Difference between revisions of "Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "'''Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma''', also known as '''benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma''' and '''hybrid hyperplastic p...") |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Hyperplastic polyp]]. | *[[Hyperplastic polyp]]. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
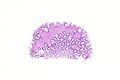
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma -- very low mag.jpg | HP with PNS - very low mag. | |||
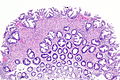
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma -- low mag.jpg | HP with PNS - low mag. | |||
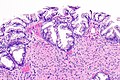
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma -- intermed mag.jpg | HP with PNS - intermed. low mag. | |||
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | HP with PNS - intermed. low mag. | |||
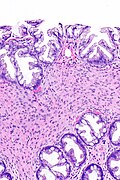
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma -- high mag.jpg | HP with PNS - high mag. | |||
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma - alt -- high mag.jpg | HP with PNS - high mag. | |||
Image: Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma -- very high mag.jpg | HP with PNS - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 00:33, 29 October 2015
Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma, also known as benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma and hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma, is a benign colorectal polyp.
General
- Rare.
- Benign.[1]
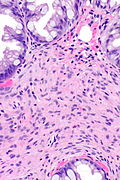
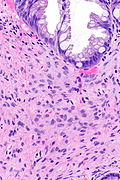
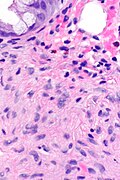
Microscopic
Features:
- Serrated epithelial cells (at the surface of the gland) - key feature.
- Serrated appearance = saw-tooth appearance, epithelium has jagged edge.
- Perineuromatous stroma.
DDx:
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Agaimy, A.; Stoehr, R.; Vieth, M.; Hartmann, A. (Nov 2010). "Benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineuriomas are true mixed epithelial-stromal polyps (hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma) with frequent BRAF mutations.". Am J Surg Pathol 34 (11): 1663-71. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f4a458. PMID 20962618.