Difference between revisions of "Vas deferens"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
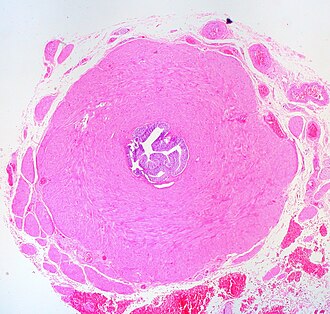
[[Image:Normal_Vas_Deferens%2C_Human_%283952564123%29.jpg|thumb|right|Vas deferens. (WC/Ed Uthman)]] | |||
The '''vas deferens''' are often seen as part of a [[prostate gland|prostatectomy]] specimen.<ref>URL: [http://www.upmccancercenters.com/cancer/prostate/radprostretropubic.html http://www.upmccancercenters.com/cancer/prostate/radprostretropubic.html]. Accessed on: 26 September 2011.</ref> They are the component of the [[spermatic cord]] that carries the sperm. | The '''vas deferens''' are often seen as part of a [[prostate gland|prostatectomy]] specimen.<ref>URL: [http://www.upmccancercenters.com/cancer/prostate/radprostretropubic.html http://www.upmccancercenters.com/cancer/prostate/radprostretropubic.html]. Accessed on: 26 September 2011.</ref> They are the component of the [[spermatic cord]] that carries the sperm. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Missed vas deferens. | *Missed vas deferens. | ||
**Intermediate size blood vessels +/- denudation. | |||
**Ureter. | |||
*Incomplete vasectomy - only partial lumen. | *Incomplete vasectomy - only partial lumen. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 42: | ||
*CD10 +ve (marker of Wolffian differentiation). | *CD10 +ve (marker of Wolffian differentiation). | ||
*Pankeratin +ve. | *Pankeratin +ve. | ||
*PAX-8 +ve (100%).<ref name=pmid32633248>{{cite journal |authors=Ortiz-Rey JA, Domínguez-de Dios J, Pérez-Schoch M, San Miguel-Fraile P, Gómez-de María C |title=[New immunohistochemistry markers to determine presence of vas deferens in vasectomy specimen.] |language=Spanish; Castilian |journal=Arch Esp Urol |volume=73 |issue=6 |pages=534–540 |date=July 2020 |pmid=32633248 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*GATA-3 +ve.<ref name=pmid33012491>{{cite journal |authors=Ortiz-Rey JA, Domínguez-de Dios J, Pérez-Schoch M, San Miguel-Fraile P, Gómez-de María C |title=[E-Cadherine and GATA-3 are useful in the confirmation of the vas deferens in vasectomy specimens] |language=Spanish; Castilian |journal=Rev Esp Patol |volume=53 |issue=4 |pages=218–225 |date=2020 |pmid=33012491 |doi=10.1016/j.patol.2020.02.005 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*ERG -ve.<ref name=pmid32633248/> | |||
*CD34 -ve.<ref name=pmid32633248/> | |||
===Sign out=== | ===Sign out=== | ||
| Line 129: | Line 136: | ||
Clinical correlation is suggested. | Clinical correlation is suggested. | ||
</pre> | |||
====No vas deferens identified==== | |||
<pre> | |||
A. CONNECTIVE TISSUE, RIGHT, "VASECTOMY": | |||
- NO VAS DEFERENS IDENTIFIED. | |||
- BENIGN FIBROMUSCULAR TISSUE WITH INTERMEDIATE BLOOD VESSELS. | |||
B. CONNECTIVE TISSUE, LEFT, "VASECTOMY": | |||
- NO VAS DEFERENS IDENTIFIED. | |||
- BENIGN FIBROMUSCULAR TISSUE WITH INTERMEDIATE BLOOD VESSELS. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
Levels were cut (x3). Clinical correlation is suggested. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 142: | Line 163: | ||
*[[Prostate gland]]. | *[[Prostate gland]]. | ||
*[[Testis]]. | *[[Testis]]. | ||
*[[Male infertility]]. | |||
*[[Epididymis]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:06, 28 March 2025
The vas deferens are often seen as part of a prostatectomy specimen.[1] They are the component of the spermatic cord that carries the sperm.
They often arrive alone -- removed for family planning (vasectomy).
Normal vas deferens
- Vasectomy redirects here.
General
- Seen in the context of vasectomy.
Note:
- Vasectomy is associated with testicular changes - increased seminiferous tubule wall thickness and decreased number of Sertoli cells.[2]
Gross
- Cylindrical piece of tissue.
Note:
- Surface should be inked.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Tubular structure - three muscle layers.
- Inner longitudinal (thin).
- Middle circular (thick).
- Outer longitudinal (thick).
- Epithelium
- Apical cells = columnar, ciliated.
- Basal cells = cuboidal.
Note:
- Muscle layers - like in bowel.
