Difference between revisions of "Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| Micro = foveolar epithelium, gastric glands (body-type or antral-type), small bowel mucosa +/-Brunner's glands | | Micro = foveolar epithelium, gastric glands (body-type or antral-type), small bowel mucosa +/-Brunner's glands | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = foveolar metaplasia | | LMDDx = foveolar metaplasia of the duodenum, foveolar gastric-type dysplasia, [[intestinal metaplasia of the stomach]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Common ~15% of cases in one series.<ref name=pmid22295146>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = Pathologic observations of the duodenum in 615 consecutive duodenal specimens: I. benign lesions. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 5 | issue = 1 | pages = 46-51 | month = | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22295146 }}</ref> | *Common ~15% of cases in one series.<ref name=pmid22295146>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = Pathologic observations of the duodenum in 615 consecutive duodenal specimens: I. benign lesions. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 5 | issue = 1 | pages = 46-51 | month = | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22295146 }}</ref> | ||
*Probably not | *Probably ''not'' caused by ''[[Helicobacter pylori]]''.<ref name=pmid20656325>{{Cite journal | last1 = Genta | first1 = RM. | last2 = Kinsey | first2 = RS. | last3 = Singhal | first3 = A. | last4 = Suterwala | first4 = S. | title = Gastric foveolar metaplasia and gastric heterotopia in the duodenum: no evidence of an etiologic role for Helicobacter pylori. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 41 | issue = 11 | pages = 1593-600 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.04.010 | PMID = 20656325 }}</ref> | ||
**''[[Helicobacter duodenitis]]'' is associated with gastric metaplasia.<ref name=pmid7769188>{{cite journal |authors=Yang H, Dixon MF, Zuo J, Fong F, Zhou D, Corthésy I, Blum A |title=Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric metaplasia in the duodenum in China |journal=J Clin Gastroenterol |volume=20 |issue=2 |pages=110–2 |date=March 1995 |pmid=7769188 |doi=10.1097/00004836-199503000-00007 |url=}}</ref> | |||
Clinical DDx:<ref name=pmid21242038/> | Clinical DDx:<ref name=pmid21242038/> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 56: | ||
#Foveolar epithelium. | #Foveolar epithelium. | ||
#Gastric glands - body-type or antral-type. | #Gastric glands - body-type or antral-type. | ||
#Small bowel mucosa +/- Brunner's glands. | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Foveolar metaplasia (isolated) - see [[ | *Foveolar metaplasia (isolated) - see [[peptic duodenitis]]. | ||
*Foveolar gastric-type dysplasia.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Park | first1 = do Y. | last2 = Srivastava | first2 = A. | last3 = Kim | first3 = GH. | last4 = Mino-Kenudson | first4 = M. | last5 = Deshpande | first5 = V. | last6 = Zukerberg | first6 = LR. | last7 = Song | first7 = GA. | last8 = Lauwers | first8 = GY. | title = Adenomatous and foveolar gastric dysplasia: distinct patterns of mucin expression and background intestinal metaplasia. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 32 | issue = 4 | pages = 524-33 | month = Apr | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31815b890e | PMID = 18300795 }}</ref> | *Foveolar gastric-type dysplasia.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Park | first1 = do Y. | last2 = Srivastava | first2 = A. | last3 = Kim | first3 = GH. | last4 = Mino-Kenudson | first4 = M. | last5 = Deshpande | first5 = V. | last6 = Zukerberg | first6 = LR. | last7 = Song | first7 = GA. | last8 = Lauwers | first8 = GY. | title = Adenomatous and foveolar gastric dysplasia: distinct patterns of mucin expression and background intestinal metaplasia. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 32 | issue = 4 | pages = 524-33 | month = Apr | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31815b890e | PMID = 18300795 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Stomach with intestinal metaplasia]]. | *[[Stomach with intestinal metaplasia]]. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 73: | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
<pre> | |||
Duodenum, Biopsy: | |||
