Difference between revisions of "Pseudomembranous colitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Clostrium difficile: fix sp.) |
(→Images: tweak) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Colonic pseudomembrane. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Colonic pseudomembrane. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = ''C. | | Synonyms = ''C. difficile colitis'' '''not''' the same from the perspective of pathology; however, ''pseudomembranous colitis'' is commonly used as synonym for ''C. difficile colitis'' by clinicians | ||
| Micro = heaped necrotic surface epithelium (described as "volanco lesions"), [[PMN]]s in lamina propria, +/-capillary fibrin thrombi | | Micro = heaped necrotic surface epithelium (described as "volanco lesions"), [[PMN]]s in lamina propria, +/-capillary fibrin thrombi | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = +/-prior treatment with antibiotics for something else | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
| Symptoms = diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever | | Symptoms = diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| Other = ''C. difficile'' toxin test positive (may be negative) | | Other = ''C. difficile'' toxin test positive (may be negative) | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = | ||
| Tx = dependent on underlying cause, antibiotics in ''C. | | Tx = dependent on underlying cause, antibiotics in ''C. difficile'' - occasionally surgical resection | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Pseudomembranous colitis''' an inflammation of the [[colon]] ([[colitis]]) with a characteristic endoscopic/gross appearance. It is closely associated with ''C. | '''Pseudomembranous colitis''' an inflammation of the [[colon]] ([[colitis]]) with a characteristic endoscopic/gross appearance. It is closely associated with ''C. difficile'' infections; however, may be seen in a number of different situations. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
{{Main|Clostridium difficile}} | {{Main|Clostridium difficile}} | ||
Epidemiology of ''[[C. difficile]]'' pseudomembranous colitis: | Epidemiology of ''[[C. difficile]]'' pseudomembranous colitis:<ref name=pmid23103666>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jones | first1 = AM. | last2 = Kuijper | first2 = EJ. | last3 = Wilcox | first3 = MH. | title = Clostridium difficile: a European perspective. | journal = J Infect | volume = 66 | issue = 2 | pages = 115-28 | month = Feb | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1016/j.jinf.2012.10.019 | PMID = 23103666 }}</ref> | ||
*Antibiotics prior to onset (classic history).<ref name=pmid23253319>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bassetti | first1 = M. | last2 = Villa | first2 = G. | last3 = Pecori | first3 = D. | last4 = Arzese | first4 = A. | last5 = Wilcox | first5 = M. | title = Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection. | journal = Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther | volume = 10 | issue = 12 | pages = 1405-23 | month = Dec | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1586/eri.12.135 | PMID = 23253319 }}</ref> | *Antibiotics prior to onset (classic history).<ref name=pmid23253319>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bassetti | first1 = M. | last2 = Villa | first2 = G. | last3 = Pecori | first3 = D. | last4 = Arzese | first4 = A. | last5 = Wilcox | first5 = M. | title = Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection. | journal = Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther | volume = 10 | issue = 12 | pages = 1405-23 | month = Dec | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1586/eri.12.135 | PMID = 23253319 }}</ref> | ||
*Typically hospitalized. | |||
*Typically older individuals. | |||
Clinical:<ref name=pmid8828001>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gröschel | first1 = DH. | title = Clostridium difficile infection. | journal = Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 203-45 | month = | year = 1996 | doi = 10.3109/10408369609083061 | PMID = 8828001 }}</ref> | |||
*Diarrhea - usu. non-bloody - classic finding. | |||
*+/-Fever. | |||
*+/-Abdominal pain. | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 67: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Pseudomembranous_colitis.JPG | Pseudomembranous colitis. (WC) | Image:Pseudomembranous_colitis_1.jpg | Pseudomembranous colitis - endoscopic image. (WC/Samir) | ||
Image:Pseudomembranous_colitis.JPG | Pseudomembranous colitis. (WC/Doc James) | |||
Image:Pseudomembranous_Colitis,_Colectomy_(Gross)_(7410584264).jpg | Pseudomembranous colitis. (WC/Euthman) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 80: | Line 88: | ||
*[[Signet ring cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Signet ring cell carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Ischemic colitis]] - in general. | *[[Ischemic colitis]] - in general. | ||
