Difference between revisions of "An introduction to head and neck pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
|||
| (195 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | This article is '''an introduction to head and neck pathology'''. Most of head and neck pathology is squamous cell carcinoma and its variants. | ||
The [[thyroid gland]] is dealt with in its own article, as is pathology of the [[salivary gland]]. | |||
Cytopathology of the head and neck is dealt with in a separate article called ''[[head and neck cytopathology]]''. | Cytopathology of the head and neck is dealt with in a separate article called ''[[head and neck cytopathology]]''. | ||
==Clinical== | =Anatomy= | ||
=== | [[Image:Blausen_0872_UpperRespiratorySystem.png|thumb|Head and neck anatomy (BruceBlaus/WC).]] | ||
*Oropharynx - includes: tonsil, tonsillar pillar, base of tongue, soft palate.<ref>URL: [https://www.cancer.org/cancer/oral-cavity-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/about/what-is-oral-cavity-cancer.html https://www.cancer.org/cancer/oral-cavity-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/about/what-is-oral-cavity-cancer.html]. Accessed on: 1 April 2021.</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/throat-cancer/oropharyngeal-cancer/soft-palate-cancer/ http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/throat-cancer/oropharyngeal-cancer/soft-palate-cancer/]. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.</ref> | |||
* | *Oral cavity - includes floor of mouth, bucca, anterior 2/3 of tongue,<ref>URL: [http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/tongue-cancer/ http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/tongue-cancer/]. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.</ref> lips, [[hard palate]], upper & lower alveolar ridge, retromolar trigone.<ref>URL: [http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/oromandibular-cancer/ http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/oromandibular-cancer/]. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.</ref> | ||
** | *Laryngopharynx. | ||
** | *Nasopharynx. | ||
** | |||
* | =Clinical= | ||
** | Common lesions:<ref name=Ref_PBoD780>{{Ref PBoD|780}}</ref> | ||
** | *[[Leukoplakia]]. | ||
**Homogeneous. | |||
**Non-homogeneous. | |||
*Erythroplakia - more worrisome for cancer than leukoplakia. | |||
==Leukoplakia== | |||
:''[[Hairy leukoplakia]] is dealt with in a separate section''. | |||
:''The typical [[benign leukoplakia]] is dealt with in a separate section''. | |||
{{Main|Leukoplakia}} | |||
==Erythroplakia== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Non-specific clinical finding - may be benign or [[malignant]]. | |||
*Strong association with non-keratinizing squamous lesions (invasive and dysplastic). | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD780>{{Ref PBoD|780}}</ref> | |||
*Unidentified red lesion. | |||
*Often [[erosion]]. | |||
=Overview= | |||
==Cysts== | |||
*[[Rathke cleft cyst]] - nasal cavity. | |||
*[[Thyroglossal duct cyst]] - midline, neck. | |||
*[[Branchial cleft cyst]] - lateral neck. | |||
==Larynx== | |||
*[[Vocal cord nodule]]. | |||
*[[Laryngeal papilloma]]. | |||
==Oral== | |||
{{Main|Oral pathology}} | |||
Infectious: | |||
*[[Hairy leukoplakia]]. | |||
*[[Oral candidiasis]]. | |||
Other: | |||
*[[Pemphigus vulgaris]]. | |||
Vascular: | |||
*[[Pyogenic granuloma]]. | |||
Pigmentation: | |||
*Focal: | |||
**[[Amalgam tattoo]]. | |||
**[[Melanocytic lesions]]. | |||
***[[Melanotic macule]]. | |||
***[[Blue nevus]]. | |||
***[[Malignant melanoma]] | |||
*Diffuse | |||
**[[Peutz-Jeghers syndrome]]. | |||
**[[Addison's disease]]. | |||
==Nasal cavity/nose== | |||
*[[Rhinoscleroma]]. | |||
*Nasal glial heterotopia.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Penner | first1 = CR. | last2 = Thompson | first2 = L. | title = Nasal glial heterotopia: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic analysis of 10 cases with a review of the literature. | journal = Ann Diagn Pathol | volume = 7 | issue = 6 | pages = 354-9 | month = Dec | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 15018118 }}</ref> | |||
