Difference between revisions of "Bile duct adenoma"
(→IHC) |
(→Images: added a case) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
*Important as it can be misdiagnosed as cancer. | *Important as it can be misdiagnosed as [[cancer]]. | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
*Disordered bile ducts within in a fibrotic stroma. | *Disordered bile ducts within in a fibrotic stroma. | ||
**'''No''' (yellow) bile within, as these lesions do not have a connection to the biliary tree. | **'''No''' (yellow) bile within, as these lesions do not have a connection to the biliary tree. | ||
**+/-Lymphocytic cuff. | **+/-Lymphocytic cuff.<ref>URL: [http://www.surgpath4u.com/caseviewer.php?case_no=152 http://www.surgpath4u.com/caseviewer.php?case_no=152]. Accessed on: 6 March 2014.</ref> | ||
Negatives: | Negatives: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
*[[Cholangiocarcinoma]]. | *[[Cholangiocarcinoma]]. | ||
*Metastatic adenocarcinoma. | *Metastatic adenocarcinoma. | ||
**[[Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma]].<ref name=pmid15725808>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hornick | first1 = JL. | last2 = Lauwers | first2 = GY. | last3 = Odze | first3 = RD. | title = Immunohistochemistry can help distinguish metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinomas from bile duct adenomas and hamartomas of the liver. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 29 | issue = 3 | pages = 381-9 | month = Mar | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 15725808 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Bile duct hamartoma]] (von Meyenburg complex). | *[[Bile duct hamartoma]] (von Meyenburg complex). | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
*[http://www.ganfyd.org/index.php?title=Image:Bile_duct_adenoma_low_power.jpg Bile duct adenoma (ganfyd.org)]. | *[http://www.ganfyd.org/index.php?title=Image:Bile_duct_adenoma_low_power.jpg Bile duct adenoma (ganfyd.org)]. | ||
*[http://www.surgpath4u.com/caseviewer.php?case_no=152 Bile duct adenoma (surgpath4u.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3926226/figure/fig1/ Bile duct adenoma - oncocytic - low mag. (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid24592348/> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3926226/figure/fig2/ Bile duct adenoma - oncocytic - high mag. (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid24592348/> | |||
[[File:5 2033397936391 sl 1.png|Bile duct adenoma]] | |||
[[File:5 2033397936391 sl 2.png|Bile duct adenoma]] | |||
[[File:5 2033397936391 sl 3.png|Bile duct adenoma]] | |||
[[File:5 2033397936391 sl 4.png|Bile duct adenoma]] | |||
[[File:5 2033397936391 sl 5.png|Bile duct adenoma]]<br> | |||
Bile duct adenoma in a 67 yo man, not radiologically detected; this is important because cholangiocarcinomas are larger than bile duct adenomas. Bile duct adenomas are usually incidental findings, as in this case. These can be very difficult diagnosis; this case was evaluated by outside consultation. A. Glandular proliferation is seen. Note the curve indicated by the arrow, indicating a subcapsular location. B. The central scar, in other locations and with metastases, a finding associated with carcinoma, is in the liver a benign sign. The intense hyalin is also a benign sign, being that of a well-developed adenoma. C. Nuclear atypia in this case is modest near the region of scar, with tortuous glands. D. As the lesion progresses away from the scar, the atypia diminishes. Mitoses and outright necrosis were not identified. E. PAS-D stain shows the red rims about the glands, a benign sign, but also red cytoplasmic droplets, which is consistent with bile duct adenoma’s being known to produce mucin. | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 41: | ||
*HepPar-1 -ve. | *HepPar-1 -ve. | ||
*Ki-67 low. | *Ki-67 low. | ||
Others:<ref name=pmid15725808/> | |||
*p53 -ve. | |||
*mCEA -ve. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:21, 2 January 2017
Bile duct adenoma is a benign liver lesion characterized composed of bile duct epithelium.
It is also known as a benign bile duct proliferation.[1]
General
- Benign.
