Difference between revisions of "Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| Image = Endometrium with hormone effect -- high mag.jpg | | Image = Endometrium with hormone effect -- high mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
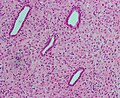
| Caption = Endometrium changes due to exogenous hormones. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = inactive glands (round/ovoid glands, simple cuboidal epithelium, no mitoses), decidualized stroma (nucleus central, eosinophilic cytoplasm, well-defined cell borders) | | Micro = inactive glands (round/ovoid glands, simple cuboidal epithelium, no mitoses), decidualized stroma (nucleus central, eosinophilic cytoplasm, well-defined cell borders) | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- intermed mag.jpg | Hormone effect - intermed. mag. | Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- intermed mag.jpg | Hormone effect - intermed. mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- high mag.jpg | Hormone effect - high mag. | Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- high mag.jpg | Hormone effect - high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- very high mag.jpg | Hormone effect - very high mag. | Image: Endometrium with hormone effect -- very high mag.jpg | Hormone effect - very high mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Revision as of 02:59, 2 March 2014
| Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
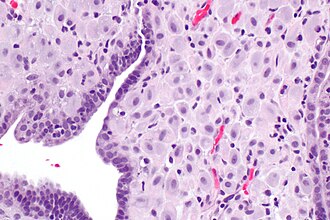 Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | inactive glands (round/ovoid glands, simple cuboidal epithelium, no mitoses), decidualized stroma (nucleus central, eosinophilic cytoplasm, well-defined cell borders) |
| LM DDx | endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes, secretory phase endometrium |
| Site | endometrium |
|
| |
| Clinical history | exogenous hormones (oral contraceptive pill or hormone releasing intrauterine device) |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10170 |
Endometrium with changes due to exogenous hormones is relatively common in endometrial samples.
Endometrial changes of oral contraception, oral contraceptive effect, OCP endometrium, and endometrium with hormonal changes redirect here.
The oral contraceptive pill is dealt with in the article oral contraceptive pill.
General
- Very common.
- Most pills a mix of progesterone and estrogen.
- The progesterone is what generates the characteristic appearance -- that is similar to pregnancy.
- Same appearance is seen with a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device, e.g. Mirena.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Inactive glands (round/ovoid glands, simple cuboidal epithelium, no mitoses).
- Stroma decidualized -- mnemonic NEW:
- Nucleus central.
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Well-defined cell borders.
DDx:
- Endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes - proliferative activity.
- Secretory phase endometrium - glandular changes of the secretory phase (cytoplasmic vacuolization), secretions in the glands.
Image
Sign out
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - NON-PROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIAL GLANDS WITH STROMAL DECIDUALIZATION, CONSISTENT WITH EXOGENOUS HORMONES.
OCP effect and shedding endometrium
ENDOMETRIUM, ASPIRATION: - ENDOMETRIUM WITH NONPROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIAL GLANDS AND STROMAL DECIDUALIZATION, COMPATIBLE WITH EXOGENOUS HORMONES. - EVIDENCE OF ENDOMETRIAL SHEDDING (BALLS OF CONDENSED STROMA ASSOCIATED NEUTROPHILS, AND BLOOD). - NEGATIVE FOR HYPERPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show endometrium with nonproliferative endometrial glands and stromal decidualization. The gland-to-stroma ratio is within normal limits.
See also
References
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1082. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.