Difference between revisions of "Joints"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Ganglion cyst: +DDx) |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
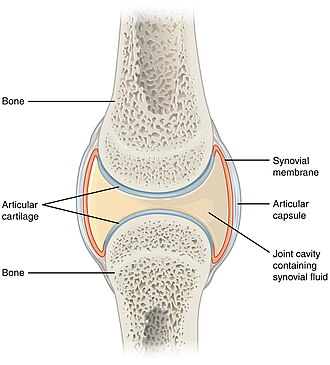
[[Image:907 Synovial Joints.jpg|thumb|right|Schematic of a synovial joint. (WC/OpenStax College)]] | |||
'''Joints''' are important for locomotion. This article collects tidbits about their [[pathology]]. | '''Joints''' are important for locomotion. This article collects tidbits about their [[pathology]]. | ||
A general differential diagnosis for joints is dealt with in the ''[[cartilage]]'' article. | |||
==Septic arthritis== | |||
:''Septic joint'' redirects here. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Uncommon. | |||
*May be treated in a one-stage ''or'' two-stage procedure.<ref name=pmid17483946>{{cite journal |author=Chen CE, Wang JW, Juhn RJ |title=Total hip arthroplasty for primary septic arthritis of the hip in adults |journal=Int Orthop |volume=32 |issue=5 |pages=573–80 |year=2008 |month=October |pmid=17483946 |pmc=2551720 |doi=10.1007/s00264-007-0366-1 |url=}}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Microorganisms - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Inflammatory cells, esp. [[neutrophils]]. ‡ | |||
*+/-[[Osteomyelitis]]. | |||
Note: | |||
*‡ There are several criteria for the number of neurophils in the context of prosthetic joints - see ''[[prosthetic joint infection]]''. | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
<pre> | |||
RIGHT FEMORAL HEAD AND SURROUNDING TISSUE, REMOVAL: | |||
- OSTEOMYELITIS, ACUTE. | |||
- OSTEONECROSIS, FOCAL. | |||
- DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE. | |||
- SOFT TISSUE WITH FOCAL NECROSIS AND COCCI MICROORGANISMS, CORRELATION | |||
WITH MICROBIOLOGY SUGGESTED. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
==Prosthetic joint infection== | ==Prosthetic joint infection== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 41: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Various criteria for the number of neutrophils exist (see below).<ref name=pmid17545426>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bori | first1 = G. | last2 = Soriano | first2 = A. | last3 = García | first3 = S. | last4 = Mallofré | first4 = C. | last5 = Riba | first5 = J. | last6 = Mensa | first6 = J. | title = Usefulness of histological analysis for predicting the presence of microorganisms at the time of reimplantation after hip resection arthroplasty for the treatment of infection. | journal = J Bone Joint Surg Am | volume = 89 | issue = 6 | pages = 1232-7 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.2106/JBJS.F.00741 | PMID = 17545426 }}</ref> | *Various criteria for the number of neutrophils exist (see below).<ref name=pmid17545426>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bori | first1 = G. | last2 = Soriano | first2 = A. | last3 = García | first3 = S. | last4 = Mallofré | first4 = C. | last5 = Riba | first5 = J. | last6 = Mensa | first6 = J. | title = Usefulness of histological analysis for predicting the presence of microorganisms at the time of reimplantation after hip resection arthroplasty for the treatment of infection. | journal = J Bone Joint Surg Am | volume = 89 | issue = 6 | pages = 1232-7 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.2106/JBJS.F.00741 | PMID = 17545426 }}</ref> | ||
**The definitions suffer from [[HPFitis]]. | **The definitions (with the exception of Morawietz ''et al.''<ref name=pmid19635104>{{Cite journal | last1 = Morawietz | first1 = L. | last2 = Tiddens | first2 = O. | last3 = Mueller | first3 = M. | last4 = Tohtz | first4 = S. | last5 = Gansukh | first5 = T. | last6 = Schroeder | first6 = JH. | last7 = Perka | first7 = C. | last8 = Krenn | first8 = V. | title = Twenty-three neutrophil granulocytes in 10 high-power fields is the best histopathological threshold to differentiate between aseptic and septic endoprosthesis loosening. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 54 | issue = 7 | pages = 847-53 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03313.x | PMID = 19635104 }}</ref>) suffer from [[HPFitis]]. | ||
*Finding of plasma | *Finding of [[plasma cell]]s and lymphocytes is '''not''' contributory for the diagnosis of infection.<ref name=pmid17545426/> | ||