- Important as it can be misdiagnosed as cancer.
Microscopic
Features:
- Disordered bile ducts within in a fibrotic stroma.
- No (yellow) bile within, as these lesions do not have a connection to the biliary tree.
- +/-Lymphocytic cuff.[2]
Negatives:
- No mitotic activity.
- No necrosis.
DDx:
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma.
- Bile duct hamartoma (von Meyenburg complex).
Images
- Bile duct adenoma (ganfyd.org).
- Bile duct adenoma (surgpath4u.com).
- Bile duct adenoma - oncocytic - low mag. (nih.gov).[1]
- Bile duct adenoma - oncocytic - high mag. (nih.gov).[1]

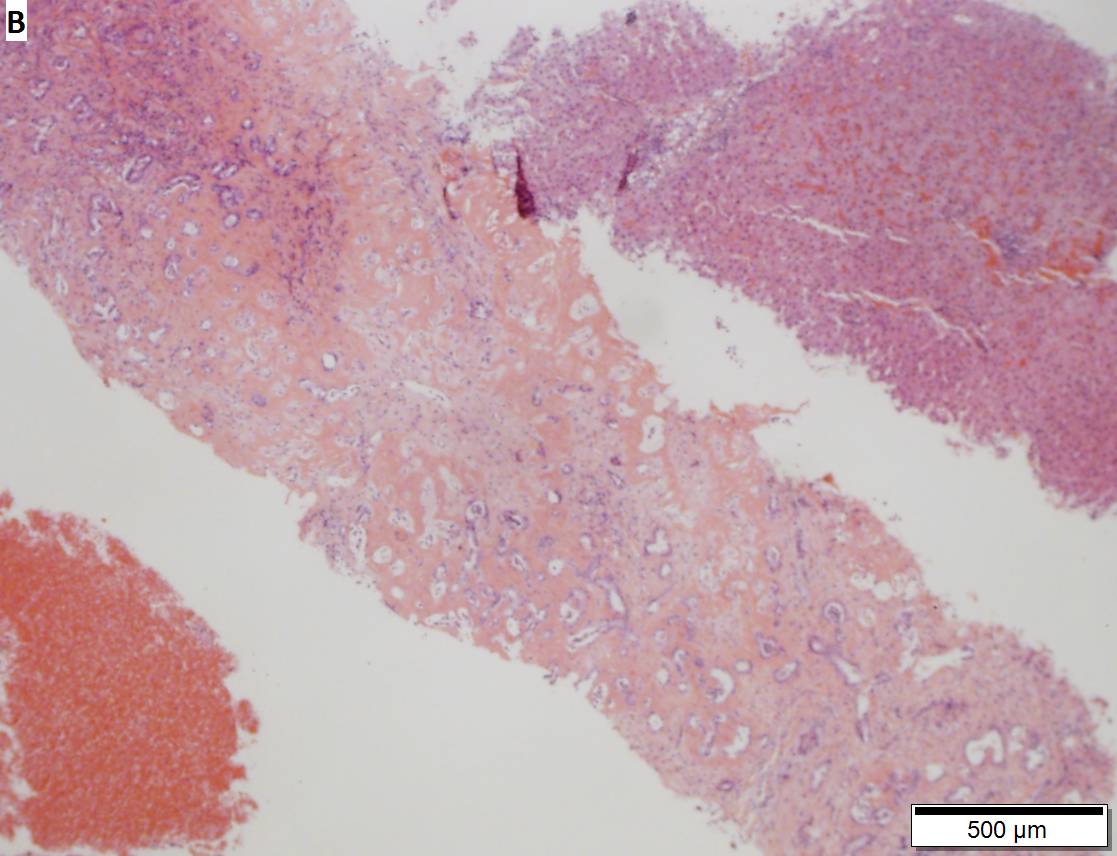
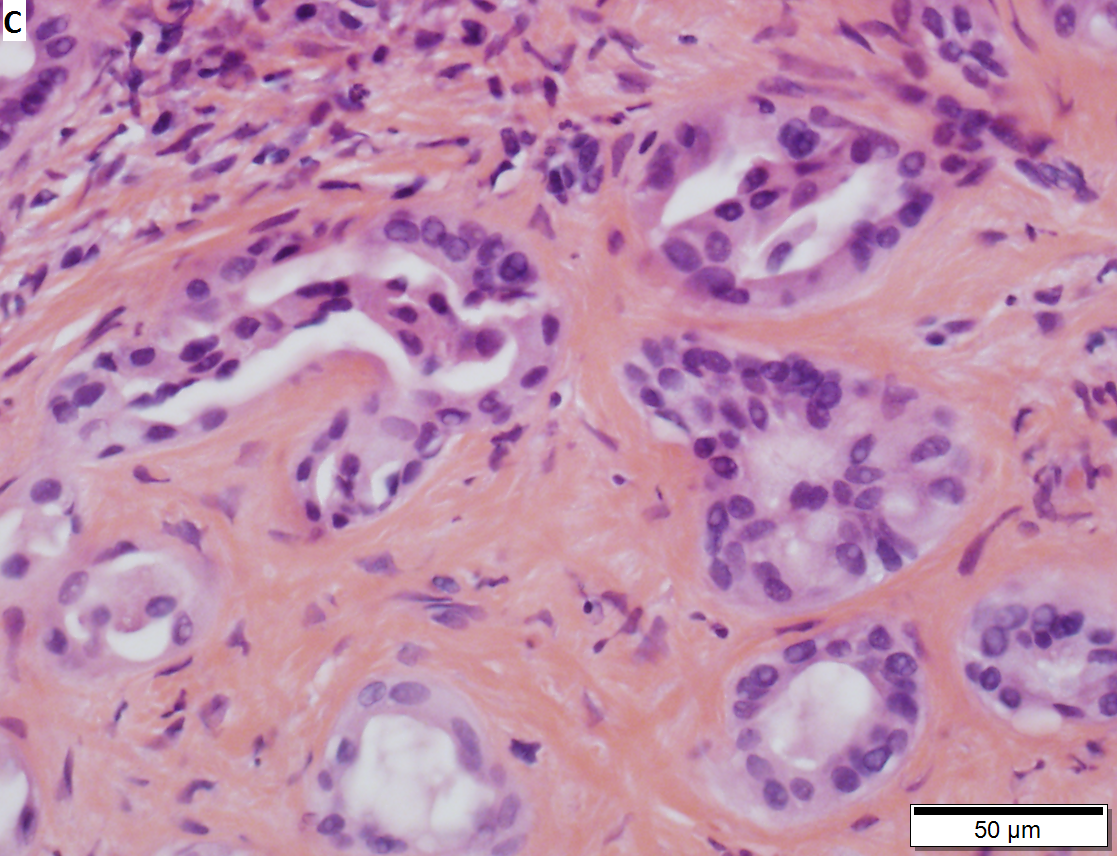
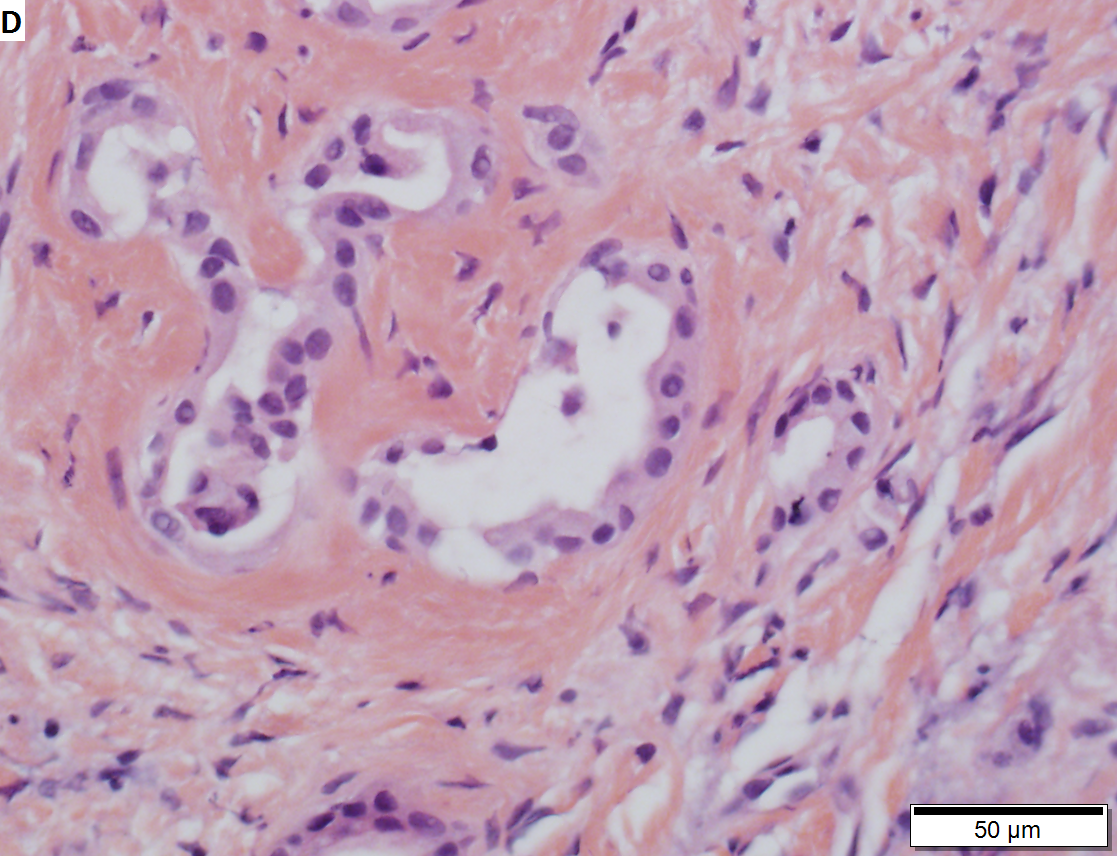

