Wilson's ~ 0.12 g/L.
- <0.20 g/L is a criteria for Wilson's disease.[6]
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin - if low think deficiency.
Hemosiderosis
- Ferritin - high.
- Iron saturation - high.
Causes:
- Hemochromatosis.
- Hemolysis, chronic.
- Cirrhosis.
Medical imaging
Blood flow:[7]
- Hepatopedal flow = normal portal vein flow.
- Hepatofugal flow = reversed portal vein flow.
Interventional measurements
Wedged to free hepatic venous pressure:[8]
- Normal = 1-4 mmHg.
- Elevated in portal hypertension.
Liver biopsy
Medical liver biopsy adequacy
Liver biopsy specimens should be:[9]
- 2.0 cm in length and contain 11-15 portal tracts,
- The core should be deeper than 1.0 cm from the liver capsule; specimens close to the capsule may lead to over grading of fibrosis.
Reporting
Specimen, procedure: - Diagnosis.
The diagnosis usually contains grading and staging information, e.g. activity 2 /4, Laennec fibrosis stage 1 /4.
In the context of medical liver disease:
- Grade = inflammation/activity.
- Stage = severity of fibrosis/architectural changes.
Notes:
- The term "acute" is infrequently used in liver pathology.
- In the liver: neutrophils is not acute -- unlike most elsewhere in the body.[10]
A microscopic checklist
Size of biopsy: Adequate Fragmentation: Absent Fibrosis: Stage 2-3/4, mostly stage 2 Fibrous septa: Present Septa with curved contours: Present – focally only Large droplet steatosis (% of hepatocytes): Present, moderate 60% Ballooning of hepatocytes: Present, rare Mallory-Denk bodies: Present, rare Portal inflammation: Present Interface activity: Minimal (0-1/4) Lobular necroinflammation: Minimal Ducts: Present in normal numbers Duct injury: Absent Ductular reaction: Absent Cholestasis: Absent Terminal hepatic venules: Present Iron stain: Absent Ground glass cells with routine stains: Absent PASD for alpha-1 antitrypsin droplets: Negative
Viral hepatitis
These are common. The diagnoses are based on serology. The serology is covered in the viral hepatitis section in the liver pathology article.
Typically classified as:[11][12]
- Acute < 6 months duration.
- Chronic > 6 months duration.
Hepatitis A
- Infection is self-limited, i.e. not persistent.
- May present as fulminant hepatic necrosis.
- Usually asymptomatic in children.[13]
- Serology is diagnostic.
Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B virus, abbreviated HBV, redirects here.
General
- May lead to hepatocellular carcinoma without cirrhosis.
- High prevalence.
- Diagnosis is by serology.
- A vaccination is available and done routinely in a many jurisdictions.[14]
Associated pathology:
Microscopic
Features:
- Lobular inflammation - this is non-specific finding.
- Hepatocyte necrosis:
- Necrotic hepatocytes look a lot like neutrophils - however:
- Cytoplasm is more pink.
- Round apoptotic bodies.
- Necrotic hepatocytes look a lot like neutrophils - however:
- Hepatocyte necrosis:
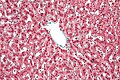
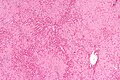
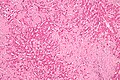
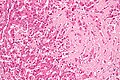
- Ground glass hepatocytes - important.
DDx:
Image
IHC
- Hepatitis B +ve.
Hepatitis C
General
- Leads to hepatocellular carcinoma in the setting of cirrhosis.
- Tends to be chronic; the "C" in "hepatitis C" stands for chronic.
- Diagnosis is by serology.
Associated pathology:
Microscopic
Features:
- Lobular inflammation - this is non-specific finding.
- Usually Grade 1, rarely Grade 2 and almost never Grade 3 or Grade 4.[15]
- Periportal steatosis in genotype 3.[16]
- Steatosis in hepatitis C is usually a secondary pathology, i.e. a separate pathologic process.[17]
DDx:
- Hepatitis B (without ground glass hepatocytes).
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis without granulomas.
- Drug reaction.
Other infections
- Hydatid disease (Hydatid cyst).
- Ascaris.