=Benign cystic lesions= | |||
:Cytology dealt with in ''[[Head and neck cytopathology]]''. | |||
===Cystic lesions - overview=== | |||
Lateral cystic lesions: | |||
*[[Branchial cleft cyst]]. | |||
*[[Cystic hygroma]]. | |||
Medial cystic lesions: | |||
*[[Thyroglossal duct cyst]]. | |||
Lateral & medial lesions: | |||
*[[Epidermoid cyst]]. | |||
*Cystic [[squamous cell carcinoma]]. | |||
==Rathke cleft cyst== | ==Rathke cleft cyst== | ||
:{{Main|Rathke cleft cyst}} | :{{Main|Rathke cleft cyst}} | ||
| Line 21: | Line 92: | ||
*Related to ''[[craniopharyngioma]]''. | *Related to ''[[craniopharyngioma]]''. | ||
== | ==Thyroglossal duct cyst== | ||
{{Main|Thyroglossal duct cyst}} | |||
== | ==Branchial cleft cyst== | ||
*[[AKA]] '' | *[[AKA]] ''branchial cleft remnant''. | ||
{{Main|Branchial cleft cyst}} | |||
== | ==Benign lymphoepithelial lesion== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''benign lymphoepithelial cyst'' | ||
{{Main|Benign lymphoepithelial lesion}} | |||
= | =Other benign= | ||
== | ==Vocal cord nodule== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''singer's nodule''. | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''vocal cord polyp''. | ||
{{Main|Vocal cord nodule}} | |||
== | ==Squamous papilloma== | ||
:Caruncle lesion is dealt with in ''[[papilloma of the caruncle]]''. | |||
:The lesion in the [[esophagus]] is dealt with in ''[[squamous papilloma of the esophagus]]''. | |||
{{Main|Squamous papilloma}} | |||
== | ==Pemphigus vulgaris== | ||
{{Main|Pemphigus vulgaris}} | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''pemphigus''. | ||
* | **Should not be confused with ''[[bullous pemphigoid]]'' (which is less serious). | ||
==Pyogenic granuloma== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''lobular capillary hemangioma''.<ref name=pmid21839350>{{Cite journal | last1 = Baglin | first1 = AC. | title = [Vascular tumors and pseudotumors. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma)]. | journal = Ann Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 4 | pages = 266-70 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.annpat.2011.05.014 | PMID = 21839350 }}</ref> | |||
{{Main|Lobular capillary hemangioma}} | |||
== | |||
=== | |||
==Plummer-Vinson syndrome== | ==Plummer-Vinson syndrome== | ||
Triad:<ref name=Ref_PBoD776>{{Ref PBoD|776}}</ref> | Triad:<ref name=Ref_PBoD776>{{Ref PBoD|776}}</ref> | ||
*Iron-deficiency anemia. | *Iron-deficiency [[anemia]]. | ||
*Glossitis. | *Glossitis. | ||
*Esophageal dysphagia (usually related to webs). | *Esophageal dysphagia (usually related to webs). | ||
== | ==Rhinoscleroma== | ||
{{Main|Rhinoscleroma}} | |||
=Neoplasms= | =Neoplasms= | ||
| Line 91: | Line 139: | ||
It includes: | It includes: | ||
*Keratocystic odontogenic tumour. | *[[Keratocystic odontogenic tumour]]. | ||
*Radicular cyst. | *[[Radicular cyst]]. | ||
*Dentigerous cyst. | *[[Dentigerous cyst]]. | ||
*Ameloblastoma. | *[[Ameloblastoma]]. | ||
*Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour. | *[[Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour]]. | ||
*Ameloblastic fibroma. | *[[Ameloblastic fibroma]]. | ||
*Odontogenic myxoma. | *[[Odontogenic myxoma]]. | ||
==Pharyngeal/nasopharyngeal specimens== | ==Pharyngeal/nasopharyngeal specimens== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 156: | ||
Work-up of negative H&E Bx differs by site: | Work-up of negative H&E Bx differs by site: | ||
* | *One large hospital: | ||
** | **LMWK (CAM5.2). | ||
** | **Pankeratin ([[AE1/AE3]]). | ||
* | *Another large hospital: | ||
**Nothing. | **Nothing. | ||
== | ==Laryngeal neoplasms== | ||
== | {{Main|Laryngeal carcinoma}} | ||
* | These are dealt with in a separate article. | ||
==Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma== | |||
*Abbreviated ''HPV-HNSCC''. | |||
{{Main|Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma}} | |||