Bile duct adenoma in a 67 yo man, not radiologically detected; this is important because cholangiocarcinomas are larger than bile duct adenomas. Bile duct adenomas are usually incidental findings, as in this case. These can be very difficult diagnosis; this case was evaluated by outside consultation. A. Glandular proliferation is seen. Note the curve indicated by the arrow, indicating a subcapsular location. B. The central scar, in other locations and with metastases, a finding associated with carcinoma, is in the liver a benign sign. The intense hyalin is also a benign sign, being that of a well-developed adenoma. C. Nuclear atypia in this case is modest near the region of scar, with tortuous glands. D. As the lesion progresses away from the scar, the atypia diminishes. Mitoses and outright necrosis were not identified. E. PAS-D stain shows the red rims about the glands, a benign sign, but also red cytoplasmic droplets, which is consistent with bile duct adenoma’s being known to produce mucin.
IHC
- CK7 +ve.
- HepPar-1 -ve.
- Ki-67 low.
Others:[3]
- p53 -ve.
- mCEA -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Johannesen, EJ.; Wu, Z.; Holly, JS. (2014). "Bile duct adenoma with oncocytic features.". Case Rep Pathol 2014: 282010. doi:10.1155/2014/282010. PMID 24592348.
- ↑ URL: http://www.surgpath4u.com/caseviewer.php?case_no=152. Accessed on: 6 March 2014.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hornick, JL.; Lauwers, GY.; Odze, RD. (Mar 2005). "Immunohistochemistry can help distinguish metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinomas from bile duct adenomas and hamartomas of the liver.". Am J Surg Pathol 29 (3): 381-9. PMID 15725808.