Difference between revisions of "Proton pump inhibitor effect"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

(create) |
m (→Microscopic: tweak) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
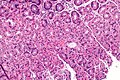
[[Image:Stomach with prominent parietal cells -- very high mag.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Stomach with PPI effect. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Proton pump inhibitor effect''', abbreviated '''PPI effect''', is a change seen in the parietal cells of the [[stomach]] due to a drug in the proton pump inhibitor class. | '''Proton pump inhibitor effect''', abbreviated '''PPI effect''', is a change seen in the parietal cells of the [[stomach]] due to a drug in the proton pump inhibitor class. | ||
Formally, it is '''stomach with proton pump inhibitor effect'''. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). | *Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). | ||
**Used to treat [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]]. | **Used to treat [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]]. | ||
===Some proton pump inhibitors=== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Generic name | |||
! Brand name(s) | |||
|- | |||
|Omeprazole | |||
|LOSEC | |||
|- | |||
|Dexlansoprazole | |||
|DEXILANT | |||
|- | |||
|Lansoprazole | |||
|PREVACID | |||
|- | |||
|Esomeprazole | |||
|NEXIUM | |||
|- | |||
|Pantoprazole | |||
|PANTOLOC | |||
|- | |||
|Rabeprazole | |||
|PARIET | |||
|} | |||
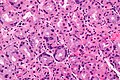
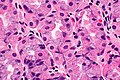
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Driman | first1 = DK. | last2 = Wright | first2 = C. | last3 = Tougas | first3 = G. | last4 = Riddell | first4 = RH. | title = Omeprazole produces parietal cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia in humans. | journal = Dig Dis Sci | volume = 41 | issue = 10 | pages = 2039-47 | month = Oct | year = 1996 | doi = | PMID = 8888719 }}</ref> | Features:<ref name=pmid8888719>{{Cite journal | last1 = Driman | first1 = DK. | last2 = Wright | first2 = C. | last3 = Tougas | first3 = G. | last4 = Riddell | first4 = RH. | title = Omeprazole produces parietal cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia in humans. | journal = Dig Dis Sci | volume = 41 | issue = 10 | pages = 2039-47 | month = Oct | year = 1996 | doi = | PMID = 8888719 }}</ref><ref>{{Pathologyoutlines| topic/stomachPPI}}</ref> | ||
*Parietal cell enlargement - '''key feature'''. | *Parietal cell enlargement - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Parietal cells typically bulge into the lumen. | |||
*G cell and enterochromaffin cell-like hyperplasia. | |||
**Compensatory change due to increased pH in gastric lumen. | |||
*Multiple fundic gland polyps (with PPI use over several months). | |||
**Polyps may regress after PPI is stopped. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Stomach with prominent parietal cells -- intermed mag.jpg | PPI effect - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Stomach with prominent parietal cells -- high mag.jpg | PPI effect - high mag. | |||
Image: Stomach with prominent parietal cells -- very high mag.jpg | PPI effect - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/nrgastro/journal/v4/n8/images/ncpgasthep0896-f3.jpg PPI effect (nature.com)]. | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 55: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Stomach]]. | *[[Stomach]]. | ||
*[[Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:36, 2 March 2020

Stomach with PPI effect. H&E stain.
Proton pump inhibitor effect, abbreviated PPI effect, is a change seen in the parietal cells of the stomach due to a drug in the proton pump inhibitor class.
Formally, it is stomach with proton pump inhibitor effect.
General
- Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI).
- Used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Some proton pump inhibitors
| Generic name | Brand name(s) |
|---|---|
| Omeprazole | LOSEC |
| Dexlansoprazole | DEXILANT |
| Lansoprazole | PREVACID |
| Esomeprazole | NEXIUM |
| Pantoprazole | PANTOLOC |
| Rabeprazole | PARIET |
Microscopic
- Parietal cell enlargement - key feature.
- Parietal cells typically bulge into the lumen.
- G cell and enterochromaffin cell-like hyperplasia.
- Compensatory change due to increased pH in gastric lumen.
- Multiple fundic gland polyps (with PPI use over several months).
- Polyps may regress after PPI is stopped.
Images
www:
Sign out
- Usually not reported.
See also
References
- ↑ Driman, DK.; Wright, C.; Tougas, G.; Riddell, RH. (Oct 1996). "Omeprazole produces parietal cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia in humans.". Dig Dis Sci 41 (10): 2039-47. PMID 8888719.
- ↑ topic/stomachPPI.html topic/stomachPPI