- Fasciola
Hydatid disease
- AKA hydatid cyst.
General
- Etiology: Echinococcus.
Microscopic
Features:
- Laminated wall +/- calcification.[18]
- Organisms -- see Echinococcus.
Images
www:
Metabolic and toxic
Alcoholic liver disease
General
- Acute and/or chronic liver changes due to excessive alcohol use - includes:
Classic lab findings in EtOH abusers
- AST & ALT elevated with AST:ALT=2:1.
- GGT elevated.
- MCV increased.
Gross pathology/radiologic findings
- Classically micronodular pattern.
- May be macronodular.
Microscopic
See:
- Steatohepatitis section and ballooning degeneration section.
Features:
- Often zone III damage.
- Cholestatsis common, i.e. yellow staining.
- NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) usu. does not have cholestasis.[21]
- Fibrosis starts at central veins.
- Neutrophils (often helpful) -- few other things have PMNs. (???)
- Neutrophils cluster around cells with Mallory hyaline.
Notes:
- If portal inflammatory infiltrates more than mild, r/o other causes i.e. viral hepatitis.
- Mallory bodies once thought to be characteristic; now considered non-specific and generally poorly understood.[22]
- Some consider alcoholic liver disease a clinical diagnosis, i.e. as a pathologist one does not diagnose it.[23]
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Abbreviated NAFLD.
- Fatty liver that is not due to alcohol; includes obesity-related fatty liver, metabolic disease/diabetes-related fatty liver.
NASH
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - see steatohepatitis section.
- Histologically indistinguishable from ASH.
- NASH is a clinical diagnosis based on exclusion of alcohol.
Steatohepatitis
Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis
- Abbreviated AIH.
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Abbreviated PBC.
Autoimmune hepatitis-primary biliary cirrhosis overlap syndrome
- Abbreviation AIH-PBC OS.
General
Epidemiology:
- Rare.
Serology:[24]
- AMA +ve.
- Anti-dsDNA +ve.
Microscopic
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Abbreviated PSC.
Hereditary
Caroli disease
General
- Genetic disease.
- Frequently associated with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD).[25]
- May be seen in isolation.[26]
Clinical:[27]
- Recurrent cholangitis.
- Recurrent cholelithiasis.
- Cholangiocarcinoma[28] - seen in ~7% of cases.[29]
Note:
- Caroli syndrome = Caroli disease + congenital hepatic fibrosis.[30]
Gross
- Dilated bile ducts.[25]
Microscopic
Features:[27]
- Dilated bile ducts.
- Periductal fibrosis. (???)
- +/-Fibrosis.
Image:
Hereditary hemochromatosis
- For secondary causes see secondary hemochromatosis.
Wilson disease
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- AKA alpha1-antiprotease inhibitor deficiency.
Other
Budd-Chiari syndrome
- AKA hepatic vein obstruction.
General
- Hepatic outflow obstruction.
Clinical triad:[32]
- Ascites.
- Abdominal pain.
- Hepatomegaly.
Etiology:
- ~50% have a myeloproliferative disease.[33]
- May be due to mass effect from a tumour.
Clinical DDx:
Microscopic
Features:[34]
- Sinusoidal dilation in zone III (congestion).
- +/-Hepatocyte drop-out.
- +/-Centrilobular fibrosis.
DDx congestion:
- Congestive heart failure (congestive hepatopathy).
- Constrictive pericarditis.
Vanishing bile duct syndrome
General
- Fatal.
DDx:[36]
- Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- GVHD.[37]
- Drugs.[38]
- Chronic rejection.[35]
Microscopic
Features:[36]
- Loss of intrahepatitic bile ducts - key feature.
- Cholestasis.
Note:
- May occur without fibrosis and inflammation; thus, can be easy to miss.
IHC
- CK7 -ve.
- Marks bile ducts.
Congestive hepatopathy
General
- Liver failure due to (right) heart failure.
- AKA cardiac cirrhosis - a term used by clinicians.
- Generally, it does not satisfy pathologic criteria for cirrhosis.[39]
Gross
- "Nutmeg" liver - yellow spotted appearance.
