Difference between revisions of "Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid19033865>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhao | first1 = C. | last2 = Vinh | first2 = TN. | last3 = McManus | first3 = K. | last4 = Dabbs | first4 = D. | last5 = Barner | first5 = R. | last6 = Vang | first6 = R. | title = Identification of the most sensitive and robust immunohistochemical markers in different categories of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 354-66 | month = Mar | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318188373d | PMID = 19033865 }}</ref> | Features:<ref name=pmid19033865>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhao | first1 = C. | last2 = Vinh | first2 = TN. | last3 = McManus | first3 = K. | last4 = Dabbs | first4 = D. | last5 = Barner | first5 = R. | last6 = Vang | first6 = R. | title = Identification of the most sensitive and robust immunohistochemical markers in different categories of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 354-66 | month = Mar | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318188373d | PMID = 19033865 }}</ref> | ||
* | |||
* | *'''Inhibin''' +ve | ||
*'''Calretinin''' +ve. | |||
*WT-1 +ve. | *WT-1 +ve. | ||
*Melan A (MART-1) +ve - marks the Leydig component. | *Melan A (MART-1) +ve - marks the Leydig component. | ||
*Vimentin +ve.<ref name=pmid20349790>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kondi-Pafiti | first1 = A. | last2 = Grapsa | first2 = D. | last3 = Kairi-Vassilatou | first3 = E. | last4 = Carvounis | first4 = E. | last5 = Hasiakos | first5 = D. | last6 = Kontogianni | first6 = K. | last7 = Fotiou | first7 = S. | title = Granulosa cell tumors of the ovary: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 21 cases. | journal = Eur J Gynaecol Oncol | volume = 31 | issue = 1 | pages = 94-8 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20349790 }}</ref> | *Vimentin +ve.<ref name=pmid20349790>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kondi-Pafiti | first1 = A. | last2 = Grapsa | first2 = D. | last3 = Kairi-Vassilatou | first3 = E. | last4 = Carvounis | first4 = E. | last5 = Hasiakos | first5 = D. | last6 = Kontogianni | first6 = K. | last7 = Fotiou | first7 = S. | title = Granulosa cell tumors of the ovary: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 21 cases. | journal = Eur J Gynaecol Oncol | volume = 31 | issue = 1 | pages = 94-8 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20349790 }}</ref> | ||
*CD99 +ve. | *CD99 +ve. | ||
*AE1/AE3 and PanKeratin can be +ve | |||
Others:<ref name=pmid20349790/> | Others:<ref name=pmid20349790/> | ||
*CD34 -ve. | *CD34 -ve. | ||
*EMA -ve. | *'''EMA''' -ve. | ||
Pan-keratins and AE1/AE3 may mark granulosa cell tumors and Sertoli cell tumors causing confusion with adenocarcinoma. EMA is a better marker to exclude an epithelial tumor as EMA is negative in sex cord-stromal tumors. Adding complexity, endometrioid adenocarcinomas may occasionally weakly express inhibin, calretinin or WT-1. | Pan-keratins and AE1/AE3 may mark granulosa cell tumors and Sertoli cell tumors causing confusion with adenocarcinoma. EMA is a better marker to exclude an epithelial tumor as EMA is negative in sex cord-stromal tumors. Adding complexity, endometrioid adenocarcinomas may occasionally weakly express inhibin, calretinin or WT-1. | ||
Revision as of 10:40, 21 March 2015
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour, also Sertoli-Leydig tumour, is a rare tumour of the gonad in the sex cord-stromal group of tumours.
General
- Sertoli and leydig cells are normal in the testis.
- Poorly differentiated tumours have sarcomatous features.[1]
- May present with masculinization (virilization).[2]
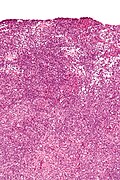
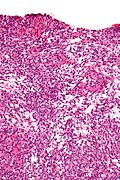
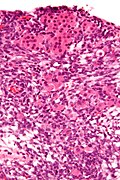
Microscopic
Features:
- Sertoli or Leydig cells.[1]
- Leydig cells:
- Polygonal pink cells
- Abundant solid or somewhat granular eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Round nuclei with fine chromatin and a small or indistinct nucleolus.
- Often in small clusters ~ 5-25 cells/cluster.
- Sertoli cells:
- Pale/clear vacuolated cytoplasm.
- Irregular nuclei with irregular/vacuolated-appearing chromatin.
- Architecture: tubules, cords or sheets.
- Leydig cells:
- Stroma.
- +/- Sarcomatous features (mucinous glands, bone, cartilage).
- Well differentiated -
- Mature Sertoli cells form tubules
- Stroma is fibrous and contains clusters of Leydig cells
- Intermediate to poorly differentiated -
- A more disorganized, more cellular, 'bluer' tumor
- Less mature Sertoli cells growing in trabeculae and nests with some tubule formation, either round or retiform.
- Leydig cells, either singly or in clusters, are present in an immature, cellular stroma.
DDx:
- Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary (sertoliform variant) - should be positive for EMA, negative for inhibin and calretinin.
- Luteinized adult granulosa cell tumour - super rare, 50% of cell with eosinophilic cytoplasm, other findings of granulosa cell tumour, e.g. Call-Exner bodies.[3]
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[4]
- Inhibin +ve
- Calretinin +ve.
- WT-1 +ve.
- Melan A (MART-1) +ve - marks the Leydig component.
- Vimentin +ve.[5]
- CD99 +ve.
- AE1/AE3 and PanKeratin can be +ve
Others:[5]
- CD34 -ve.
- EMA -ve.
Pan-keratins and AE1/AE3 may mark granulosa cell tumors and Sertoli cell tumors causing confusion with adenocarcinoma. EMA is a better marker to exclude an epithelial tumor as EMA is negative in sex cord-stromal tumors. Adding complexity, endometrioid adenocarcinomas may occasionally weakly express inhibin, calretinin or WT-1.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1103. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Xiao, H.; Li, B.; Zuo, J.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, L. (Mar 2013). "Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor: a report of seven cases and a review of the literature.". Gynecol Endocrinol 29 (3): 192-5. doi:10.3109/09513590.2012.738723. PMID 23173550.
- ↑ Ganesan, R.; Hirschowitz, L.; Baltrušaitytė, I.; McCluggage, WG. (Sep 2011). "Luteinized adult granulosa cell tumor--a series of 9 cases: revisiting a rare variant of adult granulosa cell tumor.". Int J Gynecol Pathol 30 (5): 452-9. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e318214b17f. PMID 21804396.
- ↑ Zhao, C.; Vinh, TN.; McManus, K.; Dabbs, D.; Barner, R.; Vang, R. (Mar 2009). "Identification of the most sensitive and robust immunohistochemical markers in different categories of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors.". Am J Surg Pathol 33 (3): 354-66. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318188373d. PMID 19033865.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kondi-Pafiti, A.; Grapsa, D.; Kairi-Vassilatou, E.; Carvounis, E.; Hasiakos, D.; Kontogianni, K.; Fotiou, S. (2010). "Granulosa cell tumors of the ovary: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 21 cases.". Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 31 (1): 94-8. PMID 20349790.