Difference between revisions of "Trisomy 18"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (+more) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Prominent occiput. | *Prominent occiput. | ||
*Overriding fingers - '''classic finding'''. | *Overriding fingers - '''classic finding'''. | ||
*Omphalocele. | *[[Omphalocele]] ~ 6% in a series of 85 cases.<ref name=pmid3191615>{{Cite journal | last1 = Moore | first1 = CA. | last2 = Harmon | first2 = JP. | last3 = Padilla | first3 = LM. | last4 = Castro | first4 = VB. | last5 = Weaver | first5 = DD. | title = Neural tube defects and omphalocele in trisomy 18. | journal = Clin Genet | volume = 34 | issue = 2 | pages = 98-103 | month = Aug | year = 1988 | doi = | PMID = 3191615 }}</ref> | ||
*Rocker bottom feet. | *Rocker bottom feet. | ||
*[[Horseshoe kidney]] - up to 20% of cases.<ref>URL: [http://radiopaedia.org/articles/horseshoe_kidney http://radiopaedia.org/articles/horseshoe_kidney]. Accessed on: 14 March 2012.</ref> | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Omphalocele is | *[[Omphalocele]] is usually genetic.<ref name=pmid20809116>{{Cite journal | last1 = Frolov | first1 = P. | last2 = Alali | first2 = J. | last3 = Klein | first3 = MD. | title = Clinical risk factors for gastroschisis and omphalocele in humans: a review of the literature. | journal = Pediatr Surg Int | volume = 26 | issue = 12 | pages = 1135-48 | month = Dec | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00383-010-2701-7 | PMID = 20809116 }}</ref> | ||
**Other considerations should include [[Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome]]. | **Other considerations should include [[Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome]]. | ||
====Image==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
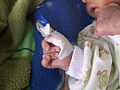
Image:Overlapping_fingers.JPG | Overlapping fingers. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===A lame short mnemonic=== | ===A lame short mnemonic=== | ||
''MOOO'': | ''MOOO'': | ||
*Micrognathnia. | *Micrognathnia. | ||
*Occiput - prominent. | |||
*[[Omphalocele]]. | |||
*Overriding fingers. | *Overriding fingers. | ||
* | |||
* | ===Another mnemonic=== | ||
''EDWARDS'':<ref>URL: [http://www.paeds.co.uk/wiki/index.php?title=Mnemonics#Edward.27s_Syndrome http://www.paeds.co.uk/wiki/index.php?title=Mnemonics#Edward.27s_Syndrome]. Accessed on: 30 May 2011.</ref> | |||
*Extra copy of chromosome '''E'''ighteen. | |||
*Digits overlap. | |||
*Wide head (prominent occiput). | |||
*Absent intellect (mental retard). | |||
*Rocker-bottom feet. | |||
*Diseased heart. | |||
*Small lower jaw (micrognathnia). | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Trisomy 13]] (Patau syndrome). | *[[Trisomy 13]] (Patau syndrome). | ||
*[[Trisomy 21]] (Down syndrome). | |||
*[[Chromosomal anomalies]]. | *[[Chromosomal anomalies]]. | ||
*[[Stillbirth]]. | *[[Stillbirth]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:28, 19 May 2013
Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, is a relatively common chromosomal abnormality.
Characteristics
- Micrognathia - small chin.
- Prominent occiput.
- Overriding fingers - classic finding.
- Omphalocele ~ 6% in a series of 85 cases.[3]
- Rocker bottom feet.
- Horseshoe kidney - up to 20% of cases.[4]
Notes:
- Omphalocele is usually genetic.[5]
- Other considerations should include Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.
Image
A lame short mnemonic
MOOO:
- Micrognathnia.
- Occiput - prominent.
- Omphalocele.
- Overriding fingers.
Another mnemonic
EDWARDS:[6]
- Extra copy of chromosome Eighteen.
- Digits overlap.
- Wide head (prominent occiput).
- Absent intellect (mental retard).
- Rocker-bottom feet.
- Diseased heart.
- Small lower jaw (micrognathnia).
See also
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome).
- Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
- Chromosomal anomalies.
- Stillbirth.
References
- ↑ Sherman, C. Recent advances in pathology (lecture). 9 May 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://johnsarm.net/trisomy_18_%28edwards%29.htm. Accessed on: 16 May 2011.
- ↑ Moore, CA.; Harmon, JP.; Padilla, LM.; Castro, VB.; Weaver, DD. (Aug 1988). "Neural tube defects and omphalocele in trisomy 18.". Clin Genet 34 (2): 98-103. PMID 3191615.
- ↑ URL: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/horseshoe_kidney. Accessed on: 14 March 2012.
- ↑ Frolov, P.; Alali, J.; Klein, MD. (Dec 2010). "Clinical risk factors for gastroschisis and omphalocele in humans: a review of the literature.". Pediatr Surg Int 26 (12): 1135-48. doi:10.1007/s00383-010-2701-7. PMID 20809116.
- ↑ URL: http://www.paeds.co.uk/wiki/index.php?title=Mnemonics#Edward.27s_Syndrome. Accessed on: 30 May 2011.