Difference between revisions of "Radiation changes"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
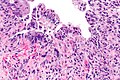
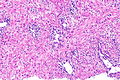
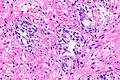
| Image = Radiation changes -- high mag.jpg | | Image = Radiation changes -- high mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Radiation changes. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Radiation changes. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = cytoplasmic vacuolation (usually abundant), enlarged nuclei - but usu. normal [[NC ratio]], no nuclear membrane irregularies, chromatin "smudgy", +/-multinucleation, +/-fibrosis (chronic change), +/-edema (acute change) | | Micro = cytoplasmic vacuolation (usually abundant), enlarged nuclei - but usu. normal [[NC ratio]], no nuclear membrane irregularies, chromatin "smudgy", +/-multinucleation, +/-fibrosis (chronic change), +/-edema (acute change) | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[pleomorphic tumours]] - esp. [[sarcoma]]s, poorly differentiated carcinomas, drug/toxin effect | | LMDDx = [[pleomorphic tumours]] - esp. [[sarcoma]]s, poorly differentiated carcinomas, drug/toxin effect, well-differentiated tumours in the background of radiation changes, "[[giant cell cystitis]]" | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = Ki-67 low, pankeratin -ve (usu.) | | IHC = Ki-67 low, pankeratin -ve (usu.) | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| Prognosis = benign | | Prognosis = benign | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = cancer recurrence, infection, new malignancy, post-surgical changes | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Radiation changes''', also '''radiation | '''Radiation changes''', also '''radiation effects''', are seen occasionally by [[pathologist]]s. They are usually a result of prior (radiation) treatments. The history is important in making this [[diagnosis]]. | ||
==General== | |||
*History of radiation treatment/exposure. | |||
*Clinical symptoms dependent on site. | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 55: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Pleomorphic tumours]]. | *[[Pleomorphic tumours]]. | ||
*Well-differentiated carcinoma, e.g. [[postradiation prostatic carcinoma]], may go unnoticed in the background of radiation-associated nuclear changes. | |||
*Atypia associated with [[drug toxicity|drugs]]. | |||
*"[[Giant cell cystitis]]" - benign mesenchymal atypia with or without inflammation. | |||
===Images=== | |||
====Rectum==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis - alt -- low mag.jpg | [[Radiation proctitis]] - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis -- intermed mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis -- high mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis -- very high mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis - 2 -- intermed mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis - 2 -- high mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Radiation proctitis - 2 alt -- high mag.jpg | Radiation proctitis - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
====Prostate gland==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Prostate with radiation changes -- low mag.jpg | Prostate with RC - low mag. | |||
Image: Prostate with radiation changes -- intermed mag.jpg | Prostate with RC - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Prostate with radiation changes -- high mag.jpg | Prostate with RC - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
====Brain==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glioblastoma-radiation changes HE.jpg | [[Glioblastoma]] with RC (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:Pathology Brain Radiation Necrosis 1.jpg | Radiation necrosis (WC/Tdvorak) | |||
File:Pathology Brain Radiation Necrosis 2.jpg | Radiation necrosis and gliosis (WC/Tdvorak) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 64: | Line 96: | ||
OF RADIATION TREATMENT. | OF RADIATION TREATMENT. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | ||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
URINARY BLADDER, TRIGONE, BIOPSY: | |||
- INFLAMED UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA, ULCERATION AND | |||
GRANULATION TISSUE FORMATION. | |||
- RADIATION CHANGES (STROMA). | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
Urinary bladder, biopsy: | |||
- Urothelial mucosa with evidence of ulceration (fibrin, | |||
necroinflammatory debris), mild stromal atypia and chronic | |||
inflammation, compatible with radiation cystitis | |||
- Negative for dysplasia | |||
- Negative for malignancy | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 120: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Radiation colitis]]. | *[[Radiation colitis]]. | ||
*[[Radiation esophagitis]]. | |||
*[[Radiation changes in cervical cytology]]. | *[[Radiation changes in cervical cytology]]. | ||
*[[Radiation changes of the endocervical epithelium]]. | |||
*[[Radiation oncology]]. | *[[Radiation oncology]]. | ||
*[[Endometrium post-ablation]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:36, 2 November 2016
| Radiation changes | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
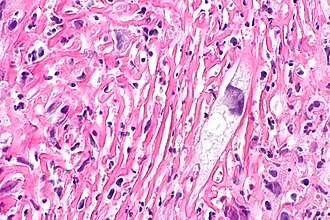 Radiation changes. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cytoplasmic vacuolation (usually abundant), enlarged nuclei - but usu. normal NC ratio, no nuclear membrane irregularies, chromatin "smudgy", +/-multinucleation, +/-fibrosis (chronic change), +/-edema (acute change) |
| LM DDx | pleomorphic tumours - esp. sarcomas, poorly differentiated carcinomas, drug/toxin effect, well-differentiated tumours in the background of radiation changes, "giant cell cystitis" |
| IHC | Ki-67 low, pankeratin -ve (usu.) |
| Site | pretty much anywhere |
|
| |
| Clinical history | history of radiation treatment/exposure - important for the diagnosis |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | cancer recurrence, infection, new malignancy, post-surgical changes |
Radiation changes, also radiation effects, are seen occasionally by pathologists. They are usually a result of prior (radiation) treatments. The history is important in making this diagnosis.
