Difference between revisions of "Secretory phase endometrium"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect /w cat.) |
Alessandro (talk | contribs) m (→Micro) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
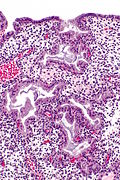
| Image = Secretory phase endometrium -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
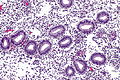
| Caption = Secretory phase. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = dependent on day post-ovulation - see microscopic | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes]], [[endometrium with hormonal changes]],[[proliferative phase endometrium]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[endometrium]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = normal finding | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Secretory phase endometrium''', abbreviated '''SPE''', is a common diagnosis in [[endometrium|endometrial]] specimens. | |||
==General== | |||
*Secretory phase = luteal phase. | |||
**Gynecologists prefer the ovarian descriptor, i.e. ''luteal phase''; pathologists go by what they see, i.e. ''Secretions'' in the (endometrial) glands. | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Thickened endometrium. | |||
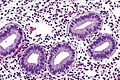
==Microscopic== | |||
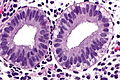
===Early secretory phase=== | |||
Features - post-ovulatory day 1-5:<ref name=Ref_DCHH237>{{Ref DCHH|237}}</ref> | |||
*Glands: secretory vacuoles. | |||
**First basal to the epithelial nuclei (infranuclear vacuoles). | |||
**Then apical to the epithelial nuclei (supranuclear vacuoles). | |||
*Mitoses may be present - common when vacuoles are subnuclear. | |||
===Mid secretory phase=== | |||
Features - post-ovulatory day 6-8:<ref name=Ref_DCHH237>{{Ref DCHH|237}}</ref> | |||
*Glands: Mucus in glands. | |||
*Stroma: Edema (empty space around the glands). | |||
===Late secretory phase=== | |||
Features - post-ovulatory day 9-12:<ref name=Ref_DCHH237>{{Ref DCHH|237}}</ref> | |||
*Stroma: | |||
**Spiral arterioles. | |||
**Predecidual changes -- mnemonic ''NEW'': | |||
**#Nucleus central. | |||
**#Eosinophilic cytoplasm '''key feature''' (may be subtle to the novice). | |||
**#Well-defined cell borders. | |||
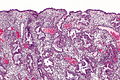
===Premenstrual=== | |||
*Stroma: [[neutrophil]]s, scattered lymphocytes, stromal balls ("blue balls"); "stromal condensation". | |||
*Glands: [[apoptosis]] at the base of the gland.<ref>Colgan T. 22 June 2009.</ref> | |||
Notes: | |||
*Stromal condensation (stromal balls) - premenstrual - stromal cells tightly packed together; nuclei molded together like in small cell tumours.<ref>GAG. 6 Oct 2009.</ref> | |||
*Gland-to-stroma ratio is increased in late secretory phase and menstruation.<ref>URL: [http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/uteruspatternapproach.html http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/uteruspatternapproach.html]. Accessed on: 6 December 2012.</ref> | |||
*Endocervical epithelium (ECE) has a morphology similar to the epithelium of secretory phase endometrium (SPE): | |||
**ECE - grey foamy appearing cytoplasm. | |||
**SPE - eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
***Most useful feature to differentiate ECE and SPE is the accompanying stroma. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes]]. | |||
*[[Endometrium with hormonal changes]]. | |||
*[[Proliferative phase endometrium]] - may have some changes of secretory endometrium; <50% of glands have subnuclear vacuoles ''or'' <50% of cells in the glands have subnuclear vacuoles.<ref name=Ref_EMB14>{{Ref EMB|14}}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
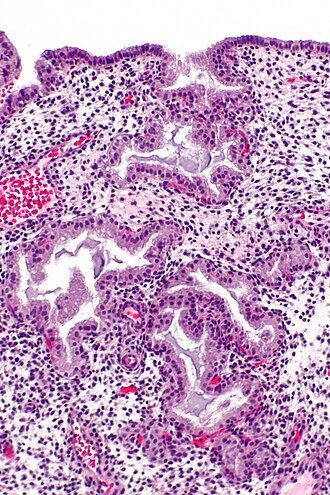
Image: Early secretory phase endometrium -- intermed mag.jpg | Early SPE - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Early secretory phase endometrium -- high mag.jpg | Early SPE - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Early secretory phase endometrium -- very high mag.jpg | Early SPE - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
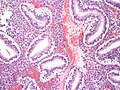
Image: Secretory phase endometrium -- low mag.jpg | Late SPE - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Secretory phase endometrium -- intermed mag.jpg | Late SPE - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Secretory phase endometrium -- high mag.jpg | Late SPE - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Endometrium_Secretory-Type_Endometrium_10x1.JPG | Early secretory phase endometrium. (WC) | |||
Image:Endometrium_Secretory_20x1.jpg | Early secretory phase endometrium. (WC) | |||
Image:Endometrial_stromal_condensation_high_mag.jpg | Endometrial stromal condensation. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, ASPIRATION: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM, EARLY. | |||
</pre> | |||
===With additional stuff=== | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
- SCANT ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
- ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA AND STRIPPED ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. | |||