*[[Granuloma|Granulomatous]] inflammation that isn't of a foreign-body type should get the usual work-up.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case174.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case174.html]. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.</ref> | *[[Granuloma|Granulomatous]] inflammation that isn't of a foreign-body type should get the usual work-up.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case174.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case174.html]. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.</ref> | ||
====Feldman criteria==== | ====Feldman criteria==== | ||
*>= Five neutrophils / [[HPF]] (x400) in at least five separate microscopic fields.<ref name=pmid17545426/><ref name=pmid21131917>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bori | first1 = G. | last2 = Muñoz-Mahamud | first2 = E. | last3 = Garcia | first3 = S. | last4 = Mallofre | first4 = C. | last5 = Gallart | first5 = X. | last6 = Bosch | first6 = J. | last7 = Garcia | first7 = E. | last8 = Riba | first8 = J. | last9 = Mensa | first9 = J. | title = Interface membrane is the best sample for histological study to diagnose prosthetic joint infection. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 579-84 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2010.219 | PMID = 21131917 | URL = http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v24/n4/full/modpathol2010219a.html }}</ref> | *>= Five neutrophils / [[HPF]] (x400) assessed in '''at least five''' separate microscopic fields.<ref name=pmid17545426/><ref name=pmid21131917>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bori | first1 = G. | last2 = Muñoz-Mahamud | first2 = E. | last3 = Garcia | first3 = S. | last4 = Mallofre | first4 = C. | last5 = Gallart | first5 = X. | last6 = Bosch | first6 = J. | last7 = Garcia | first7 = E. | last8 = Riba | first8 = J. | last9 = Mensa | first9 = J. | title = Interface membrane is the best sample for histological study to diagnose prosthetic joint infection. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 579-84 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2010.219 | PMID = 21131917 | URL = http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v24/n4/full/modpathol2010219a.html }}</ref> | ||
====Athanasou criterion==== | ====Athanasou criterion==== | ||
*>= Ten neutrophils / ten [[HPF]] (x400).<ref name=pmid17545426/> | *>= Ten neutrophils / ten [[HPF]] (x400).<ref name=pmid17545426/> | ||
====Morawietz criteria==== | |||
*23 neutrophils / 10 HPF, where the field diameter = 0.625 mm.<ref name=pmid19635104>{{Cite journal | last1 = Morawietz | first1 = L. | last2 = Tiddens | first2 = O. | last3 = Mueller | first3 = M. | last4 = Tohtz | first4 = S. | last5 = Gansukh | first5 = T. | last6 = Schroeder | first6 = JH. | last7 = Perka | first7 = C. | last8 = Krenn | first8 = V. | title = Twenty-three neutrophil granulocytes in 10 high-power fields is the best histopathological threshold to differentiate between aseptic and septic endoprosthesis loosening. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 54 | issue = 7 | pages = 847-53 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03313.x | PMID = 19635104 }}</ref> | |||
Notes: | |||
*The 0.625 mm field diameter is uncommon; it corresponds to a 25 mm eye piece with a 40x objective (25 mm/40 = 0.625 mm). | |||
**The PMNs/area is: 23 PMNs / (pi/4*0.625^2) = 7.49 PMNs/mm*mm | |||
*If one uses a 22 mm eye piece microscope and the 40x objective, the field diameter is 0.55 mm; thus, one would need to count PMNs in 12.91 HPFs ( 3.0680 mm*mm / 0.2376 mm*mm = 12.91 ) to get the same sample area. | |||
====A comparison of the criteria==== | |||
A study by Bori ''et al.''<ref name=pmid17545426/> compared the criteria of ''Feldman'' and ''Athanasou'': | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Measure | |||
! Feldman | |||
! Athanasou | |||
|- | |||
| [[Sensitivity]] | |||
| 29% | |||
| 71% | |||
|- | |||
| [[Specificity]] | |||
| 100% | |||
| 64% | |||
|} | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Tissue from Left Hip, Revision Arthroplasty: | |||
