Difference between revisions of "Giant cells"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Table) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| drug reaction, neoplasm, foreign body, infection, idiopathic, autoimmune, allergic | | drug reaction, neoplasm, foreign body, infection, idiopathic, autoimmune, allergic | ||
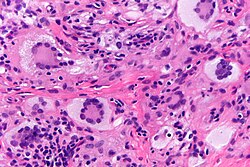
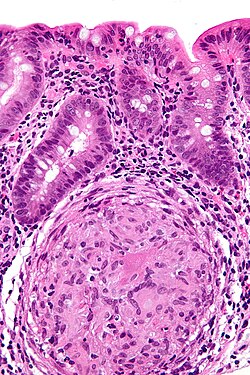
| [[granuloma|granulomatous inflammation]] | | [[granuloma|granulomatous inflammation]] | ||
| [[Image:Crohn%27s_disease_-_colon_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|150px|Granuloma (WC)]] | | [[Image:Crohn%27s_disease_-_colon_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|150px|center|Granuloma (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
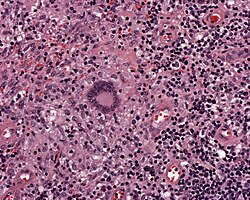
| Langhans giant cell | | Langhans giant cell | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 28 August 2014
Giant cells are "big" cells with multiple nuclei. They come in different flavours, which are suggestive of causality.
Giant cell types
List:
- Touton giant cell.
- Osteoclast-like giant cell.
- Foreign body type giant cell.
Table
| Type | Histology | DDx | Other | Image |
| Touton giant cell | nuclei form a ring around the cell periphery | juvenile xanthogranuloma, Erdheim-Chester disease | high lipid content lesions[1] | |
| Epithelioid type | scattered nuclei[2] | drug reaction, neoplasm, foreign body, infection, idiopathic, autoimmune, allergic | granulomatous inflammation | |
| Langhans giant cell | peripheral eccentric nuclei[2] | ? | not to be confused with Langerhans cells | |
| Osteoclast-like giant cells | round nuclei | osteoclasts, others | AKA osteoclast-type giant cells |
See also
- Basics.
- Giant cell lesions - includes a DDx of lesions with giant cells.
- Histiocytoses.
References
- ↑ URL: http://granuloma.homestead.com/giant_cells.html. Accessed on: 7 February 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Borley, Neil R.; Warren, Bryan F. (2007). Instant Pathology (1st ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 7. ISBN 978-1405132909.