- BENIGN SUPERFICIAL EXOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM. | |||
- SCANT BENIGN ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Evidence of shedding=== | |||
<pre> | |||
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: | |||
- SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM WITH FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF SHEDDING (EPITHELIAL | |||
APOPTOSIS, INFLAMMATORY CELLS - ESPECIALLY NEUTROPHILS). | |||
- BENIGN EXOCERVICAL AND ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Micro=== | |||
The sections show endometrium with a normal gland-to-stroma ratio. The glands are mildly dilated, tortuous and have mucus within them. The glandular epithelium is simple and non-pseudostratified. The stroma is edematous and has a decidual reaction. No mitotic activity is apparent. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Endometrium]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Endometrium]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:37, 13 February 2019
| Secretory phase endometrium | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Secretory phase. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | dependent on day post-ovulation - see microscopic |
| LM DDx | endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes, endometrium with hormonal changes,proliferative phase endometrium |
| Site | endometrium |
|
| |
| Other | normal finding |
Secretory phase endometrium, abbreviated SPE, is a common diagnosis in endometrial specimens.
General
- Secretory phase = luteal phase.
- Gynecologists prefer the ovarian descriptor, i.e. luteal phase; pathologists go by what they see, i.e. Secretions in the (endometrial) glands.
Gross
- Thickened endometrium.
Microscopic
Early secretory phase
Features - post-ovulatory day 1-5:[1]
- Glands: secretory vacuoles.
- First basal to the epithelial nuclei (infranuclear vacuoles).
- Then apical to the epithelial nuclei (supranuclear vacuoles).
- Mitoses may be present - common when vacuoles are subnuclear.
Mid secretory phase
Features - post-ovulatory day 6-8:[1]
- Glands: Mucus in glands.
- Stroma: Edema (empty space around the glands).
Late secretory phase
Features - post-ovulatory day 9-12:[1]
- Stroma:
- Spiral arterioles.
- Predecidual changes -- mnemonic NEW:
- Nucleus central.
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm key feature (may be subtle to the novice).
- Well-defined cell borders.
Premenstrual
- Stroma: neutrophils, scattered lymphocytes, stromal balls ("blue balls"); "stromal condensation".
- Glands: apoptosis at the base of the gland.[2]
Notes:
- Stromal condensation (stromal balls) - premenstrual - stromal cells tightly packed together; nuclei molded together like in small cell tumours.[3]
- Gland-to-stroma ratio is increased in late secretory phase and menstruation.[4]
- Endocervical epithelium (ECE) has a morphology similar to the epithelium of secretory phase endometrium (SPE):
- ECE - grey foamy appearing cytoplasm.
- SPE - eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Most useful feature to differentiate ECE and SPE is the accompanying stroma.
DDx:
- Endometrial hyperplasia with secretory changes.
- Endometrium with hormonal changes.
- Proliferative phase endometrium - may have some changes of secretory endometrium; <50% of glands have subnuclear vacuoles or <50% of cells in the glands have subnuclear vacuoles.[5]
Images
Sign out
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM.
ENDOMETRIUM, ASPIRATION: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM.
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM.
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM, EARLY.
With additional stuff
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. - SCANT ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. - ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA AND STRIPPED ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM. - BENIGN SUPERFICIAL EXOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM. - SCANT BENIGN ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM.
Evidence of shedding
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: - SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM WITH FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF SHEDDING (EPITHELIAL APOPTOSIS, INFLAMMATORY CELLS - ESPECIALLY NEUTROPHILS). - BENIGN EXOCERVICAL AND ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA.
Micro
The sections show endometrium with a normal gland-to-stroma ratio. The glands are mildly dilated, tortuous and have mucus within them. The glandular epithelium is simple and non-pseudostratified. The stroma is edematous and has a decidual reaction. No mitotic activity is apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 237. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ Colgan T. 22 June 2009.
- ↑ GAG. 6 Oct 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/uteruspatternapproach.html. Accessed on: 6 December 2012.
- ↑ Mazur, Michael T.; Kurman, Robert J. (2005). Diagnosis of Endometrial Biopsies and Curettings: A Practical Approach (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 14. ISBN 978-0387986159.