Microscopic
Features:[40]
- Zone III atrophy.
- Portal venule (central vein) distension.
- Perisinusoidal fibrosis - progresses to centrilobular fibrosis and then diffuse fibrosis.
- Dilation of sinusoids in all zone III areas - key feature.[41]
DDx:
- Hemangioma of the liver - should be focal lesion.
Images
Drug-induced liver disease
- AKA drug-induced liver toxicity.
Focal nodular hyperplasia
- Abbreviated FNH.
Nodular regenerative hyperplasia
General
- Associated with renal transplants, bone marrow transplants and vasculitides.[42]
- Can lead to portal hypertension and many of the associated complications.[43]
Etiology
- Arterial hypervascularity secondary to loss of hepatic vein radicles (loss of central venule in hepatic lobule).[42]
ASIDE: radicle = ramulus - smallest branch or vessel or nerve.[44]
Gross
- Diffuse nodularity - whole liver.
Microscopic
Features:[42]
- "Plump" hepatocytes surrounded by atrophic ones.
- No fibrosis.
Sinuosoidal obstruction syndrome
- May be referred to as Hepatic veno-occlusive disease.[45]
General
Clinical DDx:
Microscopic
Features:[34]
- Subendothelial swelling in hepatic venules.
Negatives:
- No thrombosis.
Polycystic kidney disease and the liver
General
Complications of PKD in the liver:[47]
- Infected cyst.
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
- Cholestasis/obstruction due to duct compression.[48]
Cysts:
- Cysts in the liver, like the kidney, are thought to enlarge with age.
Microscopic
Features:[49]
- Von Meyenburg complexes (bile duct hamartoma):
- Cluster of dilated ducts with "altered" bile.
- Surrounded by collagenous stroma.
- Separate from the portal areas.[50]
Images:
Notes:
Peliosis hepatis
General
- Associated with:
- Infections.
- Malignancy.
- Other stuff.
- Rarely biopsied.
Microscopic
Features:
- Cyst lined by endothelium.
- Usu. incomplete.
- Blood.
Total parenteral nutrition
- Abbreviated TPN.
General
- Indication: short gut syndrome, others.
Microscopic
Variable - may range from: steatosis, steatohepatitis, cholestasis, fibrosis and cirrhosis.[53]
- Steatosis (periportal) - early.
- Cholestasis - late.
Giant cell hepatitis
- AKA neonatal giant cell hepatitis.
- See: Giant cell hepatitis.
Hepatic amyloidosis
General
- Diffuse abundant amyloid within the space of Disse is associated with portal hypertension.[8]
Microscopic
Features:
- Amorphous extracellular pink stuff on H&E - see amyloid article.
DDx:
Images
Stains
- Congo red +ve.
Fulminant hepatic necrosis
General
Etiology:
- Viral, i.e. Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B; Hepatitis C - extremely rare.
- Trauma.
- Shock.
Microscopic
Features:
- Hepatocyte necrosis.
- Bile duct proliferation.
DDx:
Secondary hemochromatosis
- For the hereditary one see hereditary hemochromatosis.
General
- Iron overload secondary to blood transfusions for hereditary or acquired anemia.[56]
- Primary hemochromatosis due to a defect in iron processing - called hereditary hemochromatosis.
- Imaging considered the best test, as iron deposition is patchy.[56]
Selected hereditary causes:[56]
- Thalassemia.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Hereditary sideroblastic anemia.
Selected acquired causes:[56]
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Myelofibrosis
- Aplastic anemia, intractable.
Microscopic
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 448. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 441. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://www.clevelandclinicmeded.com/medicalpubs/diseasemanagement/hepatology/hepatitis-B/. Accessed on: 16 May 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: http://www.labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/hepatitis_b/test.html. Accessed on: 16 May 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/hepatitis-b/tab/test. Accessed on: 3 May 2012.
