Difference between revisions of "Osteoid osteoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Gross) |
(chg image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = Osteoid osteoma - | | Image = Osteoid osteoma - low mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
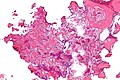
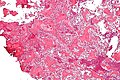
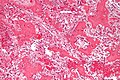
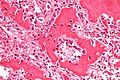
| Caption = Osteoid osteoma. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Osteoid osteoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
Revision as of 17:07, 25 August 2013
| Osteoid osteoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
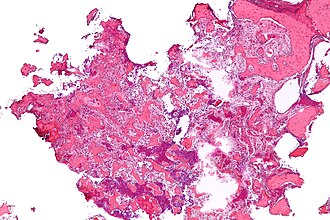 Osteoid osteoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | anastomosing bony trabeculae with variable mineralization, osteoblast rimming, no nuclear atypia of osteocytes |
| LM DDx | osteoblastoma, osteosarcoma |
| Site | bone (femur > tibia > spine > elsewhere) |
|
| |
| Clinical history | pain relieved by NSAIDs |
| Symptoms | extremely painful |
| Radiology | <= 1.5 cm (larger lesion osteoblastoma) |
| Clin. DDx | osteosarcoma |
Osteoid osteoma, abbreviated OO, is benign primary bone tumour.
General
- Benign bone lesion.
Clinical:[1]
- Extremely painful.
- Relieved by NSAIDs.
Gross
- Bone: femur > tibia > spine > elsewhere.[2][3]
- Most common location (in bone): diaphysis.[2]
- Must be <=1.5 cm by definition.[4]
- Larger lesions with the same microscopy are osteoblastomas.
Images:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Anastomosing bony trabeculae with:
- Variable mineralization.
- Mineralization (calcium phosphate) = purple on H&E stain.
- Osteoblast rimming.
- Cells line-up at edge of bone.
- Variable mineralization.
Note:
- Histomorphologically near identical/indistinguishable from osteoblastoma;[4] one needs some history to make the diagnosis.
Images
www:
Sign out
BONE, RIGHT FEMUR, EXCISION: - OSTEOID OSTEOMA.
Micro
The sections show anastomosing bony trabeculae with variable mineralization and osteoblastic rimming. Multinucleated osteoclasts are scattered through the lesion. Hemosiderin-laden macrophages are present. No osteocyte nuclear atypia is apparent. Mitotic activity is not apparent. The osteoid is not lace-like.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 285. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 URL: http://radiology.uthscsa.edu/CME/ELTXT/OOT/skeletallocation.html http://radiology.uthscsa.edu/CME/ELTXT/OOT/skeletallocation.html]. Accessed on: 7 May 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/494e15cbf0d8d. Accessed on: 7 May 2012.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 286. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ URL: http://njms2.umdnj.edu/tutorweb/gross.htm. Accessed on: 7 May 2012.