- A complete loop of epithelium should be visualized in the plane of section.
DDx:
- Missed vas deferens.
- Intermediate size blood vessels +/- denudation.
- Ureter.
- Incomplete vasectomy - only partial lumen.
IHC
Features:[3]
- CD10 +ve (marker of Wolffian differentiation).
- Pankeratin +ve.
- PAX-8 +ve (100%).[4]
- GATA-3 +ve.[5]
- ERG -ve.[4]
- CD34 -ve.[4]
Sign out
Right then left
A. VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT. B. VAS DEFERENS, LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT.
Left then right
A. VAS DEFERENS, LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT. B. VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT.
Single container
VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT AND LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOPS OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT.
Alternate
VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT AND LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOPS OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT ON BOTH SLIDE A1-1 AND SLIDE A2-1.
One container is empty
A. VAS DEFERENS ("LEFT"), VASECTOMY:
- VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOPS OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT
ON BOTH SLIDE A1-1 AND SLIDE A2-1.
- SEE COMMENT.
B. VAS DEFERENS ("RIGHT"), VASECTOMY:
- NO TISSUE IDENTIFIED, SEE COMMENT.
COMMENT:
Both specimens (left vas deferens and right vas deferens) may have been placed in
container A. See 'gross' section of report. Clinical correlation is essential.
Incomplete loop
A. VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY - INCOMPLETE LOOP OF EPITHELIUM, SEE COMMENT. B. VAS DEFERENS, LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT. COMMENT: Clinical correlation is suggested.
Oblique cut
A. VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY - OBLIQUE SECTION WITH COMPRESSED LOOP OF EPITHELIUM, SEE COMMENT. B. VAS DEFERENS, LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT. COMMENT: Clinical correlation is suggested.
Notes:
- The word loop is preferred over the words cross section as:
- The words cross section imply the cut is perpendicular to the axis.
- It is possible that a section with a loop of epithelium is the result of a non-transecting cut that generates an ovoid defect in the wall of the vas deferens.
No definite epithelium
A. VAS DEFERENS, LEFT, VASECTOMY: - VAS DEFERENS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS, LOOP OF EPITHELIUM AND MUSCLE LAYERS PRESENT. B. VAS DEFERENS, RIGHT, VASECTOMY: - COMPATIBLE WITH VAS DEFERENS, WITHOUT COMPLETE LOOP OF EPITHELIUM, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT - PART B: Definite vas deferens epithelium is not identified; however, the muscle layering seen is compatible with a vas deferens. Levels were cut (x4). Clinical correlation is suggested.
No vas deferens identified
A. CONNECTIVE TISSUE, RIGHT, "VASECTOMY": - NO VAS DEFERENS IDENTIFIED. - BENIGN FIBROMUSCULAR TISSUE WITH INTERMEDIATE BLOOD VESSELS. B. CONNECTIVE TISSUE, LEFT, "VASECTOMY": - NO VAS DEFERENS IDENTIFIED. - BENIGN FIBROMUSCULAR TISSUE WITH INTERMEDIATE BLOOD VESSELS. COMMENT: Levels were cut (x3). Clinical correlation is suggested.
Vasitis nodosa
Main article: Vasitis nodosa
Bilateral absence of the vas deferens
- Seen in cystic fibrosis.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.upmccancercenters.com/cancer/prostate/radprostretropubic.html. Accessed on: 26 September 2011.
- ↑ Jarow, JP.; Budin, RE.; Dym, M.; Zirkin, BR.; Noren, S.; Marshall, FF. (Nov 1985). "Quantitative pathologic changes in the human testis after vasectomy. A controlled study.". N Engl J Med 313 (20): 1252-6. doi:10.1056/NEJM198511143132003. PMID 4058505.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Sasaki, K.; Bastacky, SI.; Zynger, DL.; Parwani, AV. (Dec 2009). "Use of immunohistochemical markers to confirm the presence of vas deferens in vasectomy specimens.". Am J Clin Pathol 132 (6): 893-8. doi:10.1309/AJCPQZX4WS8UPKGG. PMID 19926581.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ortiz-Rey JA, Domínguez-de Dios J, Pérez-Schoch M, San Miguel-Fraile P, Gómez-de María C (July 2020). "[New immunohistochemistry markers to determine presence of vas deferens in vasectomy specimen.]" (in Spanish; Castilian). Arch Esp Urol 73 (6): 534–540. PMID 32633248.
- ↑ Ortiz-Rey JA, Domínguez-de Dios J, Pérez-Schoch M, San Miguel-Fraile P, Gómez-de María C (2020). "[E-Cadherine and GATA-3 are useful in the confirmation of the vas deferens in vasectomy specimens]" (in Spanish; Castilian). Rev Esp Patol 53 (4): 218–225. doi:10.1016/j.patol.2020.02.005. PMID 33012491.