Difference between revisions of "Giant cell arteritis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Giant cell arteritis -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
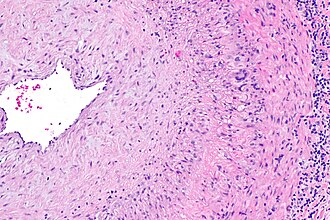
| Caption = Giant cell arteritis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = temporal arteritis | |||
| Micro = large artery with intramural inflammatory cells (often [[granuloma|granulomatous]]); destruction of arterial wall, i.e. fibrinoid necrosis (pink anucleate arterial wall) | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = large [[blood vessels]] - see ''[[vasculitides]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = patient older than 50 years | |||
| Signs = loss of vision, weight loss, chills, fever | |||
| Symptoms = headache, double vision, scalp tenderness | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = ESR elevated | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good if treated | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other causes of headache | |||
| Tx = steroids | |||
}} | |||
'''Giant cell arteritis''' (abbreviated '''GCA'''), also known as '''temporal arteritis''', is a type of large vessel [[vasculitis]]. | '''Giant cell arteritis''' (abbreviated '''GCA'''), also known as '''temporal arteritis''', is a type of large vessel [[vasculitis]]. | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 17 December 2014
| Giant cell arteritis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Giant cell arteritis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | temporal arteritis |
|
| |
| LM | large artery with intramural inflammatory cells (often granulomatous); destruction of arterial wall, i.e. fibrinoid necrosis (pink anucleate arterial wall) |
| Site | large blood vessels - see vasculitides |
|
| |
| Clinical history | patient older than 50 years |
| Signs | loss of vision, weight loss, chills, fever |
| Symptoms | headache, double vision, scalp tenderness |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Blood work | ESR elevated |
| Prognosis | good if treated |
| Clin. DDx | other causes of headache |
| Treatment | steroids |
Giant cell arteritis (abbreviated GCA), also known as temporal arteritis, is a type of large vessel vasculitis.
General
- Classically afflicts the temporal artery.
Clinical features:
- Classic finding: jaw claudication, in a patient older than 50 years.
- Other findings: headache, vision loss or diplopia, scalp tenderness, polymyalgia, weight loss, chills, fever.
Work-up:
- CRP, ESR, temporal artery biopsy.
- ESR normal (>50 years old): <20 mm/hr males, <30 mm/hr females.[1]
Treatment:
- Treat right away with high dose steroids.
- Biopsy is confirmatory.
Microscopic
Features:
- Artery with intramural inflammatory cells.
- Classically granulomatous inflammation.
- Granulomas not required for the diagnosis!
- Classically granulomatous inflammation.
- Destruction of arterial wall, e.g. fibrinoid necrosis (pink anucleate arterial wall).
Image(s):
Sign out
Negative
TEMPORAL ARTERY, LEFT, BIOPSY: - MEDIUM SIZE ARTERY WITHOUT PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: A negative biopsy does not rule out the possibility of giant cell (temporal) arteritis, as this may be a focal disorder. The clinical management is dependent upon the clinical impression.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003638.htm. Accessed on: 17 August 2012.