General
- History of radiation treatment/exposure.
- Clinical symptoms dependent on site.
Gross
- +/-Erythema (early)
- +/-Fibrotic appearing tissue (late).
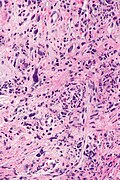
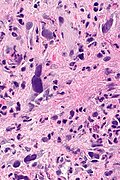
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Cytoplasmic vacuolation - usually abundant.
- Nucleus:
- Enlarged nucleus - but normal NC ratio.
- No nuclear membrane irregularies.
- Chromatin: "smudgy".
- +/-Multinucleation.
- +/-Fibrosis (chronic change).
- +/-Edema (acute change).
Important note:
- The atypical cells are stromal cells; these survive the radiation. The epithelium is usually normal in the context of chronic changes.
- Pleomorphism is often suggestive of malignancy. Paradoxically, in the context of radiation, less pleomorphic (clonal-appearing) cells may be malignant!
DDx:
- Pleomorphic tumours.
- Well-differentiated carcinoma, e.g. postradiation prostatic carcinoma, may go unnoticed in the background of radiation-associated nuclear changes.
- Atypia associated with drugs.
- "Giant cell cystitis" - benign mesenchymal atypia with or without inflammation.
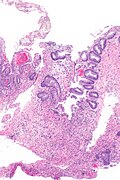
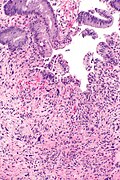
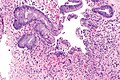
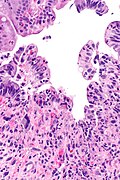
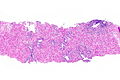
Images
Rectum
Radiation proctitis - low mag. (WC)
Prostate gland
Brain
Glioblastoma with RC (WC/jensflorian)
IHC
- Pankeratin -ve.
- KI-67 low.
Sign out
RECTUM, BIOPSY: - SQUAMOUS MUCOSA WITH MARKED ACUTE INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES. - GRANULATION TISSUE. - LARGE ATYPICAL STROMAL CELLS AND FIBROSIS, COMPATIBLE WITH THE HISTORY OF RADIATION TREATMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
URINARY BLADDER, TRIGONE, BIOPSY: - INFLAMED UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA, ULCERATION AND GRANULATION TISSUE FORMATION. - RADIATION CHANGES (STROMA). - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Urinary bladder, biopsy: - Urothelial mucosa with evidence of ulceration (fibrin, necroinflammatory debris), mild stromal atypia and chronic inflammation, compatible with radiation cystitis - Negative for dysplasia - Negative for malignancy
Micro
Scattered rare large atypical cells with a preserved nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio are present. Fibrosis is present.
See also
- Radiation colitis.
- Radiation esophagitis.
- Radiation changes in cervical cytology.
- Radiation changes of the endocervical epithelium.
- Radiation oncology.
- Endometrium post-ablation.