Difference between revisions of "Post-infectious glomerulonephritis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→EM) |
(+infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Post-infectious_glomerulonephritis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
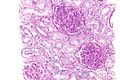
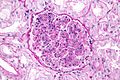
| Caption = Post-infectious glomerulonephritis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = +/-neutrophils in glomerulus, [[glomerular crescents]] | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = subepithelial deposits, hump-like | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = granular immune deposits | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[kidney]] - see ''[[medical kidney diseases]]'' | |||
| Assdx = post-infection, e.g. [[pneumonia]] | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = [[nephritic syndrome]] (proteinuria, [[hypertension]], azotemia, [[RBC]] casts, oliguria, hematuria) | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = usually good | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Post-infectious glomerulonephritis''', abbreviated '''PIGN''', is a rarely biopsied glomerulonephritis classically associated with a streptococcal infection. | '''Post-infectious glomerulonephritis''', abbreviated '''PIGN''', is a rarely biopsied glomerulonephritis classically associated with a streptococcal infection. | ||
Latest revision as of 06:24, 11 April 2015
| Post-infectious glomerulonephritis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Post-infectious glomerulonephritis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | +/-neutrophils in glomerulus, glomerular crescents |
| EM | subepithelial deposits, hump-like |
| IF | granular immune deposits |
| Site | kidney - see medical kidney diseases |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | post-infection, e.g. pneumonia |
| Signs | nephritic syndrome (proteinuria, hypertension, azotemia, RBC casts, oliguria, hematuria) |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | usually good |
Post-infectious glomerulonephritis, abbreviated PIGN, is a rarely biopsied glomerulonephritis classically associated with a streptococcal infection.
General
Clinical:
Microscopic
Features:
- +/-Neutrophils - in glomerulus.
- Glomerular crescents.
Images
www:
IF
- Granular immune deposits.
EM
- Subepithelial deposits - hump-like.[3]
- Larger when measured perpendicular to the basement membrane, if compared to membranous nephropathy.
- Typically focal.
See also
References
- ↑ Barbiano Di Belgiojoso, G.; Genderini, A.; Ferrario, F.. "[Post-infectious glomerulonephritis].". G Ital Nefrol 20 (2): 184-99. PMID 12746805.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Stratta, P.; Musetti, C.; Barreca, A.; Mazzucco, G. (Jun 2014). "New trends of an old disease: the acute post infectious glomerulonephritis at the beginning of the new millenium.". J Nephrol 27 (3): 229-39. doi:10.1007/s40620-013-0018-z. PMID 24777751.
- ↑ Sung, HY.; Lim, CH.; Shin, MJ.; Kim, BS.; Kim, YO.; Song, HC.; Kim, SY.; Choi, EJ. et al. (Dec 2007). "A case of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage.". J Korean Med Sci 22 (6): 1074-8. PMID 18162726.