*Pseudomembranes associated with [[collagenous colitis]] - small case series reported.<ref name=pmid14508399>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yuan | first1 = S. | last2 = Reyes | first2 = V. | last3 = Bronner | first3 = MP. | title = Pseudomembranous collagenous colitis. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 27 | issue = 10 | pages = 1375-9 | month = Oct | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 14508399 }}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 97: | ||
www: | www: | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case153.html Pseudomembranous colitis (upmc.edu)]. | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case153.html Pseudomembranous colitis (upmc.edu)]. | ||
==Sign out== | |||
*It is worth mentioning that ''pseudomembranous colitis'' has a [[differential diagnosis]] when considered from the morphology. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Ischemic colitis]]. | *[[Ischemic colitis]]. | ||
*[[Colon]]. | *[[Colon]]. | ||
*[[Toxic megacolon]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:50, 14 August 2018
| Pseudomembranous colitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
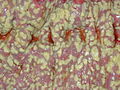
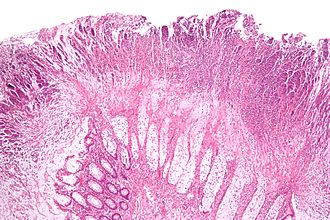 Colonic pseudomembrane. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | C. difficile colitis not the same from the perspective of pathology; however, pseudomembranous colitis is commonly used as synonym for C. difficile colitis by clinicians |
|
| |
| LM | heaped necrotic surface epithelium (described as "volanco lesions"), PMNs in lamina propria, +/-capillary fibrin thrombi |
| LM DDx | cap polyposis, signet ring cell carcinoma (uncommonly), ischemic colitis in general |
| Site | colon |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-prior treatment with antibiotics for something else |
| Symptoms | diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Endoscopy | pseudomembranes (pale yellow (or white) irregular, raised mucosal lesions), interlesional mucosa often near normal grossly |
| Prognosis | dependent on comorbidities |
| Other | C. difficile toxin test positive (may be negative) |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause, antibiotics in C. difficile - occasionally surgical resection |
Pseudomembranous colitis an inflammation of the colon (colitis) with a characteristic endoscopic/gross appearance. It is closely associated with C. difficile infections; however, may be seen in a number of different situations.
General
- Pseudomembranous colitis is a histomorphologic description which has a DDx. In other words, it can be caused by a number of things.
Etiology
DDx of pseudomembranous colitis:[1]
- C. difficile.
- Known as C. difficile colitis.
- Ischemic colitis.
- Volvulus.
- Other infections.
Etiology:
- Anything that causes a severe mucosal injury.
Clostridium difficile
Main article: Clostridium difficile
Epidemiology of C. difficile pseudomembranous colitis:[2]
- Antibiotics prior to onset (classic history).[3]
- Typically hospitalized.
- Typically older individuals.
Clinical:[4]
- Diarrhea - usu. non-bloody - classic finding.
- +/-Fever.
- +/-Abdominal pain.
Gross
Features:[5]
- Pseudomembranes:
- Pale yellow (or white) irregular, raised mucosal lesions.
- Early lesions: typical <10 mm.
- Interlesional mucosa often near normal grossly.
Images
Microscopic
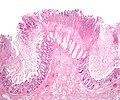
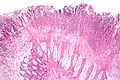
Features:[1]
- Heaped necrotic surface epithelium.
- Described as "volanco lesions" - this is what is seen endoscopically.
- PMNs in lamina propria.
- +/-Capillary fibrin thrombi.
Notes:
- Pseudomembranes arise from the crypts.
- Rarely have (benign) signet ring cell-like cells.[6]
DDx:
- Cap polyposis - very rare.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma.
- Ischemic colitis - in general.
- Pseudomembranes associated with collagenous colitis - small case series reported.[7]
Images
www:
Sign out
- It is worth mentioning that pseudomembranous colitis has a differential diagnosis when considered from the morphology.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 837-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Jones, AM.; Kuijper, EJ.; Wilcox, MH. (Feb 2013). "Clostridium difficile: a European perspective.". J Infect 66 (2): 115-28. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2012.10.019. PMID 23103666.
- ↑ Bassetti, M.; Villa, G.; Pecori, D.; Arzese, A.; Wilcox, M. (Dec 2012). "Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection.". Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 10 (12): 1405-23. doi:10.1586/eri.12.135. PMID 23253319.
- ↑ Gröschel, DH. (1996). "Clostridium difficile infection.". Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 33 (3): 203-45. doi:10.3109/10408369609083061. PMID 8828001.
- ↑ URL: http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/GI/1749.htm. Accessed on: 22 May 2012.
- ↑ Abdulkader, I.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.; Forteza, J. (Apr 2003). "Signet-ring cells associated with pseudomembranous colitis.". Virchows Arch 442 (4): 412-4. doi:10.1007/s00428-003-0779-1. PMID 12684766.
- ↑ Yuan, S.; Reyes, V.; Bronner, MP. (Oct 2003). "Pseudomembranous collagenous colitis.". Am J Surg Pathol 27 (10): 1375-9. PMID 14508399.