Difference between revisions of "Hashimoto's thyroiditis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
**[[MALT lymphoma]]. | **[[MALT lymphoma]]. | ||
**[[Diffuse large B cell lymphoma]] (DLBCL). | **[[Diffuse large B cell lymphoma]] (DLBCL). | ||
*[[Papillary thyroid carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid24619663>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhang | first1 = Y. | last2 = Dai | first2 = J. | last3 = Wu | first3 = T. | last4 = Yang | first4 = N. | last5 = Yin | first5 = Z. | title = The study of the coexistence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis with papillary thyroid carcinoma. | journal = J Cancer Res Clin Oncol | volume = 140 | issue = 6 | pages = 1021-6 | month = Jun | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1007/s00432-014-1629-z | PMID = 24619663 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 13 September 2016
| Hashimoto's thyroiditis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
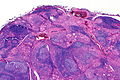
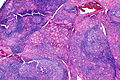
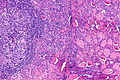
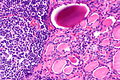
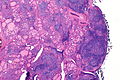
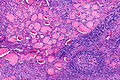
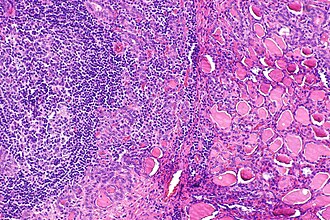 Lymphocytic thyroiditis with serologic evidence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | polymorphous lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with germinal centres, +/-nuclear clearing common, +/-oncocytic metaplasia |
| LM DDx | lymphocytic thyroiditis (no serologic evidence of Hashimoto), papillary thyroid carcinoma, MALT lymphoma, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Hürthle cell neoplasm |
| IHC | CD3, CD20, CD10, BCL6, BCL2, kappa, lambda - to demonstrated mixed population of lymphocytes |
| Molecular | B-Cell clonality testing negative |
| Site | thyroid gland |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | increased risk of lymphoma |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Blood work | antimicrosomal (antithyroid peroxidase) positive |
| Prognosis | benign |
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also Hashimoto's disease, is an inflammatory (autoimmune disorder) of the thyroid gland that causes hypothyroidism.
General
- This is a clinical diagnosis.
- The histomorphologic findings, generally, are not diagnostic.
Etiology:
- Autoimmune disease leading to hypothyroidism.
- Often genetic/part of a syndrome.
Clinical
Serology:[1]
- Antimicrosomal (antithyroid peroxidase) +ve.
- Antithyroglobulin +ve.
- Normal: <4.0 IU/mL.[2]
Associated pathology:[1]
- Increased risk of B-cell lymphoma; these are classically:[3]
- MALT lymphoma.
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma.[4]
Microscopic
Features:
- Lymphocytic infiltrate - key feature.
- Nuclear clearing common.
- May confuse with papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- Polymorphous lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with germinal centres.[5]
- +/-Oncocytic metaplasia.
Notes:
- Histologically often not possible to separate from "non-specific" thyroiditis.[6]
DDx:
- Lymphocytic thyroiditis.
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- MALT lymphoma.
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
- Hürthle cell neoplasm.
Images
IHC
- Panel to exclude lymphoma may be required, e.g. CD3, CD20, CD10, BCL6, BCL2, kappa, lambda.
Molecular
- Occasionally done to exclude lymphoma - see MALT lymphoma and DLBCL.
Sign out
Total Thyroid, Thyroidectomy: - Lymphocytic thyroiditis compatible with clinical history of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. - NEGATIVE for malignancy.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Poropatich C, Marcus D, Oertel YC (1994). "Hashimoto's thyroiditis: fine-needle aspirations of 50 asymptomatic cases". Diagn. Cytopathol. 11 (2): 141–5. PMID 7813361. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/112701408/abstract?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0.
- ↑ URL: http://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/test-catalog/Clinical+and+Interpretive/84382. Accessed on: 15 October 2015.
- ↑ Ohye, H.; Fukata, S.; Hirokawa, M. (Nov 2007). "[Malignant lymphoma of the thyroid].". Nihon Rinsho 65 (11): 2092-8. PMID 18018576.
- ↑ Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wu, T.; Yang, N.; Yin, Z. (Jun 2014). "The study of the coexistence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis with papillary thyroid carcinoma.". J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140 (6): 1021-6. doi:10.1007/s00432-014-1629-z. PMID 24619663.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 672. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 560. ISBN 978-0781740517.