== | ==Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma== | ||
*Abbreviated ''SNUC''. | |||
* | {{Main|Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma}} | ||
==Nasopharyngeal carcinoma== | |||
* | *Abbreviated ''NPC''. | ||
{{Main|Nasopharyngeal carcinoma}} | |||
==Squamous lesions== | ==Squamous lesions== | ||
| Line 142: | Line 190: | ||
**There are several subtypes of SCC. | **There are several subtypes of SCC. | ||
==Squamous | ==Squamous dysplasia of the head and neck== | ||
{{Main|Squamous dysplasia of the head and neck}} | |||
== | ==Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck== | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck}} | |||
==Small cell anaplastic carcinoma== | ==Small cell anaplastic carcinoma== | ||
| Line 231: | Line 200: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Metastatic small cell carcinoma of the lung. | *Metastatic [[small cell carcinoma]] of the lung. | ||
==Granular cell tumour== | ==Granular cell tumour== | ||
{{Main|Granular cell tumour}} | {{Main|Granular cell tumour}} | ||
==Olfactory neuroblastoma== | ==Olfactory neuroblastoma== | ||
:See also: ''[[neuroblastoma]]''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''esthesioneuroblastoma''. | *[[AKA]] ''esthesioneuroblastoma''. | ||
{{Main|Olfactory neuroblastoma}} | |||
==Craniopharyngioma== | ==Craniopharyngioma== | ||
| Line 262: | Line 216: | ||
==Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma== | ==Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma== | ||
:See also: ''[[Angiofibroma]]''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma''. | *[[AKA]] ''juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma''. | ||
{{Main|Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma}} | |||
==Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma== | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''low grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features''. | ||
{{Main|Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma}} | |||
=Nasal polyps= | |||
{{Main|Nasal polyps}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Latest revision as of 17:37, 4 March 2022
This article is an introduction to head and neck pathology. Most of head and neck pathology is squamous cell carcinoma and its variants.
The thyroid gland is dealt with in its own article, as is pathology of the salivary gland.
Cytopathology of the head and neck is dealt with in a separate article called head and neck cytopathology.
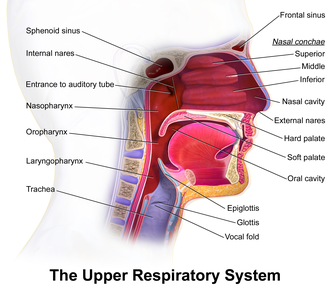
Anatomy
- Oropharynx - includes: tonsil, tonsillar pillar, base of tongue, soft palate.[1][2]
- Oral cavity - includes floor of mouth, bucca, anterior 2/3 of tongue,[3] lips, hard palate, upper & lower alveolar ridge, retromolar trigone.[4]
- Laryngopharynx.
- Nasopharynx.
Clinical
Common lesions:[5]
- Leukoplakia.
- Homogeneous.
- Non-homogeneous.
- Erythroplakia - more worrisome for cancer than leukoplakia.
Leukoplakia
- Hairy leukoplakia is dealt with in a separate section.
- The typical benign leukoplakia is dealt with in a separate section.
Main article: Leukoplakia
Erythroplakia
General
- Non-specific clinical finding - may be benign or malignant.
- Strong association with non-keratinizing squamous lesions (invasive and dysplastic).
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Unidentified red lesion.
- Often erosion.
Overview
Cysts
- Rathke cleft cyst - nasal cavity.
- Thyroglossal duct cyst - midline, neck.
- Branchial cleft cyst - lateral neck.
Larynx
Oral
Main article: Oral pathology
Infectious:
Other:
Vascular:
Pigmentation:
- Focal:
- Diffuse
Nasal cavity/nose
- Rhinoscleroma.
- Nasal glial heterotopia.[6]
Benign cystic lesions
- Cytology dealt with in Head and neck cytopathology.
Cystic lesions - overview
Lateral cystic lesions:
Medial cystic lesions:
Lateral & medial lesions:
- Epidermoid cyst.
- Cystic squamous cell carcinoma.
Rathke cleft cyst
- Main article: Rathke cleft cyst
- Arises from intermediate lobe - embryonic remnant.
- Benign cystic lesion without calcification.
- Related to craniopharyngioma.