- Connective tissue with focally increased neutrophils (at least | |||
11 neutrophils/HPF). | |||
- Negative for microorganisms with routine stains. | |||
- NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
Comment: | |||
The findings raise the possibility of a joint infection; correlation with | |||
cultures is required. | |||
1 HPF = 0.2376 mm*mm. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Block letters==== | |||
<pre> | |||
HEMATOMA, RIGHT HIP, IRRIGATION AFTER HIP REPLACEMENT/TISSUE REMOVAL: | |||
- FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE WITH POSTSURGICAL CHANGES INCLUDING: | |||
-- FOREIGN-BODY TYPE MULTINUCLEATED GIANT CELLS AND FOREIGN MATERIAL. | |||
-- GRANULATION TISSUE. | |||
-- FAT NECROSIS (FOCAL). | |||
- FIBRIN, BLOOD. | |||
- NEUTROPHILS IN BLOOD VESSEL WALLS/PERIVASCULAR (FOCAL), SEE COMMENT. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAIN. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
Up to 17 neutrophils per high power field (0.55 mm field diameter) are seen. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
FEMUR, LEFT, BIOPSY: | |||
- BONE MARROW WITH A PATCHY MILD FOCAL PROMINENCE OF PLASMA CELLS AND NEUTROPHILS. | |||
- FIBROUS TISSUE WITH HEMOSIDERIN, ISOLATED NEUTROPHILS AND RARE | |||
MACROPHAGES. | |||
- BONE FRAGMENTS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MICROABSCESS FORMATION. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAINS. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
BONE AND SOFT TISSUE, LEFT HIP, EXCISION: | |||
- FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE, SKELETAL MUSCLE AND FRAGMENTS OF BONE WITH SURGICAL CHANGES. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MICROABSCESS FORMATION. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAINS. | |||
</pre> | |||
==Juxta-articular myxoma== | ==Juxta-articular myxoma== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 151: | ||
==Ganglion cyst== | ==Ganglion cyst== | ||
{{Main|Ganglion cyst}} | |||
==Rheumatoid arthritis== | |||
{{Main|Rheumatoid arthritis}} | |||
==Acute synovitis== | |||
{{Main|Acute synovitis}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Latest revision as of 14:03, 11 October 2018
Joints are important for locomotion. This article collects tidbits about their pathology.
A general differential diagnosis for joints is dealt with in the cartilage article.
Septic arthritis
- Septic joint redirects here.
General
- Uncommon.
- May be treated in a one-stage or two-stage procedure.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Microorganisms - key feature.
- Inflammatory cells, esp. neutrophils. ‡
- +/-Osteomyelitis.
Note:
- ‡ There are several criteria for the number of neurophils in the context of prosthetic joints - see prosthetic joint infection.
Sign out
RIGHT FEMORAL HEAD AND SURROUNDING TISSUE, REMOVAL: - OSTEOMYELITIS, ACUTE. - OSTEONECROSIS, FOCAL. - DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE. - SOFT TISSUE WITH FOCAL NECROSIS AND COCCI MICROORGANISMS, CORRELATION WITH MICROBIOLOGY SUGGESTED. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Prosthetic joint infection
General
- Bits of tissue come for frozen section to r/o infection.
- The interface membrane (not the pseudocapsule) should be sampled to obtain a high sensitivity.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Neutrophils - key feature.
Notes:
- Various criteria for the number of neutrophils exist (see below).[3]
- Finding of plasma cells and lymphocytes is not contributory for the diagnosis of infection.[3]
- Granulomatous inflammation that isn't of a foreign-body type should get the usual work-up.[5]
Feldman criteria
Athanasou criterion
Morawietz criteria
- 23 neutrophils / 10 HPF, where the field diameter = 0.625 mm.[4]
Notes:
- The 0.625 mm field diameter is uncommon; it corresponds to a 25 mm eye piece with a 40x objective (25 mm/40 = 0.625 mm).
- The PMNs/area is: 23 PMNs / (pi/4*0.625^2) = 7.49 PMNs/mm*mm
- If one uses a 22 mm eye piece microscope and the 40x objective, the field diameter is 0.55 mm; thus, one would need to count PMNs in 12.91 HPFs ( 3.0680 mm*mm / 0.2376 mm*mm = 12.91 ) to get the same sample area.
