Difference between revisions of "Rhabdomyoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = | | Image = Rhabdomyoma -- high mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = Rhabdomyoma. [[H&E stain]]. (WC) | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
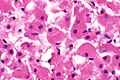
| Micro = spider cells (large polygonal cells (~10-20x RBC diameter), abundant cytoplasm with clearing) | | Micro = spider cells (large polygonal cells (~10-20x RBC diameter), abundant cytoplasm with clearing) | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
*Vimentin -ve/+ve. | *Vimentin -ve/+ve. | ||
*S-100 -ve. | *S-100 -ve. | ||
**Positive in granular cell tumour and | **Positive in granular cell tumour and hibernoma. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:47, 22 April 2024
| Rhabdomyoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
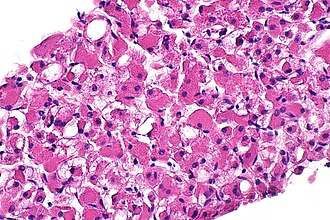 Rhabdomyoma. H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
| LM | spider cells (large polygonal cells (~10-20x RBC diameter), abundant cytoplasm with clearing) |
| Subtypes | fetal rhabdomyoma, adult rhabdomyoma |
| LM DDx | granular cell tumour, hibernoma, oncocytoma |
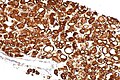
| IHC | desmin +ve, actin +ve, myoglobin +ve, S-100 -ve |
| Site | heart (see cardiac tumours), head and neck |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | benign |
Rhabdomyoma a benign muscle tumour. Often seen in the context of tuberous sclerosis.
General
- May be seen in the context of tuberous sclerosis.
- Rare benign mesenchymal tumour - may be seen in the head and neck.[1]
- Can cause death if in the heart.[2]
Gross
- Solid, white/tan colour.
Image:
Microscopic
Features - cardiac:[3]
- Spider cells:
- Large polygonal cells (~10-20x RBC diameter):
- Abundant cytoplasm filled with glycogen.
- Large polygonal cells (~10-20x RBC diameter):
Note:
- Fetal rhabdomyomas may have pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia.[1]
DDx:
Images
www
IHC
Features:[1]
- Desmin +ve (21 of 21 adult cases[4]).
- Myogoblin +ve.
- Actin +ve (21 of 21 adult cases[4]).
- Vimentin -ve/+ve.
- S-100 -ve.
- Positive in granular cell tumour and hibernoma.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hansen, T.; Katenkamp, D. (Nov 2005). "Rhabdomyoma of the head and neck: morphology and differential diagnosis.". Virchows Arch 447 (5): 849-54. doi:10.1007/s00428-005-0038-8. PMID 16133368.
- ↑ Neri, M.; Di Donato, S.; Maglietta, R.; Pomara, C.; Riezzo, I.; Turillazzi, E.; Fineschi, V. (Dec 2012). "Sudden death as presenting symptom caused by cardiac primary multicentric left ventricle rhabdomyoma, in an 11-month-old baby. An immunohistochemical study.". Diagn Pathol 7: 169. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-7-169. PMID 23206573.
- ↑ URL: http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/cardio/rhabdomyoma.html. Accessed on: 19 October 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kapadia, SB.; Meis, JM.; Frisman, DM.; Ellis, GL.; Heffner, DK.; Hyams, VJ. (Jun 1993). "Adult rhabdomyoma of the head and neck: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study.". Hum Pathol 24 (6): 608-17. PMID 8505039.