- Duodenal mucosa with gastric (body-type) heterotopia, otherwise within normal limits. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Block letters=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | ||
| Line 78: | Line 85: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Alternate=== | ====Alternate==== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | ||
| Line 88: | Line 95: | ||
*[[Duodenum]]. | *[[Duodenum]]. | ||
*[[Stomach]]. | *[[Stomach]]. | ||
*[[Gastric heterotopia]]. | |||
*[[Pseudopyloric mucous glands]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:47, 5 February 2024
| Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
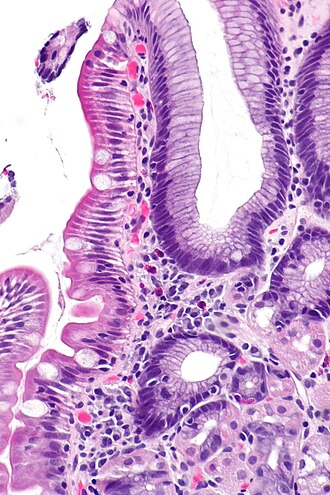 Gastric heterotopia in the duodenum. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | foveolar epithelium, gastric glands (body-type or antral-type), small bowel mucosa +/-Brunner's glands |
| LM DDx | foveolar metaplasia of the duodenum, foveolar gastric-type dysplasia, intestinal metaplasia of the stomach |
| Gross | nodules/polyps |
| Site | duodenum |
|
| |
| Prevalence | relatively common ~15% |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | duodenal polyp, duodenal ulcer, tumour/submucosal tumour, duodenal carcinoma, duodenitis |
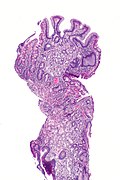
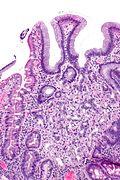
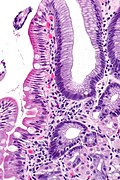
Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum is a relatively common finding of the duodenum.
General
- Common ~15% of cases in one series.[1]
- Probably not caused by Helicobacter pylori.[2]
- Helicobacter duodenitis is associated with gastric metaplasia.[3]
Clinical DDx:[4]
- Duodenal polyp, duodenal ulcer, tumour/submucosal tumour, duodenal carcinoma, and duodenitis.
Classification
According to Terada it can be subdivided into:[4]
- Foveolar epithelium with gastric pits
- Foveolar epithelium only.
Note:
- This article considers the former (foveolar epithelium with gastric pits) as gastric heterotopia. The later (foveolar epithelium only) is dealt with in the context of peptic duodenitis.
Gross
- Typically nodules/polyps.[5]
Microscopic
Features:
- Foveolar epithelium.
- Gastric glands - body-type or antral-type.
- Small bowel mucosa +/- Brunner's glands.
DDx:
- Foveolar metaplasia (isolated) - see peptic duodenitis.
- Foveolar gastric-type dysplasia.[6]
- Stomach with intestinal metaplasia.
Images
www:
Sign out
Duodenum, Biopsy: - Duodenal mucosa with gastric (body-type) heterotopia, otherwise within normal limits.
Block letters
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH GASTRIC (BODY-TYPE) HETEROTOPIA. - NEGATIVE FOR SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY.
Alternate
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA AND BRUNNER'S GLANDS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA, BODY-TYPE MUCOSA.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Terada, T. (2012). "Pathologic observations of the duodenum in 615 consecutive duodenal specimens: I. benign lesions.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5 (1): 46-51. PMID 22295146.
- ↑ Genta, RM.; Kinsey, RS.; Singhal, A.; Suterwala, S. (Nov 2010). "Gastric foveolar metaplasia and gastric heterotopia in the duodenum: no evidence of an etiologic role for Helicobacter pylori.". Hum Pathol 41 (11): 1593-600. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.04.010. PMID 20656325.
- ↑ Yang H, Dixon MF, Zuo J, Fong F, Zhou D, Corthésy I, Blum A (March 1995). "Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric metaplasia in the duodenum in China". J Clin Gastroenterol 20 (2): 110–2. doi:10.1097/00004836-199503000-00007. PMID 7769188.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Terada, T. (Mar 2011). "Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract: a histopathologic study of 158 cases.". Pathol Res Pract 207 (3): 148-50. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2010.12.004. PMID 21242038.
- ↑ Shousha, S.; Spiller, RC.; Parkins, RA. (Jan 1983). "The endoscopically abnormal duodenum in patients with dyspepsia: biopsy findings in 60 cases.". Histopathology 7 (1): 23-34. PMID 6840712.
- ↑ Park, do Y.; Srivastava, A.; Kim, GH.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Deshpande, V.; Zukerberg, LR.; Song, GA.; Lauwers, GY. (Apr 2008). "Adenomatous and foveolar gastric dysplasia: distinct patterns of mucin expression and background intestinal metaplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 32 (4): 524-33. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31815b890e. PMID 18300795.