- ↑ Diagnostic accuracy of serum ceruloplasmin in Wilson disease: determination of sensitivity and specificity by ROC curve analysis among ATP7B-genotyped subjects. Mak CM, Lam CW, Tam S. Clin Chem. 2008 Aug;54(8):1356-62. Epub 2008 Jun 12. PMID 18556333. URL: http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/54/8/1356.pdf. Accessed on: 28 September 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://insidesurgery.com/2010/12/hepatopedal-hepatofugal-flow/. Accessed on: 2 December 2011.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Bion, E.; Brenard, R.; Pariente, EA.; Lebrec, D.; Degott, C.; Maitre, F.; Benhamou, JP. (Feb 1991). "Sinusoidal portal hypertension in hepatic amyloidosis.". Gut 32 (2): 227-30. PMC 1378815. PMID 1864548. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1378815/.
- ↑ Burt, Alastair D.;Portmann, Bernard C.;Ferrell, Linda D. (2006). MacSween's Pathology of the Liver (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 418. ISBN 978-0-443-10012-3.
- ↑ OA. September 2009.
- ↑ "Terminology of chronic hepatitis, hepatic allograft rejection, and nodular lesions of the liver: summary of recommendations developed by an international working party, supported by the World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Los Angeles, 1994.". Am J Gastroenterol 89 (8 Suppl): S177-81. Aug 1994. PMID 8048409.
- ↑ URL: http://familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-b.html. Accessed on: 2 May 2012.
- ↑ Jeong SH, Lee HS (2010). "Hepatitis A: clinical manifestations and management". Intervirology 53 (1): 15–9. doi:10.1159/000252779. PMID 20068336.
- ↑ Leuridan, E.; Van Damme, P. (Jul 2011). "Hepatitis B and the need for a booster dose.". Clin Infect Dis 53 (1): 68-75. doi:10.1093/cid/cir270. PMID 21653306.
- ↑ STC. 6 December 2010.
- ↑ Yoon EJ, Hu KQ. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and hepatic steatosis. Int J Med Sci. 2006;3(2):53-6. Epub 2006 Apr 1. PMID 16614743. Avialable at: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1415843. Accessed on: September 9, 2009.
- ↑ OA. September 2009.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 448. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/170539-overview. Accessed on: 3 May 2012.
- ↑ STC. 6 December 2010.
- ↑ STC. 6 December 2010.
- ↑ Jensen K, Gluud C (November 1994). "The Mallory body: theories on development and pathological significance (Part 2 of a literature survey)". Hepatology 20 (5): 1330-42. PMID 7927269.
- ↑ MG. September 2009.
- ↑ Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Pappas, G.; Pendino, GM.; Quarneti, C.; Cicola, R.; Menichella, R.; Ferri, S. et al. (Jun 2009). "The serological profile of the autoimmune hepatitis/primary biliary cirrhosis overlap syndrome.". Am J Gastroenterol 104 (6): 1420-5. doi:10.1038/ajg.2009.126. PMID 19491855.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 263200
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 600643
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Yonem, O.; Bayraktar, Y. (Apr 2007). "Clinical characteristics of Caroli's syndrome.". World J Gastroenterol 13 (13): 1934-7. PMID 17461493.
- ↑ Yonem, O.; Bayraktar, Y. (Apr 2007). "Clinical characteristics of Caroli's disease.". World J Gastroenterol 13 (13): 1930-3. PMID 17461492.
- ↑ Karim, AS. (Aug 2004). "Caroli's disease.". Indian Pediatr 41 (8): 848-50. PMID 15347876.
- ↑ Brancatelli, G.; Federle, MP.; Vilgrain, V.; Vullierme, MP.; Marin, D.; Lagalla, R.. "Fibropolycystic liver disease: CT and MR imaging findings.". Radiographics 25 (3): 659-70. doi:10.1148/rg.253045114. PMID 15888616.
- ↑ URL: http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/orfpath/develop.htm. Accessed on: 1 December 2011.
- ↑ Fox, MA.; Fox, JA.; Davies, MH. (2011). "Budd-Chiari syndrome--a review of the diagnosis and management.". Acute Med 10 (1): 5-9. PMID 21573256.