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Main article: Thyroglossal duct cyst
Branchial cleft cyst
- AKA branchial cleft remnant.
Main article: Branchial cleft cyst
Benign lymphoepithelial lesion
- AKA benign lymphoepithelial cyst
Main article: Benign lymphoepithelial lesion
Other benign
Vocal cord nodule
Main article: Vocal cord nodule
Squamous papilloma
- Caruncle lesion is dealt with in papilloma of the caruncle.
- The lesion in the esophagus is dealt with in squamous papilloma of the esophagus.
Main article: Squamous papilloma
Pemphigus vulgaris
Main article: Pemphigus vulgaris
- AKA pemphigus.
- Should not be confused with bullous pemphigoid (which is less serious).
Pyogenic granuloma
Main article: Lobular capillary hemangioma
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Triad:[8]
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
- Glossitis.
- Esophageal dysphagia (usually related to webs).
Rhinoscleroma
Main article: Rhinoscleroma
Neoplasms
Odontogenic tumours and cysts
Main article: Odontogenic tumours and cysts
This is a rather large topic and dealt with in a separate article.
It includes:
- Keratocystic odontogenic tumour.
- Radicular cyst.
- Dentigerous cyst.
- Ameloblastoma.
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour.
- Ameloblastic fibroma.
- Odontogenic myxoma.
Pharyngeal/nasopharyngeal specimens
- Specimens may be challenging to interpret as there is normally an abundance of lymphoid cells.
- Malignant tissue can look benign.[9]
- May be difficult to differentiate from other malignancies.
Histology
- Upper airway distant from areas with friction: respiratory type epithelium.
Work-up of negative H&E Bx differs by site:
- One large hospital:
- LMWK (CAM5.2).
- Pankeratin (AE1/AE3).
- Another large hospital:
- Nothing.
Laryngeal neoplasms
Main article: Laryngeal carcinoma
These are dealt with in a separate article.
Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Abbreviated HPV-HNSCC.
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
- Abbreviated SNUC.
Main article: Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Abbreviated NPC.
Main article: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Squamous lesions
- Premalignant lesions
- Mild dysplasia.
- Low risk of progression to invasive lesions.
- Moderate dysplasia.
- Severe dysplasia/carcinoma in situ (CIS).
- Histologically severe dysplasia and CIS cannot be differentiated reliably; ergo, there can be considered the same thing.
- Severe dysplasia is not a necessary intermediate for cancer, i.e. invasive squamous cell carcinoma may be present with moderate dysplasia.
- Mild dysplasia.
- Invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
- "Microinvasive" squamous cell carcinoma - term should be avoided as there is no concenus on what it means.
- There are several subtypes of SCC.
Squamous dysplasia of the head and neck
Main article: Squamous dysplasia of the head and neck
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Small cell anaplastic carcinoma
- Rare.
DDx:
- Metastatic small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Granular cell tumour
Main article: Granular cell tumour
Olfactory neuroblastoma
- See also: neuroblastoma.
- AKA esthesioneuroblastoma.
Main article: Olfactory neuroblastoma
Craniopharyngioma
Main article: Craniopharyngioma
- Cystic lesion +/- calcifications +/-squamous nests.
- Related to Rathke cleft cyst.
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
- See also: Angiofibroma.
- AKA juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma.
Main article: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma
- AKA low grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features.
Main article: Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma
Nasal polyps
Main article: Nasal polyps
See also
References
- ↑ URL: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/oral-cavity-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/about/what-is-oral-cavity-cancer.html. Accessed on: 1 April 2021.
- ↑ URL: http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/throat-cancer/oropharyngeal-cancer/soft-palate-cancer/. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.
- ↑ URL: http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/tongue-cancer/. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.
- ↑ URL: http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/teens/cancer-basics/explore-cancer-types/oral-cancers/oromandibular-cancer/. Accessed on: 15 November 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 780. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Penner, CR.; Thompson, L. (Dec 2003). "Nasal glial heterotopia: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic analysis of 10 cases with a review of the literature.". Ann Diagn Pathol 7 (6): 354-9. PMID 15018118.
- ↑ Baglin, AC. (Aug 2011). "[Vascular tumors and pseudotumors. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma)].". Ann Pathol 31 (4): 266-70. doi:10.1016/j.annpat.2011.05.014. PMID 21839350.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 776. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ S. Raphael. December 2008.