Difference between revisions of "Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = squamous epithelium with (1) superficial clearing of the cytoplasm, and (2) thickening | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[esophagus]] | |||
| Assdx = [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]] (???) | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = ingestion of hot liquids (???) | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = raised grey/white lesions | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus''' is an uncommon benign change of the [[esophagus]] with a distinctive endoscopic appearance. | '''Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus''' is an uncommon benign change of the [[esophagus]] with a distinctive endoscopic appearance. | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 16 May 2015
| Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
|
| |
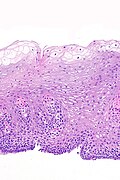
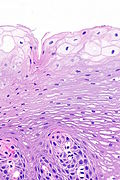
| LM | squamous epithelium with (1) superficial clearing of the cytoplasm, and (2) thickening |
| Site | esophagus |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | gastroesophageal reflux disease (???) |
| Clinical history | ingestion of hot liquids (???) |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Endoscopy | raised grey/white lesions |
| Prognosis | benign |
Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus is an uncommon benign change of the esophagus with a distinctive endoscopic appearance.
General
- Uncommon - seen 3.5% of consecutive 2328 upper endoscopies.[1]
- Benign.[2]
- May be associated with GERD;[1] however, lesions do not resolve with PPI treatment.[2]
- Possible association with ingestion of hot liquids.[3]
Gross/endoscopic
- Distinctive endoscopic appearance - grey/white raised lesion.[3]
Image
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Squamous epithelium with:
- Superficial clearing of the cytoplasm.
- Thickening.
Images
www
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vadva, MD.; Triadafilopoulos, G. (Jul 1993). "Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux.". J Clin Gastroenterol 17 (1): 79-83. PMID 8409304.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Tsai, SJ.; Lin, CC.; Chang, CW.; Hung, CY.; Shieh, TY.; Wang, HY.; Shih, SC.; Chen, MJ. (Jan 2015). "Benign esophageal lesions: endoscopic and pathologic features.". World J Gastroenterol 21 (4): 1091-8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1091. PMID 25632181.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Lopes, S.; Figueiredo, P.; Amaro, P.; Freire, P.; Alves, S.; Cipriano, MA.; Gouveia, H.; Sofia, C. et al. (May 2010). "Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus: an unusually endoscopic appearance.". Rev Esp Enferm Dig 102 (5): 341-2. PMID 20524767.