- ↑ Plessier, A.; Valla, DC. (Aug 2008). "Budd-Chiari syndrome.". Semin Liver Dis 28 (3): 259-69. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1085094. PMID 18814079.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Aydinli, M.; Bayraktar, Y. (May 2007). "Budd-Chiari syndrome: etiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis.". World J Gastroenterol 13 (19): 2693-6. PMID 17569137. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i19/2693.htm.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Inomata, Y.; Tanaka, K. (2001). "Pathogenesis and treatment of bile duct loss after liver transplantation.". J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 8 (4): 316-22. doi:10.1007/s0053410080316. PMID 11521176.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Reau, NS.; Jensen, DM. (Feb 2008). "Vanishing bile duct syndrome.". Clin Liver Dis 12 (1): 203-17, x. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2007.11.007. PMID 18242505.
- ↑ Yeh, KH.; Hsieh, HC.; Tang, JL.; Lin, MT.; Yang, CH.; Chen, YC. (Aug 1994). "Severe isolated acute hepatic graft-versus-host disease with vanishing bile duct syndrome.". Bone Marrow Transplant 14 (2): 319-21. PMID 7994249.
- ↑ Chitturi, S.; Farrell, GC. (Apr 2001). "Drug-induced cholestasis.". Semin Gastrointest Dis 12 (2): 113-24. PMID 11352118.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/151792-overview. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/151792-diagnosis. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Suggested by OA. September 2009.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 922. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Bissonnette, J.; Généreux, A.; Côté, J.; Nguyen, B.; Perreault, P.; Bouchard, L.; Pomier-Layrargues, G. (Aug 2012). "Hepatic hemodynamics in 24 patients with nodular regenerative hyperplasia and symptomatic portal hypertension.". J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27 (8): 1336-40. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07168.x. PMID 22554152.
- ↑ Dorland's Medical Dictionary. 30th Ed.
- ↑ DeLeve, LD.; Shulman, HM.; McDonald, GB. (Feb 2002). "Toxic injury to hepatic sinusoids: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease).". Semin Liver Dis 22 (1): 27-42. doi:10.1055/s-2002-23204. PMID 11928077..
- ↑ Helmy, A. (Jan 2006). "Review article: updates in the pathogenesis and therapy of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.". Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23 (1): 11-25. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02742.x. PMID 16393276.
- ↑ Burt, Alastair D.;Portmann, Bernard C.;Ferrell, Linda D. (2006). MacSween's Pathology of the Liver (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 174-5. ISBN 978-0-443-10012-3.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=9184868. Accessed on: 23 September 2009.
- ↑ Burt, Alastair D.;Portmann, Bernard C.;Ferrell, Linda D. (2006). MacSween's Pathology of the Liver (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 176. ISBN 978-0-443-10012-3.
- ↑ Meyenburg complex. Stedman's Medical Dictionary. 27th Ed.
- ↑ Bile duct hamartomas--the von Meyenburg complex. Salles VJ, Marotta A, Netto JM, Speranzini MB, Martins MR. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007 Feb;6(1):108-9. PMID 17287178.
- ↑ [The von Meyenburg complex] Schwab SA, Bautz W, Uder M, Kuefner MA. Rontgenpraxis. 2008;56(6):241-4. German. PMID 19294869.
- ↑ Guglielmi FW, Boggio-Bertinet D, Federico A, et al. (September 2006). "Total parenteral nutrition-related gastroenterological complications". Dig Liver Dis 38 (9): 623–42. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2006.04.002. PMID 16766237.
- ↑ Li, SJ.; Nussbaum, MS.; McFadden, DW.; Gapen, CL.; Dayal, R.; Fischer, JE. (Aug 1988). "Addition of glucagon to total parenteral nutrition (TPN) prevents hepatic steatosis in rats.". Surgery 104 (2): 350-7. PMID 3135627.
- ↑ Stanko, RT.; Nathan, G.; Mendelow, H.; Adibi, SA. (Jan 1987). "Development of hepatic cholestasis and fibrosis in patients with massive loss of intestine supported by prolonged parenteral nutrition.". Gastroenterology 92 (1): 197-202. PMID 3096806.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 56.3 Gattermann, N. (Jul 2009). "The treatment of secondary hemochromatosis.". Dtsch Arztebl Int 106 (30): 499-504, I. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2009.0499. PMC 2735704. PMID 19727383. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2735704/.