Difference between revisions of "Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→General: Update) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = SEGA HE.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = SEGA | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[ganglioglioma]], [[pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma]], [[glioblastoma]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = GFAP +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = brain - usu. wall of ventricles | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = rare - esp. in young adults | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good (WHO Grade I) | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma''', abbreviated '''SEGA''', is a low-grade astrocytoma associated with [[tuberous sclerosis complex]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Associated with [[tuberous sclerosis complex]] (TSC).<ref name=pmid21455842>{{Cite journal | last1 = Grajkowska | first1 = W. | last2 = Kotulska | first2 = K. | last3 = Jurkiewicz | first3 = E. | last4 = Roszkowski | first4 = M. | last5 = Daszkiewicz | first5 = P. | last6 = Jóźwiak | first6 = S. | last7 = Matyja | first7 = E. | title = Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas with atypical histological features mimicking malignant gliomas. | journal = Folia Neuropathol | volume = 49 | issue = 1 | pages = 39-46 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21455842 }}</ref> | |||
** 6-14% of all TSC patients will develop a SEGA. | |||
** Sporadic examples of SEGA may represent undetected TSC patients (i.e., low-level somatic mosaicism)<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Overwater | first1 = IE. | last2 = Swenker | first2 = R. | last3 = van der Ende | first3 = EL. | last4 = Hanemaayer | first4 = KB. | last5 = Hoogeveen-Westerveld | first5 = M. | last6 = van Eeghen | first6 = AM. | last7 = Lequin | first7 = MH. | last8 = van den Ouweland | first8 = AM. | last9 = Moll | first9 = HA. | title = Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. | journal = Eur J Hum Genet | volume = 24 | issue = 12 | pages = 1688-1695 | month = 12 | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1038/ejhg.2016.85 | PMID = 27406250 }}</ref>. | |||
*Associated with epilepsy. | |||
*WHO Grade I. | |||
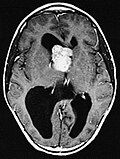
==Gross/radiology== | |||
*Well-demarcated. | |||
*Often projecting into a ventricle. | |||
*May be calcified | |||
*Circumscribed tumour. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:MRI of brain with sub-ependymal giant cell astrocytoma.jpg | SEGA in Tuberous sclerosis. (WC/AFIP) | |||
Image:Sega_gross.jpg | SEGA. (WC/AFIP) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=upmc_case179/><ref name=pmid9595853>{{Cite journal | last1 = Taraszewska | first1 = A. | last2 = Kroh | first2 = H. | last3 = Majchrowski | first3 = A. | title = Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: clinical, histologic and immunohistochemical characteristic of 3 cases. | journal = Folia Neuropathol | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 181-6 | month = | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9595853 }}</ref> | |||
*Giant cells with nuclear atypia ("bizarre cells", "ganglioid cells"). | |||
**[[Vesicular nuclei]]. | |||
**[[Nuclear pseudoinclusions]].<ref name=upmc179>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html]. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
*Elongated cells in a fibrillary background. | |||
*Abundant [[mast cell]]s.<ref name=upmc179>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html]. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Lymphocytic infiltrates. | |||
*Endothelial proliferations and/or necrosis are not a sign of malignancy. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:SEGA HE.jpg | SEGA. (WC/Sbrandner) | |||
Image:SEGA NF.jpg | SEGA - NF stain. (WC/Sbrandner) | |||
Image:SEGA GFAP x100.jpg | SEGA - GFAP stain. (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:SEGA GFAP.jpg | SEGA -GFAP stain. (WC/Sbrandner) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html SEGA (upmc.edu)].<ref name=upmc_case179>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179.html]. Accessed on: 29 July 2011.</ref> | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case500.html SEGA - another case (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid9595853/><ref name=pmid8546029>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hirose | first1 = T. | last2 = Scheithauer | first2 = BW. | last3 = Lopes | first3 = MB. | last4 = Gerber | first4 = HA. | last5 = Altermatt | first5 = HJ. | last6 = Hukee | first6 = MJ. | last7 = VandenBerg | first7 = SR. | last8 = Charlesworth | first8 = JC. | title = Tuber and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and immunoelectron and microscopic study. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 90 | issue = 4 | pages = 387-99 | month = | year = 1995 | doi = | PMID = 8546029 }}</ref> | |||
*GFAP +ve. (50%) | |||
*Vimentin +ve. (100%) | |||
