Difference between revisions of "Non-specific interstitial pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Microscopic: +images) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Non-specfic_interstitial_pneumonia_(NSIP),_cellular_variant.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = NSIP. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = diffuse fibrosis (uniform fibrosis (unlike [[UIP]]), +/-''linear fibrosis'' (fibrosis that follows alveolar walls + no architectural distortion), +/-lymphoid nodules (assoc. with collagen vascular disease), +/-focal [[organizing pneumonia]] | |||
| Subtypes = idiopathic NSIP, NSIP due to an underlying cause | |||
| LMDDx = [[organizing pneumonia]], [[collagen vascular disease]], drug reaction, [[hypersensitivity pneumonitis]], [[lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[lung]] - see ''[[diffuse lung diseases]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = cough | |||
| Symptoms = dyspnea | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = lower lung zone fibrosis, patchy ground glass, no honeycombing | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = corticosteroids (?) | |||
}} | |||
'''Non-specific interstitial pneumonia''', abbreviated '''NSIP''', is an uncommon type of [[diffuse lung disease]]. | '''Non-specific interstitial pneumonia''', abbreviated '''NSIP''', is an uncommon type of [[diffuse lung disease]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Better prognosis than [[UIP]]. | *Better prognosis than [[UIP]]. | ||
*Some radiologists and pathologists don't believe in this entity. | *May respond to corticosteroids.<ref name=pmid22690098>{{cite journal |author=Lee JY, Jin SM, Lee BJ, ''et al.'' |title=Treatment response and long term follow-up results of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |journal=J. Korean Med. Sci. |volume=27 |issue=6 |pages=661–7 |year=2012 |month=June |pmid=22690098 |pmc=3369453 |doi=10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.661 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Some radiologists and pathologists don't believe in this entity.{{fact}} | |||
Associations:<ref name=Ref_WMSP92>{{Ref WMSP|92}}</ref> | Associations:<ref name=Ref_WMSP92>{{Ref WMSP|92}}</ref> | ||
*Connective tissue disease. | *[[Connective tissue disease]].<ref name=pmid21437858>{{cite journal |author=Hauber HP, Bittmann I, Kirsten D |title=[Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)] |language=German |journal=Pneumologie |volume=65 |issue=8 |pages=477–83 |year=2011 |month=August |pmid=21437858 |doi=10.1055/s-0030-1256284 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Rheumatoid arthritis]]. | *[[Rheumatoid arthritis]]. | ||
Note: | |||
*If no underlying cause is present it is known as ''idiopathic NSIP''. | |||
Clinical features (typical) of the idiopathic form:<ref name=pmid20178304>{{cite journal |author=Romagnoli M, Poletti V |title=[Update on non-specific interstitial pneumonia: a pattern, a clinical entity or different phenotypes? Surgical or bronchoscopic diagnosis?] |language=Italian |journal=Recenti Prog Med |volume=100 |issue=12 |pages=531–4 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=20178304 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Middle-aged, never-smoker women. | |||
*[[Dyspnea]]. | |||
*Cough. | |||
*Ground glass on HRCT. | |||
*Very good prognosis. | |||
==Gross/Radiology== | ==Gross/Radiology== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 70: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Collagen vascular disease. | *[[Collagen vascular disease]]. | ||
*Drug reaction. | *[[Drug reaction]]. | ||
*[[Hypersensitivity pneumonitis]] (extrinic allergic alveolitis). | *[[Hypersensitivity pneumonitis]] (extrinic allergic alveolitis). | ||
*[[Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia]] (LIP) - much more inflammation. | *[[Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia]] (LIP) - much more inflammation. | ||
*[[Organizing pneumonia]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
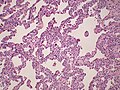
Image: Non-specfic_interstitial_pneumonia_(NSIP),_cellular_variant.jpg | NSIP - cellular. (WC/Rosen) | |||
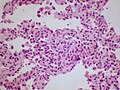
Image: Non-specfic_interstitial_pneumonia_(NSIP),_cellular_variant_2.jpg | NSIP - cellular. (WC/Rosen) | |||
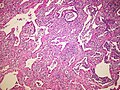
Image: Non-specfic interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), fibrosing variant.jpg | NSIP - fibrosing. (WC/Rosen) | |||
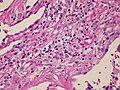
Image: Non-specfic interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), fibrosing variant_2.jpg | NSIP - fibrosing. (WC/Rosen) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:53, 17 March 2015
| Non-specific interstitial pneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
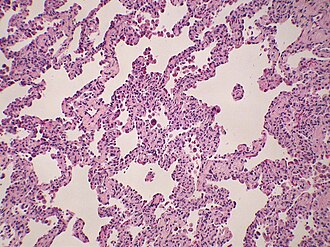 NSIP. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | diffuse fibrosis (uniform fibrosis (unlike UIP), +/-linear fibrosis (fibrosis that follows alveolar walls + no architectural distortion), +/-lymphoid nodules (assoc. with collagen vascular disease), +/-focal organizing pneumonia |
| Subtypes | idiopathic NSIP, NSIP due to an underlying cause |
| LM DDx | organizing pneumonia, collagen vascular disease, drug reaction, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia |
| Site | lung - see diffuse lung diseases |
|
| |
| Signs | cough |
| Symptoms | dyspnea |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | lower lung zone fibrosis, patchy ground glass, no honeycombing |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | corticosteroids (?) |
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia, abbreviated NSIP, is an uncommon type of diffuse lung disease.
General
- Better prognosis than UIP.
- May respond to corticosteroids.[1]
- Some radiologists and pathologists don't believe in this entity.[citation needed]
Associations:[2]
Note:
- If no underlying cause is present it is known as idiopathic NSIP.
Clinical features (typical) of the idiopathic form:[4]
- Middle-aged, never-smoker women.
- Dyspnea.
- Cough.
- Ground glass on HRCT.
- Very good prognosis.
Gross/Radiology
- No honeycombing.
- Fibrosis usually lower lung zone.
- Patchy ground glass.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Diffuse fibrosis:
- Uniform fibrosis (unlike UIP).
- "Linear fibrosis" has a good prognosis - should be mentioned in the report.
- Linear fibrosis = fibrosis that follows alveolar walls + no architectural distortion.
- +/-Lymphoid nodules - association with collagen vascular disease. (???)
- +/-Focal organizing pneumonia.
Notes:
- Inflammation in NSIP usually more prominent than in UIP.
- No honeycombing - key difference between UIP and NSIP.
DDx:
- Collagen vascular disease.
- Drug reaction.
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (extrinic allergic alveolitis).
- Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP) - much more inflammation.
- Organizing pneumonia.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Lee JY, Jin SM, Lee BJ, et al. (June 2012). "Treatment response and long term follow-up results of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia". J. Korean Med. Sci. 27 (6): 661–7. doi:10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.661. PMC 3369453. PMID 22690098. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3369453/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 92. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Hauber HP, Bittmann I, Kirsten D (August 2011). "[Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)]" (in German). Pneumologie 65 (8): 477–83. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1256284. PMID 21437858.
- ↑ Romagnoli M, Poletti V (December 2009). "[Update on non-specific interstitial pneumonia: a pattern, a clinical entity or different phenotypes? Surgical or bronchoscopic diagnosis?]" (in Italian). Recenti Prog Med 100 (12): 531–4. PMID 20178304.