A comparison of the criteria
A study by Bori et al.[3] compared the criteria of Feldman and Athanasou:
| Measure | Feldman | Athanasou |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 29% | 71% |
| Specificity | 100% | 64% |
Sign out
Tissue from Left Hip, Revision Arthroplasty: - Connective tissue with focally increased neutrophils (at least 11 neutrophils/HPF). - Negative for microorganisms with routine stains. - NEGATIVE for malignancy. Comment: The findings raise the possibility of a joint infection; correlation with cultures is required. 1 HPF = 0.2376 mm*mm.
Block letters
HEMATOMA, RIGHT HIP, IRRIGATION AFTER HIP REPLACEMENT/TISSUE REMOVAL: - FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE WITH POSTSURGICAL CHANGES INCLUDING: -- FOREIGN-BODY TYPE MULTINUCLEATED GIANT CELLS AND FOREIGN MATERIAL. -- GRANULATION TISSUE. -- FAT NECROSIS (FOCAL). - FIBRIN, BLOOD. - NEUTROPHILS IN BLOOD VESSEL WALLS/PERIVASCULAR (FOCAL), SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAIN. COMMENT: Up to 17 neutrophils per high power field (0.55 mm field diameter) are seen.
FEMUR, LEFT, BIOPSY: - BONE MARROW WITH A PATCHY MILD FOCAL PROMINENCE OF PLASMA CELLS AND NEUTROPHILS. - FIBROUS TISSUE WITH HEMOSIDERIN, ISOLATED NEUTROPHILS AND RARE MACROPHAGES. - BONE FRAGMENTS. - NEGATIVE FOR MICROABSCESS FORMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAINS.
BONE AND SOFT TISSUE, LEFT HIP, EXCISION: - FIBROADIPOSE TISSUE, SKELETAL MUSCLE AND FRAGMENTS OF BONE WITH SURGICAL CHANGES. - NEGATIVE FOR MICROABSCESS FORMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR MICROORGANISMS WITH ROUTINE STAINS.
Juxta-articular myxoma
- Abbreviated JAM.
General
- Classically present as a mass or with pain.[6]
- May recur.
- Described as (microscopically) indistinguishable from intramuscular myxoma.[7]
Gross
Features:
- Close to large joints - classically around the knee.
- >85% of cases around the knee in one large series.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Myxomatous stroma.
- +/-Cystic changes.
- Large nuclei with hyperchromasia and nuclear scalloping.[8]
DDx:
- Ganglion cyst.
- Intramuscular myxoma - surrounded by muscle.
Images:
Morton neuroma
Main article: Morton neuroma
Ganglion cyst
Main article: Ganglion cyst
Rheumatoid arthritis
Main article: Rheumatoid arthritis
Acute synovitis
Main article: Acute synovitis
See also
References
- ↑ Chen CE, Wang JW, Juhn RJ (October 2008). "Total hip arthroplasty for primary septic arthritis of the hip in adults". Int Orthop 32 (5): 573–80. doi:10.1007/s00264-007-0366-1. PMC 2551720. PMID 17483946. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2551720/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bori, G.; Muñoz-Mahamud, E.; Garcia, S.; Mallofre, C.; Gallart, X.; Bosch, J.; Garcia, E.; Riba, J. et al. (Apr 2011). "Interface membrane is the best sample for histological study to diagnose prosthetic joint infection.". Mod Pathol 24 (4): 579-84. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.219. PMID 21131917.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Bori, G.; Soriano, A.; García, S.; Mallofré, C.; Riba, J.; Mensa, J. (Jun 2007). "Usefulness of histological analysis for predicting the presence of microorganisms at the time of reimplantation after hip resection arthroplasty for the treatment of infection.". J Bone Joint Surg Am 89 (6): 1232-7. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00741. PMID 17545426.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Morawietz, L.; Tiddens, O.; Mueller, M.; Tohtz, S.; Gansukh, T.; Schroeder, JH.; Perka, C.; Krenn, V. (Jun 2009). "Twenty-three neutrophil granulocytes in 10 high-power fields is the best histopathological threshold to differentiate between aseptic and septic endoprosthesis loosening.". Histopathology 54 (7): 847-53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03313.x. PMID 19635104.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case174.html. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Meis, JM.; Enzinger, FM. (Jun 1992). "Juxta-articular myxoma: a clinical and pathologic study of 65 cases.". Hum Pathol 23 (6): 639-46. PMID 1592386.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 624. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case38/micro.html. Accessed on: 2 January 2011.