*S100 +ve. (100%) | |||
*Neurofilament +/-ve (ganglionic component). | |||
*Synaptophysin +/-ve (ganglionic component).. | |||
*[[TTF-1]] (7 out of 7).<ref name=pmid25669749>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hewer | first1 = E. | last2 = Vajtai | first2 = I. | title = Consistent nuclear expression of thyroid transcription factor 1 in subependymal giant cell astrocytomas suggests lineage-restricted histogenesis. | journal = Clin Neuropathol | volume = 34 | issue = 3 | pages = 128-31 | month = | year = | doi = 10.5414/NP300818 | PMID = 25669749 }}</ref> | |||
*Olig2-ve.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Overwater | first1 = IE. | last2 = Swenker | first2 = R. | last3 = van der Ende | first3 = EL. | last4 = Hanemaayer | first4 = KB. | last5 = Hoogeveen-Westerveld | first5 = M. | last6 = van Eeghen | first6 = AM. | last7 = Lequin | first7 = MH. | last8 = van den Ouweland | first8 = AM. | last9 = Moll | first9 = HA. | title = Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. | journal = Eur J Hum Genet | volume = 24 | issue = 12 | pages = 1688-1695 | month = 12 | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1038/ejhg.2016.85 | PMID = 27406250 }}</ref> | |||
* MIB-1 usu. low (1-5%). | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Neuropathology tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Neuropathology tumours]] | |||
[[Category:WHO grade I tumours]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:37, 14 October 2019
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
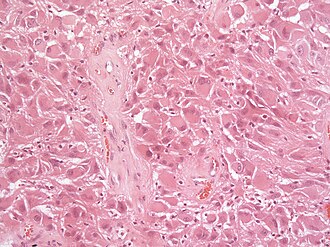 Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | SEGA |
| LM DDx | ganglioglioma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, glioblastoma |
| IHC | GFAP +ve |
| Site | brain - usu. wall of ventricles |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare - esp. in young adults |
| Prognosis | good (WHO Grade I) |
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, abbreviated SEGA, is a low-grade astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis complex.
General
- Associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC).[1]
- 6-14% of all TSC patients will develop a SEGA.
- Sporadic examples of SEGA may represent undetected TSC patients (i.e., low-level somatic mosaicism)[2].
- Associated with epilepsy.
- WHO Grade I.
Gross/radiology
- Well-demarcated.
- Often projecting into a ventricle.
- May be calcified
- Circumscribed tumour.
Microscopic
- Giant cells with nuclear atypia ("bizarre cells", "ganglioid cells").
- Glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Elongated cells in a fibrillary background.
- Abundant mast cells.[5]
- Lymphocytic infiltrates.
- Endothelial proliferations and/or necrosis are not a sign of malignancy.
Images
www:
IHC
- GFAP +ve. (50%)
- Vimentin +ve. (100%)
- S100 +ve. (100%)
- Neurofilament +/-ve (ganglionic component).
- Synaptophysin +/-ve (ganglionic component)..
- TTF-1 (7 out of 7).[7]
- Olig2-ve.[8]
- MIB-1 usu. low (1-5%).
See also
References
- ↑ Grajkowska, W.; Kotulska, K.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Roszkowski, M.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Matyja, E. (2011). "Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas with atypical histological features mimicking malignant gliomas.". Folia Neuropathol 49 (1): 39-46. PMID 21455842.
- ↑ Overwater, IE.; Swenker, R.; van der Ende, EL.; Hanemaayer, KB.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; van Eeghen, AM.; Lequin, MH.; van den Ouweland, AM. et al. (12 2016). "Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex.". Eur J Hum Genet 24 (12): 1688-1695. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.85. PMID 27406250.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179.html. Accessed on: 29 July 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Taraszewska, A.; Kroh, H.; Majchrowski, A. (1997). "Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma: clinical, histologic and immunohistochemical characteristic of 3 cases.". Folia Neuropathol 35 (3): 181-6. PMID 9595853.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case179/micro.html. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ Hirose, T.; Scheithauer, BW.; Lopes, MB.; Gerber, HA.; Altermatt, HJ.; Hukee, MJ.; VandenBerg, SR.; Charlesworth, JC. (1995). "Tuber and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and immunoelectron and microscopic study.". Acta Neuropathol 90 (4): 387-99. PMID 8546029.
- ↑ Hewer, E.; Vajtai, I.. "Consistent nuclear expression of thyroid transcription factor 1 in subependymal giant cell astrocytomas suggests lineage-restricted histogenesis.". Clin Neuropathol 34 (3): 128-31. doi:10.5414/NP300818. PMID 25669749.
- ↑ Overwater, IE.; Swenker, R.; van der Ende, EL.; Hanemaayer, KB.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; van Eeghen, AM.; Lequin, MH.; van den Ouweland, AM. et al. (12 2016). "Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex.". Eur J Hum Genet 24 (12): 1688-1695. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.85. PMID 27406250.