Difference between revisions of "Intramucosal colorectal carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
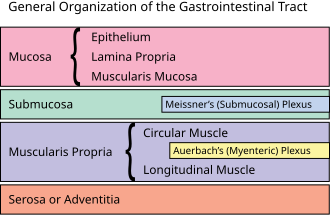
[[Image:GI Organization.svg|thumb|300px|right|The layers of the GI tract from inside (mucosa) to outside (serosa/adventitia). (WC)]] | |||
'''Intramucosal colorectal carcinoma''' is a confusing term for ''high grade (colorectal) dysplasia'' that should be avoided.<ref name=pmid22943008>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fleming | first1 = M. | last2 = Ravula | first2 = S. | last3 = Tatishchev | first3 = SF. | last4 = Wang | first4 = HL. | title = Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects. | journal = J Gastrointest Oncol | volume = 3 | issue = 3 | pages = 153-73 | month = Sep | year = 2012 | doi = 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2012.030 | PMID = 22943008 }}</ref> | '''Intramucosal colorectal carcinoma''' is a confusing term for ''high grade (colorectal) dysplasia'' that should be avoided.<ref name=pmid22943008>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fleming | first1 = M. | last2 = Ravula | first2 = S. | last3 = Tatishchev | first3 = SF. | last4 = Wang | first4 = HL. | title = Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects. | journal = J Gastrointest Oncol | volume = 3 | issue = 3 | pages = 153-73 | month = Sep | year = 2012 | doi = 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2012.030 | PMID = 22943008 }}</ref> | ||
''Intramucosal rectal carcinoma'', ''intramucosal colonic carcinoma'', ''intramucosal colonic adenocarcinoma'' | '''Intramucosal rectal carcinoma''', '''intramucosal colonic carcinoma''', '''intramucosal colonic adenocarcinoma''', '''intramucosal rectal adenocarcinoma''', '''intramucosal adenocarcinoma of the colon''', and '''colorectal adenocarcinoma in situ''' redirect here. | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*[[Colorectal adenocarcinoma]] is defined by invasion into the submucosa. | *[[Colorectal adenocarcinoma]] is defined by invasion into the submucosa. | ||
**This is different than elsewhere in the GI tract, where cancer is defined by invasion through the basement membrane, i.e. into the lamina propria. | **This is different than elsewhere in the GI tract, where cancer is defined by invasion through the basement membrane, i.e. into the lamina propria. | ||
**Rationale: | **Rationale: atypical (cancer-like) cells in lamina propria do ''not'' have [[metastasis|metastatic]] potential as there are no lymphatics in the colorectal lamina propria.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lewin | first1 = MR. | last2 = Fenton | first2 = H. | last3 = Burkart | first3 = AL. | last4 = Sheridan | first4 = T. | last5 = Abu-Alfa | first5 = AK. | last6 = Montgomery | first6 = EA. | title = Poorly differentiated colorectal carcinoma with invasion restricted to lamina propria (intramucosal carcinoma): a follow-up study of 15 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 12 | pages = 1882-6 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318057fac2 | PMID = 18043043 }}</ref> | ||
Note: | |||
*If one wants to differentiate ''adenocarcinoma in situ'' and ''high-grade dysplasia'': | |||
**''Adenocarcinoma in situ'' has ''invasion into the lamina propria'' and ''high-grade dysplasia'' does ''not'' have lamina propria invasion. Thus, the difference amounts to seeing a [[desmoplastic stroma]] or infiltrative cells; if one of these is present it is ''adenocarcinoma in situ'', if both are ''not'' it is ''dysplasia''. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 17: | ||
*[[Traditional adenoma]]. | *[[Traditional adenoma]]. | ||
*[[Intramucosal carcinoma]]. | *[[Intramucosal carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Colorectal cancer staging]]. | |||
*[[Pseudoinvasion]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 06:29, 19 March 2018
Intramucosal colorectal carcinoma is a confusing term for high grade (colorectal) dysplasia that should be avoided.[1]
Intramucosal rectal carcinoma, intramucosal colonic carcinoma, intramucosal colonic adenocarcinoma, intramucosal rectal adenocarcinoma, intramucosal adenocarcinoma of the colon, and colorectal adenocarcinoma in situ redirect here.
Background
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma is defined by invasion into the submucosa.
- This is different than elsewhere in the GI tract, where cancer is defined by invasion through the basement membrane, i.e. into the lamina propria.
- Rationale: atypical (cancer-like) cells in lamina propria do not have metastatic potential as there are no lymphatics in the colorectal lamina propria.[2]
Note:
- If one wants to differentiate adenocarcinoma in situ and high-grade dysplasia:
- Adenocarcinoma in situ has invasion into the lamina propria and high-grade dysplasia does not have lamina propria invasion. Thus, the difference amounts to seeing a desmoplastic stroma or infiltrative cells; if one of these is present it is adenocarcinoma in situ, if both are not it is dysplasia.
See also
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Traditional adenoma.
- Intramucosal carcinoma.
- Colorectal cancer staging.
- Pseudoinvasion.
References
- ↑ Fleming, M.; Ravula, S.; Tatishchev, SF.; Wang, HL. (Sep 2012). "Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects.". J Gastrointest Oncol 3 (3): 153-73. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2012.030. PMID 22943008.
- ↑ Lewin, MR.; Fenton, H.; Burkart, AL.; Sheridan, T.; Abu-Alfa, AK.; Montgomery, EA. (Dec 2007). "Poorly differentiated colorectal carcinoma with invasion restricted to lamina propria (intramucosal carcinoma): a follow-up study of 15 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (12): 1882-6. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318057fac2. PMID 18043043.